

发电技术 ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 226-232.DOI: 10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.24023
李展1, 杨振勇1, 刘磊1, 陈振山1, 季卫鸣2, 洪烽2
收稿日期:2024-01-31
出版日期:2024-04-30
发布日期:2024-04-29
作者简介:基金资助:Zhan LI1, Zhenyong YANG1, Lei LIU1, Zhensan CHEN1, Weiming JI2, Feng HONG2
Received:2024-01-31
Published:2024-04-30
Online:2024-04-29
Supported by:摘要:
为研究火电机组深度调峰工况下炉侧蒸发段、过热段蓄热系数对机组一次调频能力的影响,以暂态稳定程序PSD-BPA中的典型模型为基础,同时考虑火电机组实际以炉跟机协调方式下的控制逻辑,搭建适用于火电深度调峰工况下的精细化仿真模型。通过某额定功率
中图分类号:
李展, 杨振勇, 刘磊, 陈振山, 季卫鸣, 洪烽. 火电机组深度调峰工况下炉侧蓄热系数对一次调频能力的影响分析[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 226-232.
Zhan LI, Zhenyong YANG, Lei LIU, Zhensan CHEN, Weiming JI, Feng HONG. Analysis of the Influence of Furnace Side Heat Storage Coefficient on Primary Frequency Modulation Capacity Under Deep Modulation Condition of Thermal Power Unit[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2024, 45(2): 226-232.
| 特征参数 | 扰动转差/(r/min) | |
|---|---|---|
机组功率 主汽压力 | 6 | 0.898 |
| 6 | 0.973 |
表1 35%Pe工况下R2值
Tab. 1 R2 value under working condition of 35%Pe
| 特征参数 | 扰动转差/(r/min) | |
|---|---|---|
机组功率 主汽压力 | 6 | 0.898 |
| 6 | 0.973 |
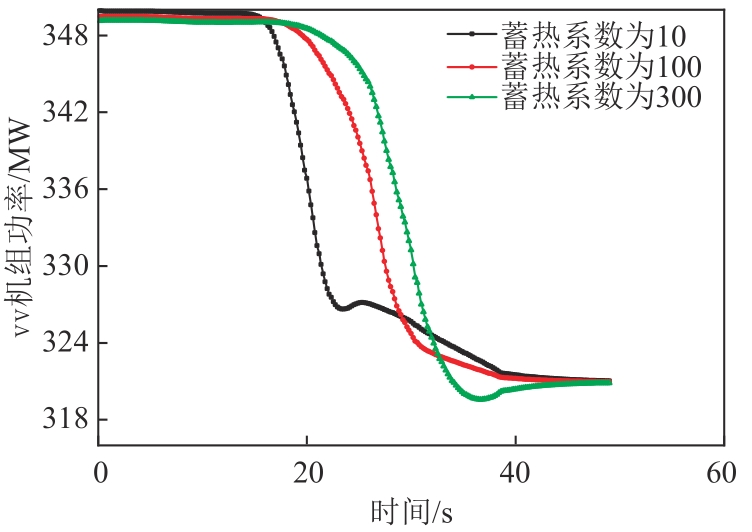
图5 不同蒸发段蓄热系数下6 r/min减负荷方向机组功率变化图
Fig. 5 Power variation diagram of the unit in the direction of 6 r/min load reduction under different evaporation section heat storage coefficient
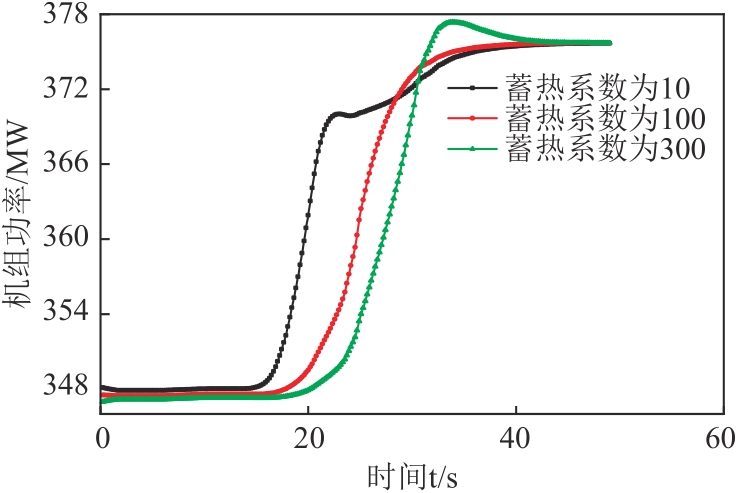
图6 不同蒸发段蓄热系数下6 r/min增负荷方向机组功率变化图
Fig. 6 Power variation diagram of the unit in the direction of 6 r/min load increase under different evaporation section heat storage coefficient
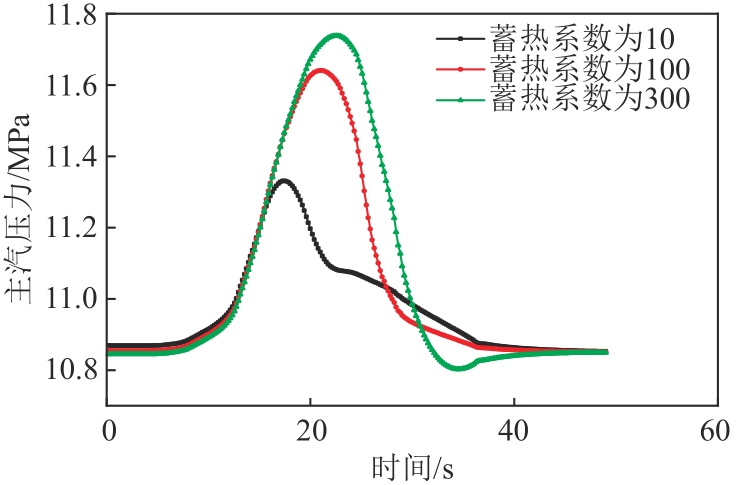
图7 不同蒸发段蓄热系数下6 r/min减负荷方向主汽压力变化图
Fig. 7 Pressure variation diagram of the unit in the direction of 6 r/min load reduction under different evaporation section heat storage coefficient
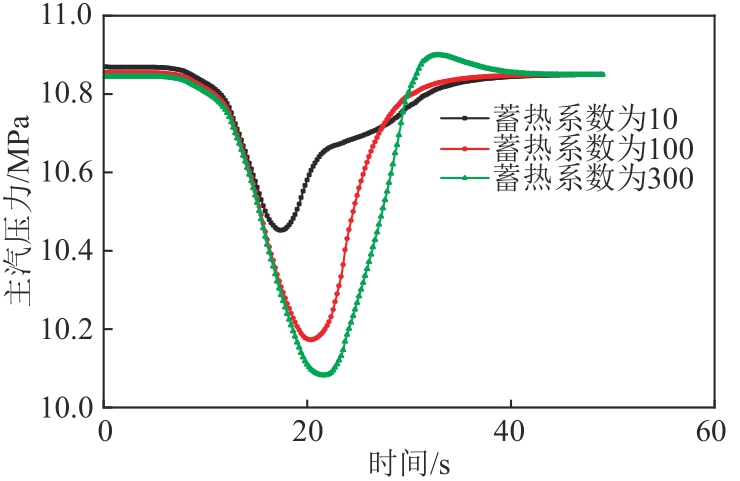
图8 不同蒸发段蓄热系数下6 r/min增负荷方向主汽压力变化图
Fig. 8 Pressure variation diagram of the unit in the direction of 6 r/min load increase under different evaporation section heat storage coefficient
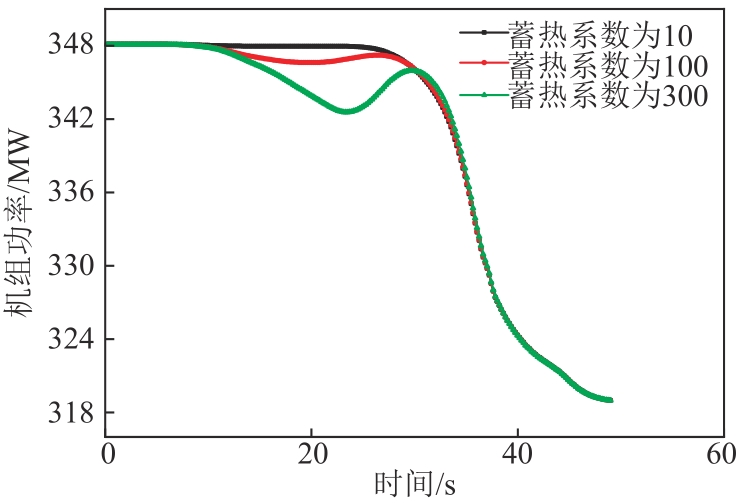
图9 不同过热段蓄热系数下6 r/min减负荷方向机组功率变化图
Fig. 9 Power variation diagram of the unit in the direction of 6 r/min load reduction under different heat storage coefficient of superheat section
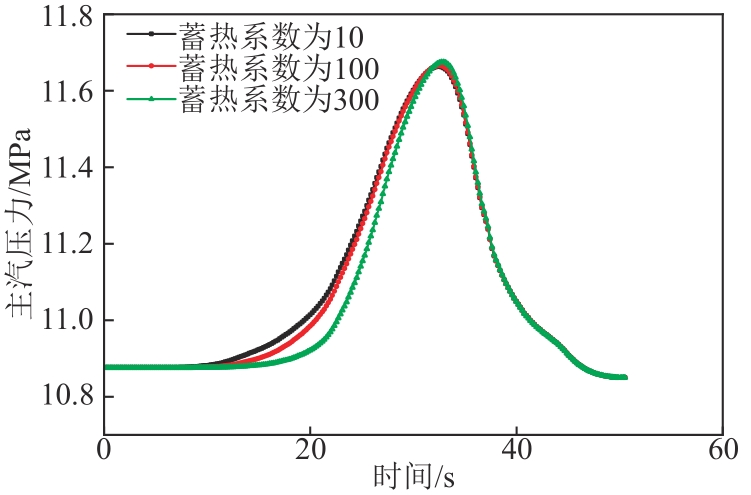
图10 不同过热段蓄热系数下6 r/min减负荷方向机组主汽压力变化图
Fig. 10 Pressure variation diagram of the unit in the direction of 6 r/min load reduction under different heat storage coefficient of superheat section
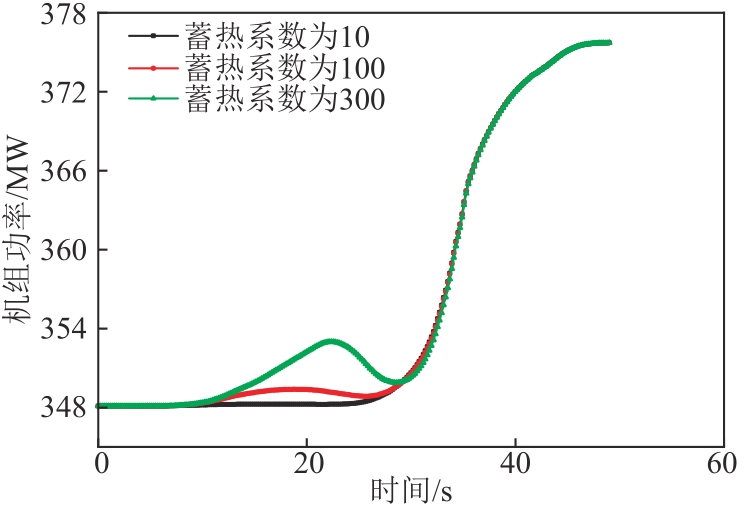
图11 不同过热段蓄热系数下6 r/min增负荷方向机组功率变化图
Fig. 11 Power variation diagram of the unit in the direction of 6 r/min load increase under different heat storage coefficient of superheat section
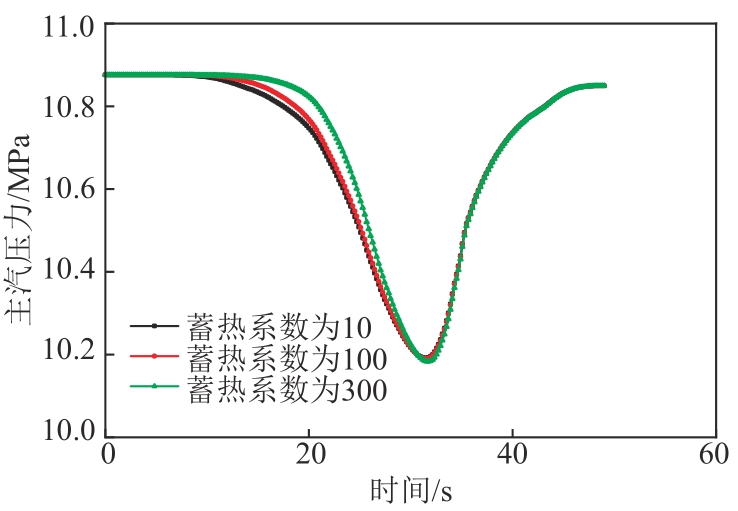
图12 不同过热段蓄热系数下6 r/min增负荷方向主汽压力变化图
Fig. 12 Pressure variation diagram of the unit in the direction of 6 r/min load increase under different heat storage coefficient of superheat section
| 1 | 袁岑颉, 戴敏敏, 周旭, 等 . 电力市场环境下火电机组调频性能提升研究[J]. 浙江电力, 2022, 41(6): 84-91. |
| YUAN C J, DAI M M, ZHOU X, et al . Research on frequency modulation performance improvement of thermal power units in the context of power market[J].Zhejiang Electric Power, 2022, 41(6): 84-91. | |
| 2 | 田云峰, 郭嘉阳, 刘永奇, 等 . 用于电网稳定性计算的再热凝汽式汽轮机数学模型[J]. 电网技术, 2007, 31(5): 39-44. doi:10.3321/j.issn:1000-3673.2007.05.009 |
| TIAN Y F, GUO J Y, LIU Y Q, et al . A mathematical model of rehear turbine for power grid stability calculation[J]. Power System Technology, 2007, 31(5): 39-44. doi:10.3321/j.issn:1000-3673.2007.05.009 | |
| 3 | 王永庆, 赵嘉, 曹越, 等 . 超临界机组及其一次调频控制系统的辨识与仿真[J]. 热能动力工程, 2018, 33(2): 111-116. doi:10.16146/j.cnki.rndlgc.2018.02.016 |
| WANG Y Q, ZHAO J, CAO Y, et al . Identification and simulation of a supercritical unit and its primary frequency modulation and control system[J]. Journal of Engineering for Thermal Energy and Power, 2018, 33(2): 111-116. doi:10.16146/j.cnki.rndlgc.2018.02.016 | |
| 4 | 盛锴, 邹鑫, 邱靖, 等 . 火电机组一次调频功率响应特性精细化建模[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54(6): 111-118. doi:10.11930/j.issn.1004-9649.202101111 |
| SHENG K, ZOU X, QIU J, et al . Refined modeling for power response characteristic of thermal power unit under primary frequency control[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54(6): 111-118. doi:10.11930/j.issn.1004-9649.202101111 | |
| 5 | 于国强, 崔晓波, 史毅越, 等 . 基于改进群优化算法的深度调峰机组一次调频建模[J]. 中国电力, 2020, 53(6): 147-152. doi:10.11930/j.issn.1004-9649.201910003 |
| YU G Q, CUI X B, SHI Y Y, et al . Primary frequency regulation modeling of deep peak regulation unit based on improved group optimization algorithm[J].Electric Power, 2020, 53(6): 147-152. doi:10.11930/j.issn.1004-9649.201910003 | |
| 6 | 郭越, 徐飞, 郝玲, 等 . 一次调频中的锅炉建模与参数在线确定[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43(17): 6551-6562. |
| GUO Y, XU F, HAO L, et al . Boiler modeling and online parameters identification for primary frequency regulation[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43(17): 6551-6562. | |
| 7 | 王学华, 姚力, 陈学州, 等 . 超超临界百万机组20%负荷深度调峰运行试验研究[J]. 能源与节能, 2024(1): 1-6. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-0802.2024.01.001 |
| WANG X H, YAO L, CHEN X Z, et al . 20% load deep peak shaving operation test of ultra-supercritical million units[J]. Energy and Energy Conservation, 2024(1): 1-6. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-0802.2024.01.001 | |
| 8 | 吕建, 白东海, 温武 . 新型电力系统下基于深度调峰的火电机组控制技术研究[J]. 山西电力, 2023(6): 49-53. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-0320.2023.06.011 |
| LV J, BAI D H, WEN W . Research on control technology of thermal power units based on deep peak regulation in new power systems[J]. Shanxi Electric Power, 2023(6): 49-53. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-0320.2023.06.011 | |
| 9 | 张洪福, 高明明, 于浩洋, 等 . 300 MW深度调峰循环流化床机组负荷响应特性研究[J]. 动力工程学报, 2023, 43(9): 1116-1122. |
| ZHANG H F, GAO M M, YU H Y, et al . Study on load response characteristics of a 300 MW circulating fluidized bed unit with deep peak regulation[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2023, 43(9): 1116-1122. | |
| 10 | 于国强, 刘克天, 胡尊民, 等 . 大规模新能源并网下火电机组深度调峰优化调度[J]. 电力工程技术, 2023, 42(1): 243-250. doi:10.12158/j.2096-3203.2023.01.029 |
| YU G Q, LIU K T, HU Z M, et al . Optimal scheduling of deep peak regulation for thermal power units in power grid with large-scale new energy[J].Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2023, 42(1): 243-250. doi:10.12158/j.2096-3203.2023.01.029 | |
| 11 | 袁春峰, 刘锴慧, 张帆, 等 . 火电机组一次调频技术研究进展综述[J]. 南方能源建设,2022,9(3):1-8. doi:10.16516/j.gedi.issn2095-8676.2022.03.001 |
| YUAN C F, LIU K H, ZHANG F, et al . Review on the research progress of primary frequency modulation technology for thermal power units[J]. Southern Energy Construction, 2022, 9(3): 1-8. doi:10.16516/j.gedi.issn2095-8676.2022.03.001 | |
| 12 | 赵国钦, 蓝茂蔚, 李杨, 等 . 基于最小二乘支持向量机的火电厂烟气含氧量预测模型优化研究[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(4): 534-542. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.21088 |
| ZHAO G Q, LAN M W, LI Y, et al . Study on optimization of prediction model of flue gas oxygen content in thermal power plant based on least squares support vector machine[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2023, 44(4): 534-542. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.21088 | |
| 13 | 顾正皓, 包劲松, 张宝, 等 . 考虑主蒸汽压力的燃煤机组调速模型的分析与改进[J]. 中国电力, 2016, 49(9): 93-98. doi:10.11930/j.issn.1004-9649.2016.09.093.06 |
| GU Z H, BAO J S, ZHANG B, et al . Analysis and improvement of speed governor model considering the main steam pressure influences[J]. Electric Power, 2016, 49(9): 93-98. doi:10.11930/j.issn.1004-9649.2016.09.093.06 | |
| 14 | 隋云任, 梁双印, 黄登超, 等 . 飞轮储能辅助燃煤机组调频动态过程仿真研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40(8): 2597-2606. |
| SUI Y R, LIANG S Y, HUANG D C, et al . Simulation study on frequency modulation process of coal burning plants with auxiliary of flywheel energy storage[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(8): 2597-2606. | |
| 15 | 谢昌亚, 朱龙飞, 胡娱欧, 等 . 660 MW超临界火电机组汽轮机及其调速系统精细化模型研究和应用[J]. 热能动力工程, 2023, 38(6): 58-67. |
| XIE C Y, ZHU L F, HU Y O, et al . Research and application of refined model for 660 MW supercritical thermal power unit steam turbine and its governing system[J]. Journal of Engineering for Thermal Energy and Power, 2023, 38(6): 58-67. | |
| 16 | 邓拓宇, 田亮, 刘吉臻 . 超超临界直流锅炉蓄热能力的定量分析[J]. 动力工程学报, 2012, 32(1): 10-14. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7607.2012.01.002 |
| DENG T Y, TIAN L, LIU J Z . Quantitative analysis on heat storage capacity of ultra-supercritical once-through boilers[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2012, 32(1): 10-14. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7607.2012.01.002 | |
| 17 | 杨玉龙, 王淞, 陈韬, 等 . 基于蓄热水箱温度可行域模糊确定的电锅炉优化调度方法[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44(7): 111-120. |
| YANG Y L, WANG S, CHEN T, et al . Optimal scheduling method of electric boiler based on fuzzy determination of temperature feasible region of hot water storage tank[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2023, 44(7): 111-120. | |
| 18 | 周鑫, 程松, 任景, 等 . 含储热型热电联产机组的电力系统源荷联合优化调峰方法[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2023, 38(5): 12-21. |
| ZHOU X, CHENG S, REN J, et al . A source-load joint optimization peak regulation method of power system with heat storage combined heat and power units[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2023, 38(5): 12-21. |
| [1] | 刘旺, 陈连, 龚高阳, 李智华, 薛文华, 石金刚, 谢军, 李雷雷, 姚荣财, 王召鹏, 杨延西, 邓毅, 张晨辉. 基于数字孪生的空气预热器预测性维护模式研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(4): 622-632. |
| [2] | 代华松, 浦绍旭, 柴国旭, 金李, 陈为平, 解明亮. 350 MW超临界流化床机组深度调峰研究与应用[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 401-411. |
| [3] | 陈晓峰, 左川, 赵宁, 黄凯, 王惠杰. 集成蓄热装置的火电机组调峰特性分析[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 392-400. |
| [4] | 丁湧. 1 000 MW超超临界燃煤锅炉深度调峰研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 382-391. |
| [5] | 杨正, 孙亦鹏, 温志强, 程亮, 李战国. 深度调峰工况下超临界机组的干湿态转换策略研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 233-239. |
| [6] | 贾志军, 范伟, 任少君, 魏唐斌. 600 MW亚临界机组长时间深度调峰燃烧稳定性研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 216-225. |
| [7] | 郑淇薇, 王华霆, 陈衡, 潘佩媛, 徐钢. 深度调峰背景下火电机组热电解耦技术路径对比分析[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 207-215. |
| [8] | 张思海, 李超然, 万广亮, 刘印学, 徐海楠, 黄中, 杨海瑞. 330 MW 循环流化床锅炉深度调峰技术[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 199-206. |
| [9] | 王放放, 杨鹏威, 赵光金, 李琦, 刘晓娜, 马双忱. 新型电力系统下火电机组灵活性运行技术发展及挑战[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 189-198. |
| [10] | 安吉振, 郑福豪, 刘一帆, 陈衡, 徐钢. 基于大数据分析的火电机组引风机故障预警研究[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(4): 557-564. |
| [11] | 楚帅, 王爱华, 葛维春, 李音璇, 崔岱. 电网调控集中式储热降低弃风率分析方法[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(1): 18-24. |
| [12] | 冯伟忠, 李励. “双碳”目标下煤电机组低碳、零碳和负碳化转型发展路径研究与实践[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43(3): 452-461. |
| [13] | 刘兰华, 狄林文, 董兴万, 王瑞林. 抛物槽式聚光太阳能集热回路动态特性研究[J]. 发电技术, 2021, 42(6): 673-681. |
| [14] | 刘云锋, 李宇峰, 王健, 马义良, 关淳. 汽轮机深度调峰的水蚀问题研究[J]. 发电技术, 2021, 42(4): 473-479. |
| [15] | 牛斌, 李丽锋, 孙倩, 张培华. 超临界循环流化床机组全负荷段深度调峰方法研究[J]. 发电技术, 2021, 42(2): 273-279. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||