

发电技术 ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 72-82.DOI: 10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.23117
杨琛, 牛锋杰, 韩茂林, 周宁, 周定璇
收稿日期:2023-12-06
修回日期:2024-03-01
出版日期:2025-02-28
发布日期:2025-02-27
作者简介:基金资助:Chen YANG, Fengjie NIU, Maolin HAN, Ning ZHOU, Dingxuan ZHOU
Received:2023-12-06
Revised:2024-03-01
Published:2025-02-28
Online:2025-02-27
Supported by:摘要:
目的 光伏阵列在复杂室外工作条件下,发生的故障类型多样且程度不同,为了判断光伏阵列的工作状态,提出一种基于改进灰狼算法优化极限学习机(improved grey wolf optimized extreme learning machine,IGWO-ELM)的故障诊断方法。 方法 首先,针对9种故障仿真输出特性进行分析,建立了由短路电流、开路电压、最大功率点电流、最大功率点电压、填充因子组成的5维故障特征向量。其次,针对灰狼算法初始位置分布不均匀、全局搜索和局部开发过程不均衡的缺点,引入Circle映射和非线性收敛因子,提出一种改进的灰狼优化算法,优化极限学习机的输入层权重和隐含层节点偏置,以提高算法性能。最后,搭建仿真模型和实验平台并获取故障数据,基于K折交叉验证对数据集进行划分,代入IGWO-ELM模型进行正确率验证,并与其他算法模型进行对比。 结果 IGWO-ELM模型对光伏阵列不同故障具有较高的识别率,对仿真数据和实验数据的分类正确率分别达到98.32%和95.48%。 结论 基于IGWO-ELM的故障诊断方法识别率高,迭代次数少,收敛速度快,可有效判断光伏阵列的工作状态。
中图分类号:
杨琛, 牛锋杰, 韩茂林, 周宁, 周定璇. 基于改进灰狼算法优化极限学习机的光伏阵列故障诊断方法研究[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(1): 72-82.
Chen YANG, Fengjie NIU, Maolin HAN, Ning ZHOU, Dingxuan ZHOU. Research on Fault Diagnosis Method of Photovoltaic Arrays Based on Improved Grey Wolf Algorithm Optimized Extreme Learning Machine[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2025, 46(1): 72-82.
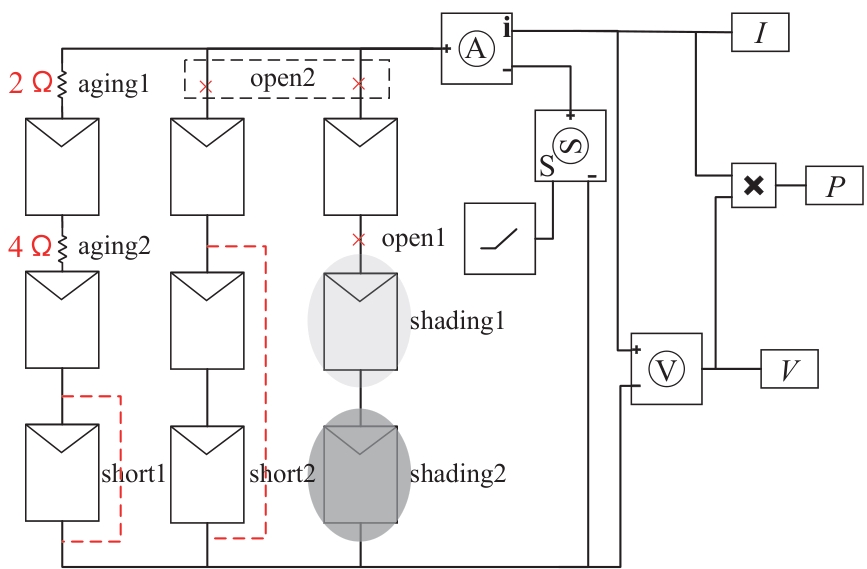
图1 光伏阵列Simulink仿真模型open1、open2为开路故障;short1、short2为短路故障;aging1、aging2为异常老化故障;shading1、shading2为部分阴影故障。
Fig. 1 Simulink simulation model of photovoltaic arrays
| 编号 | 故障类型 | 运行条件 | 标志 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 无故障 | 正常 | normal |
| 2 | 短路故障 | 1个组件短路 | short1 |
| 3 | 短路故障 | 1条支路2个组件短路 | short2 |
| 4 | 开路故障 | 1条支路开路 | open1 |
| 5 | 开路故障 | 2条支路开路 | open2 |
| 6 | 异常老化故障 | 老化且串联电阻为2 Ω | aging1 |
| 7 | 异常老化故障 | 老化且串联电阻为4 Ω | aging2 |
| 8 | 部分阴影故障 | 部分阴影(当前辐照度×0.6) | shading1 |
| 9 | 部分阴影故障 | 部分阴影(当前辐照度×0.3) | shading2 |
表1 故障类型描述
Tab. 1 Description of fault types
| 编号 | 故障类型 | 运行条件 | 标志 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 无故障 | 正常 | normal |
| 2 | 短路故障 | 1个组件短路 | short1 |
| 3 | 短路故障 | 1条支路2个组件短路 | short2 |
| 4 | 开路故障 | 1条支路开路 | open1 |
| 5 | 开路故障 | 2条支路开路 | open2 |
| 6 | 异常老化故障 | 老化且串联电阻为2 Ω | aging1 |
| 7 | 异常老化故障 | 老化且串联电阻为4 Ω | aging2 |
| 8 | 部分阴影故障 | 部分阴影(当前辐照度×0.6) | shading1 |
| 9 | 部分阴影故障 | 部分阴影(当前辐照度×0.3) | shading2 |
| 故障类型 | 平均训练识别率/% | 平均测试识别率/% |
|---|---|---|
| 平均值 | 98.21 | 98.32 |
| normal | 99.459 6 | 99.52 |
| short1 | 100 | 99.56 |
| short2 | 100 | 98.44 |
| open1 | 99.158 4 | 99.56 |
| open2 | 99.339 5 | 98.93 |
| aging1 | 86.007 1 | 89.35 |
| aging2 | 99.940 1 | 100 |
| shading1 | 100 | 100 |
| shading2 | 100 | 99.53 |
表2 IGWO-ELM各故障类型诊断结果 (each fault type)
Tab. 2 IGWO-ELM diagnostic results of
| 故障类型 | 平均训练识别率/% | 平均测试识别率/% |
|---|---|---|
| 平均值 | 98.21 | 98.32 |
| normal | 99.459 6 | 99.52 |
| short1 | 100 | 99.56 |
| short2 | 100 | 98.44 |
| open1 | 99.158 4 | 99.56 |
| open2 | 99.339 5 | 98.93 |
| aging1 | 86.007 1 | 89.35 |
| aging2 | 99.940 1 | 100 |
| shading1 | 100 | 100 |
| shading2 | 100 | 99.53 |
| 编号 | 运行条件 | 标志 |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1个组件短路+老化(串联电阻为2 Ω) | mixed1 |
| 11 | 1条支路开路+老化(串联电阻为4 Ω)+部分阴影 | mixed2 |
表3 混合故障类型描述
Tab. 3 Description of mixed fault types
| 编号 | 运行条件 | 标志 |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1个组件短路+老化(串联电阻为2 Ω) | mixed1 |
| 11 | 1条支路开路+老化(串联电阻为4 Ω)+部分阴影 | mixed2 |
| 算法名称 | 平均训练识别率/% | 平均测试识别率/% |
|---|---|---|
| PSO-ELM | 98.30 | 97.86 |
| GWO-ELM | 98.29 | 97.88 |
| IGWO-ELM | 98.21 | 98.32 |
表4 不同模型的故障诊断结果对比
Tab. 4 Comparison of fault diagnosis results ofdifferent models
| 算法名称 | 平均训练识别率/% | 平均测试识别率/% |
|---|---|---|
| PSO-ELM | 98.30 | 97.86 |
| GWO-ELM | 98.29 | 97.88 |
| IGWO-ELM | 98.21 | 98.32 |
| 类型 | 平均训练识别率/% | 平均测试识别率/% |
|---|---|---|
| 4维特征向量 | 97.89 | 98.11 |
| 5维特征向量 | 98.21 | 98.32 |
表5 不同特征向量的故障诊断结果 (feature vectors)
Tab. 5 Fault diagnosis results of different
| 类型 | 平均训练识别率/% | 平均测试识别率/% |
|---|---|---|
| 4维特征向量 | 97.89 | 98.11 |
| 5维特征向量 | 98.21 | 98.32 |
| 故障类型 | 平均训练识别率/% | 平均测试识别率/% |
|---|---|---|
| 平均值 | 94.57 | 95.48 |
| normal | 94.72 | 96.25 |
| short1 | 100 | 100 |
| short2 | 100 | 100 |
| open1 | 77.083 3 | 81.25 |
| open2 | 100 | 100 |
| aging1 | 93.61 | 93.75 |
| aging2 | 97.22 | 98.75 |
| shading1 | 92.50 | 92.50 |
| shading2 | 100 | 100 |
表6 IGWO实验数据故障诊断结果
Tab. 6 Fault diagnosis results of IGWO experimental data
| 故障类型 | 平均训练识别率/% | 平均测试识别率/% |
|---|---|---|
| 平均值 | 94.57 | 95.48 |
| normal | 94.72 | 96.25 |
| short1 | 100 | 100 |
| short2 | 100 | 100 |
| open1 | 77.083 3 | 81.25 |
| open2 | 100 | 100 |
| aging1 | 93.61 | 93.75 |
| aging2 | 97.22 | 98.75 |
| shading1 | 92.50 | 92.50 |
| shading2 | 100 | 100 |
| 1 | 舟丹 .太阳能光伏产业发展现状[J].中外能源,2023,28(2):50. |
| ZHOU D .Solar photovoltaic industry development status[J].Sino-Global Energy,2023,28(2):50. | |
| 2 | 舟丹 .我国光伏发电发展现状[J].中外能源,2023,28(1):41. |
| ZHOU D .Development status of photovoltaic power generation in China[J].Sino-Global Energy,2023,28(1):41. | |
| 3 | CHEN Z, CHEN Y, WU L,et al .Deep residual network based fault detection and diagnosis of photovoltaic arrays using current-voltage curves and ambient conditions[J].Energy Conversion and Management,2019,198:111793. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2019.111793 |
| 4 | 杨帅,曾文伟,杨凌云,等 .基于GOA-SVM的光伏阵列故障诊断方法研究[J].电力科学与技术学报,2024,39(5):172-180. |
| YANG S, ZENG W W, YANG L Y,et al .Research on fault diagnosis method for photovoltaic array based on GOA-SVM[J].Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology,2024,39(5):172-180. | |
| 5 | 罗程浩,胡骅,魏云冰,等 .局部阴影下基于IBOA-INC的光伏复合MPPT控制[J].电测与仪表,2024,61(5):182-189. |
| LUO C H, HU H, WEI Y B,et al .MPPT control of photovoltaic composite based on IBOA-INC under partial shading[J].Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation,2024,61(5):182-189. | |
| 6 | 陆江,袁廷璧,彭咏龙,等 .基于统计推断的异常光伏组件识别方法[J].智慧电力,2023,51(11):38-44. |
| LU J, YUAN T B, PENG Y L,et al .Anomalous photovoltaic module identification method based on statistical inference[J].Smart Power,2023,51(11):38-44. | |
| 7 | 武文栋,施保华,郑传良,等 .基于改进麻雀搜索算法优化RBF神经网络的光伏阵列故障诊断[J].智慧电力,2023,51(2):77-83. |
| WU W D, SHI B H, ZHENG C L,et al .Fault diagnosis of photovoltaic array based on improved sparrow search algorithm optimized RBF neural network[J].Smart Power,2023,51(2):77-83. | |
| 8 | 王小宇,刘波,孙凯,等 .光伏阵列故障诊断技术综述[J].电工技术学报,2024,39(20):6526-6543. |
| WANG X Y, LIU B, SUN K,et al .A review of photovoltaic array fault diagnosis technology[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society,2024,39(20):6526-6543. | |
| 9 | APPIAH A Y, ZHANG X, AYAWLI B B K,et al .Review and performance evaluation of photovoltaic array fault detection and diagnosis techniques[J].International Journal of Photoenergy,2019,2019(1):6953530. doi:10.1155/2019/6953530 |
| 10 | TSANAKAS J A, CHRYSOSTOMOU D, BOTSARIS P N,et al .Fault diagnosis of photovoltaic modules through image processing and Canny edge detection on field thermographic measurements[J].International Journal of Sustainable Energy,2015,34(6):351-372. doi:10.1080/14786451.2013.826223 |
| 11 | 刘强,郭珂,毛明轩,等 .一种基于串联等效电阻的光伏故障检测方法[J].太阳能学报,2020,41(10):119-126. |
| LIU Q, GUO K, MAO M X,et al .A photovoltaic fault detection method based on series equivalent resistance[J].Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica,2020,41(10):119-126. | |
| 12 | 孟佳彬,李智华,吴春华,等 .基于SSTDR的光伏系统对地故障检测方法[J].太阳能学报,2020,41(10):109-118. |
| MENG J B, LI Z H, WU C H,et al .Ground fault detection method for pv system based on sstdr[J].Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica,2020,41(10):109-118. | |
| 13 | ROY S, ALAM M K, KHAN F,et al .An irradiance-independent,robust ground-fault detection scheme for PV arrays based on spread spectrum time-domain reflectometry (SSTDR)[J].IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics,2018,33(8):7046-7057. doi:10.1109/tpel.2017.2755592 |
| 14 | 王元章,吴春华,周笛青,等 .基于BP神经网络的光伏阵列故障诊断研究[J].电力系统保护与控制,2013,41(16):108-114. |
| WANG Y Z, WU C H, ZHOU D Q,et al .A survey of fault diagnosis for PV array based on BP neural network[J].Power System Protection and Control,2013,41(16):108-114. | |
| 15 | 李元良,丁坤,陈富东,等 .基于快速过采样主成分分析法的光伏阵列故障诊断[J].电网技术,2019,43(1):308-315. |
| LI Y L, DING K, CHEN F D,et al .Fault diagnosis method of PV array based on fast OS-PCA[J].Power System Technology,2019,43(1):308-315. | |
| 16 | 徐先峰,李芷菡,刘状壮,等 .基于半监督学习标签传播-极端随机树算法的光伏阵列故障诊断及定位[J].电网技术,2023,47(3):1038-1047. |
| XU X F, LI Z H, LIU Z Z,et al .Fault diagnosis and localization of photovoltaic arrays based on semi-supervised learning label propagation-extra tree algorithm[J].Power System Technology,2023,47(3):1038-1047. | |
| 17 | 丁坤,陈富东,翁帅,等 .基于I-V特性灰色关联分析的光伏阵列健康状态评估[J].电网技术,2021,45(8):3087-3095. |
| DING K, CHEN F D, WENG S,et al .Health state evaluation of photovoltaic array based on I-V characteristics and grey relational analysis[J].Power System Technology,2021,45(8):3087-3095. | |
| 18 | 刘圣洋,冬雷,王晓晓,等 .基于高斯核模糊C均值聚类的光伏阵列故障诊断方法[J].太阳能学报,2021,42(5):286-294. |
| LIU S Y, DONG L, WANG X X,et al .Photovoltaic array fault diagnosis based on GKFCM[J].Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica,2021,42(5):286-294. | |
| 19 | HUANG J M, WAI R J, YANG G J .Design of hybrid artificial bee colony algorithm and semi-supervised extreme learning machine for PV fault diagnoses by considering dust impact[J].IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics,2020,35(7):7086-7099. doi:10.1109/tpel.2019.2956812 |
| 20 | CHEN J, YANG Y, MEI T,et al .Research on fault diagnosis for TCT photovoltaic array based on BA-KELM model[C]//2019 34rd Youth Academic Annual Conference of Chinese Association of Automation (YAC).Jinzhou,China:IEEE,2019:233-238. doi:10.1109/yac.2019.8787637 |
| 21 | 陈世群,杨耿杰,高伟 .一种基于BOA-SAE-EELM的光伏阵列故障诊断方法[J].太阳能学报,2022,43(4):154-161. |
| CHEN S Q, YANG G J, GAO W .A fault diagnosis method for photovoltaic array via BOA-SAE-EELM[J].Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica,2022,43(4):154-161. | |
| 22 | 赵靖英,吴晶晶,张雪辉,等 .基于萤火虫扰动麻雀搜索算法-极限学习机的光伏阵列故障诊断方法研究[J].电网技术,2023,47(4):1612-1625. |
| ZHAO J Y, WU J J, ZHANG X H,et al .Fault diagnosis of photovoltaic arrays based on sparrow search algorithm with firefly perturbation-extreme learning machine[J].Power System Technology,2023,47(4):1612-1625. | |
| 23 | MIRJALILI S, MIRJALILI S M, LEWIS A .Grey wolf optimizer[J].Advances in Engineering Software,2014,69:46-61. doi:10.1016/j.advengsoft.2013.12.007 |
| 24 | 闫浩,张恒超,李敏,等 .基于CNN-SVM的三相四线接线异常诊断算法[J].电网与清洁能源,2024,40(8):64-73. |
| YAN H, ZHANG H C, LI M,et al .Research on three-phase four-conductor wiring anomaly diagnosis algorithm based on CNN-SVM[J].Power System and Clean Energy,2024,40(8):64-73. | |
| 25 | 钟成,翟迪,陆阳,等 .基于改进灰狼算法的电力管廊覆盖优化技术[J].中国电力,2023,56(8):68-76. |
| ZHONG C, ZHAI D, LU Y,et al .Coverage optimization technology of power pipe gallery based on improved gray wolf algorithm[J].Electric Power,2023,56(8):68-76. | |
| 26 | ARORA S, ANAND P .Chaotic grasshopper optimization algorithm for global optimization[J].Neural Computing and Applications,2019,31(8):4385-4405. doi:10.1007/s00521-018-3343-2 |
| 27 | 刘帼巾,刘达明,缪建华,等 .基于变分模态分解和改进灰狼算法优化深度置信网络的自动转换开关故障识别[J].电工技术学报,2024,39(4):1221-1233. |
| LIU G J, LIU D M, MIAO J H,et al .Fault identification of automatic transfer switching equipment based on VMD-WPE and IGWO optimized DBN[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society,2024,39(4):1221-1233. | |
| 28 | 张达敏,徐航,王依柔,等 .嵌入Circle映射和逐维小孔成像反向学习的鲸鱼优化算法[J].控制与决策,2021,36(5):1173-1180. |
| ZHANG D M, XU H, WANG Y R,et al .Whale optimization algorithm for embedded Circle mapping and onedimensional oppositional learning based small hole imaging[J].Control and Decision,2021,36(5):1173-1180. | |
| 29 | HUANG G B, ZHU Q Y, SIEW C K .Extreme learning machine:theory and applications[J].Neurocomputing,2006,70(1/2/3):489-501. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.126 |
| 30 | 杨茂,张书天,王勃 .基于因果正则化极限学习机的风电功率短期预测方法[J].电力系统保护与控制,2024,52(11):127-136. |
| YANG M, ZHANG S T, WANG B .Short-term wind power forecasting method based on a causal regularized extreme learning machine[J].Power System Protection and Control,2024,52(11):127-136. | |
| 31 | 刘展,刘健洵,包琰洋,等 .基于图正则化堆叠自编码器的风机轴承故障诊断方法[J].发电技术,2024,45(6):1146-1152. |
| LIU Z, LIU J X, BAO Y Y,et al .Bearing faults diagnosis method based on stacked auto-encoder with graph regularization for wind turbines[J].Power Generation Technology,2024,45(6):1146-1152. |
| [1] | 刘展, 刘健洵, 包琰洋, 李大字. 基于图正则化堆叠自编码器的风机轴承故障诊断方法[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(6): 1146-1152. |
| [2] | 赵明阳, 殷林林, 韦文涛, 陈云, 刘日晨, 李军. 高压涡轮动叶叶尖掉块对气动性能及振动的影响[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(5): 856-867. |
| [3] | 刘佳, 孙佰仲, 高梓维. 高水分褐煤流动性离散元数值模拟[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(5): 969-974. |
| [4] | 王耀函, 张扬帆, 赵庆旭, 王晓东, 梁恺, 王玙. 低电压穿越过程中风电机组载荷特性联合仿真研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(4): 705-715. |
| [5] | 陈晓峰, 左川, 赵宁, 黄凯, 王惠杰. 集成蓄热装置的火电机组调峰特性分析[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 392-400. |
| [6] | 李展, 杨振勇, 刘磊, 陈振山, 季卫鸣, 洪烽. 火电机组深度调峰工况下炉侧蓄热系数对一次调频能力的影响分析[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 226-232. |
| [7] | 陈代俊, 陈里里, 李阳涛. 联合循环发电站电力输出预测[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(1): 99-105. |
| [8] | 董光德, 李道明, 陈咏涛, 马兴, 付昂, 穆钢, 肖白. 基于粒子群优化与卷积神经网络的电能质量扰动分类方法[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(1): 136-142. |
| [9] | 张航, 周传杰, 张林, 陈节涛, 徐春梅, 彭道刚. 基于概率神经网络-小波神经网络-DS信息融合的电厂引风机故障诊断[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43(6): 951-958. |
| [10] | 杨万开, 王兴国, 王书扬. 渝鄂柔性直流输电接入电网高频谐振与抑制分析[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43(3): 492-500. |
| [11] | 邹晓阳, 潘卫国. 海上浮式风机动力学仿真分析研究进展[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43(2): 249-259. |
| [12] | 罗耿. 山地光伏阵列布置方法和排间距计算[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43(2): 320-327. |
| [13] | 刘兰华, 狄林文, 董兴万, 王瑞林. 抛物槽式聚光太阳能集热回路动态特性研究[J]. 发电技术, 2021, 42(6): 673-681. |
| [14] | 白明亮, 张冬雪, 刘金福, 刘娇, 于达仁. 基于深度自编码器和支持向量数据描述的燃气轮机高温部件异常检测[J]. 发电技术, 2021, 42(4): 422-430. |
| [15] | 陈尚年, 李录平, 张世海, 欧阳敏南, 樊昂, 文贤馗. 汽轮发电机组振动故障诊断技术研究进展[J]. 发电技术, 2021, 42(4): 489-499. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||