

发电技术 ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 514-524.DOI: 10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.22175
董中豪1, 卢啸风1, 史丽超2, 杨增增2, 孔繁盛2, 王鹏2, 林国强3, 赵鹏3
收稿日期:2022-03-07
出版日期:2023-08-31
发布日期:2023-08-29
通讯作者:
卢啸风
作者简介:基金资助:Zhonghao DONG1, Xiaofeng LU1, Lichao SHI2, Zengzeng YANG2, Fansheng KONG2, Peng WANG2, Guoqiang LIN3, Peng ZHAO3
Received:2022-03-07
Published:2023-08-31
Online:2023-08-29
Contact:
Xiaofeng LU
Supported by:摘要:
为研究炉膛耐火材料热惯性对循环流化床(circulating fluidized bed,CFB)锅炉调峰特性的影响,基于300 MW亚临界CFB锅炉实际运行工况,以数值计算方式对其进行了研究。发现耐火材料热惯性受耐火材料导热系数和耐火材料厚度影响。当耐火材料导热系数由1 W/(m?K)增加到15 W/(m?K)时,耐火材料热平衡时间由5 812 s降低到3 426 s;耐火材料厚度由30 mm增大至90 mm时,热平衡时间由3 267 s增加到7 771 s。实炉按1%/min、2%/min、3%/min速率由50%升至100%额定负荷工况时,若密相区采用传统耐火材料,则平衡时间分别为82、65、60 min;当采用高导热耐火材料,则相应减少到65、46、40 min。根据计算结果拟合了耐火材料吸热速率变化公式;为考察密相区耐火材料热惯性对给煤策略的影响,定义并计算了耐火材料热惯性给煤影响系数。
中图分类号:
董中豪, 卢啸风, 史丽超, 杨增增, 孔繁盛, 王鹏, 林国强, 赵鹏. 炉膛耐火材料热惯性对循环流化床锅炉调峰速率的影响[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(4): 514-524.
Zhonghao DONG, Xiaofeng LU, Lichao SHI, Zengzeng YANG, Fansheng KONG, Peng WANG, Guoqiang LIN, Peng ZHAO. Influence of Thermal Inertia of Refractory Material in Furnace on the Peak Regulating Rate of Circulating Fluidized Bed Boiler[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2023, 44(4): 514-524.
| 分布位置 | 耐火防磨浇注料/mm | 耐火保温砖/mm | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 炉膛 | 布风板 | 77 | — |
| 炉膛锥段 | 60 | — | |
| 屏式受热面 | 50 | — | |
| 旋风分离器 | 分离器入口 | 25 | — |
| 分离器筒段 | 25 | — | |
| 分离器锥段 | 25 | — | |
| 立管及回料阀 | 立管 | 150 | 250 |
| 回料阀 | 150 | 250 | |
| 返料腿 | 150 | 250 | |
表1 300 MW亚临界CFB锅炉耐火材料分布
Tab. 1 Distribution of refractory materials for 300 MW subcritical CFB boiler
| 分布位置 | 耐火防磨浇注料/mm | 耐火保温砖/mm | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 炉膛 | 布风板 | 77 | — |
| 炉膛锥段 | 60 | — | |
| 屏式受热面 | 50 | — | |
| 旋风分离器 | 分离器入口 | 25 | — |
| 分离器筒段 | 25 | — | |
| 分离器锥段 | 25 | — | |
| 立管及回料阀 | 立管 | 150 | 250 |
| 回料阀 | 150 | 250 | |
| 返料腿 | 150 | 250 | |
| 参数 | 传统耐火材料 | 耐火保温砖 | 高导热耐火材料 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 导热率λ/[W/(m⋅K)] | 1.5 | 0.093+0.000 16T | 12.55/900 ℃ 11.28/800 ℃ |
| 密度ρ/(kg/m3) | 2750 | 500 | 3 560 |
| 比热容cp /(kJ∙kg-1∙K-1) | 0.92+ 0.000 147T | 0.769+0.000 26T | 1.229/900 ℃ |
表2 耐火材料热物理性质
Tab. 2 Thermophysical properties of refractory materials
| 参数 | 传统耐火材料 | 耐火保温砖 | 高导热耐火材料 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 导热率λ/[W/(m⋅K)] | 1.5 | 0.093+0.000 16T | 12.55/900 ℃ 11.28/800 ℃ |
| 密度ρ/(kg/m3) | 2750 | 500 | 3 560 |
| 比热容cp /(kJ∙kg-1∙K-1) | 0.92+ 0.000 147T | 0.769+0.000 26T | 1.229/900 ℃ |
| 部位 | 耐火防磨浇注料 | 耐火保温砖 | 总计 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 炉膛 | 布风板 | 27.53 | — | 166.46 |
| 炉膛锥段 | 115.17 | — | ||
| 屏式受热面 | 23.76 | — | ||
| 旋风分离器 | 分离器入口 | 37.81 | — | 151.49 |
| 分离器筒段 | 76.14 | — | ||
| 分离器锥段 | 37.57 | — | ||
| 立管及回料阀 | 立管 | 44.69 | 16.59 | 308.75 |
| 回料阀 | 30.11 | 10.95 | ||
| 返料腿 | 147.99 | 58.42 | ||
表3 300 MW亚临界CFB锅炉耐火材料质量分布 (t)
Tab. 3 Mass distribution of refractory materials for 300 MW subcritical CFB boiler
| 部位 | 耐火防磨浇注料 | 耐火保温砖 | 总计 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 炉膛 | 布风板 | 27.53 | — | 166.46 |
| 炉膛锥段 | 115.17 | — | ||
| 屏式受热面 | 23.76 | — | ||
| 旋风分离器 | 分离器入口 | 37.81 | — | 151.49 |
| 分离器筒段 | 76.14 | — | ||
| 分离器锥段 | 37.57 | — | ||
| 立管及回料阀 | 立管 | 44.69 | 16.59 | 308.75 |
| 回料阀 | 30.11 | 10.95 | ||
| 返料腿 | 147.99 | 58.42 | ||
| 参数 | 工况1 | 工况2 |
|---|---|---|
| 耐火材料导热率λ/[W/(m⋅K)] | 1,1.2,2,3,4,5,10,15 | 1.2 |
| 炉侧换热系数hf/[W/(m2⋅K)] | 360 | 360 |
| 耐火材料厚度δr/mm | 60 | 30,40,50,60,70,80,90 |
| 耐火材料密度ρ/(kg/m3) | 2 750 | 2 750 |
| 耐火材料比热容cp /[J/(kg⋅K)] | 1 092 | 1 092 |
| 工质温度tb/℃ | 330 | 330 |
| 初始温度T1/℃ | 850 | 850 |
| 终止温度T2/℃ | 950 | 950 |
表4 耐火材料热惯性影响因素计算工况
Tab. 4 Calculation working condition of influence factors of thermal inertia of refractory materials
| 参数 | 工况1 | 工况2 |
|---|---|---|
| 耐火材料导热率λ/[W/(m⋅K)] | 1,1.2,2,3,4,5,10,15 | 1.2 |
| 炉侧换热系数hf/[W/(m2⋅K)] | 360 | 360 |
| 耐火材料厚度δr/mm | 60 | 30,40,50,60,70,80,90 |
| 耐火材料密度ρ/(kg/m3) | 2 750 | 2 750 |
| 耐火材料比热容cp /[J/(kg⋅K)] | 1 092 | 1 092 |
| 工质温度tb/℃ | 330 | 330 |
| 初始温度T1/℃ | 850 | 850 |
| 终止温度T2/℃ | 950 | 950 |
| 材料类型 | 锅炉运行工况 | 锅炉变负荷速率/ (%/min) | 耐火材料厚度/ mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 传统耐火材料 | 50%~100%,100%~50% | 1,2,3 | 60 |
| 高导热耐火材料 | 50%~100%,100%~50% | 1,2,3 | 60 |
表5 炉膛密相区耐火材料热惯性计算工况
Tab. 5 Thermal inertia calculation conditions of refractory materials in dense phase area of furnace
| 材料类型 | 锅炉运行工况 | 锅炉变负荷速率/ (%/min) | 耐火材料厚度/ mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 传统耐火材料 | 50%~100%,100%~50% | 1,2,3 | 60 |
| 高导热耐火材料 | 50%~100%,100%~50% | 1,2,3 | 60 |
| 参数 | 100% BRL | 75% BRL | 50% BRL |
|---|---|---|---|
| 主蒸汽流量/(t/h) | 966 | 779 | 466 |
| 主蒸汽温度/℃ | 541 | 541 | 541 |
| 主蒸汽压力/MPa | 16.10 | 14.49 | 11.37 |
| 给水温度/℃ | 276 | 255 | 233 |
| 给水压力/MPa | 17.92 | 15.75 | 12.59 |
| 汽包压力/MPa | 17.51 | 15.46 | 12.37 |
| 炉膛密相区床温/℃ | 950 | 900 | 850 |
| 给煤量/(t/h) | 204.90 | 157.13 | 108.59 |
| 燃料低位发热量/(kJ/kg) | 13 498 | 13 498 | 13 498 |
表6 300 MW亚临界循环流化床锅炉运行参数
Tab. 6 Operation parameters of 300 MW subcritical CFB boiler
| 参数 | 100% BRL | 75% BRL | 50% BRL |
|---|---|---|---|
| 主蒸汽流量/(t/h) | 966 | 779 | 466 |
| 主蒸汽温度/℃ | 541 | 541 | 541 |
| 主蒸汽压力/MPa | 16.10 | 14.49 | 11.37 |
| 给水温度/℃ | 276 | 255 | 233 |
| 给水压力/MPa | 17.92 | 15.75 | 12.59 |
| 汽包压力/MPa | 17.51 | 15.46 | 12.37 |
| 炉膛密相区床温/℃ | 950 | 900 | 850 |
| 给煤量/(t/h) | 204.90 | 157.13 | 108.59 |
| 燃料低位发热量/(kJ/kg) | 13 498 | 13 498 | 13 498 |
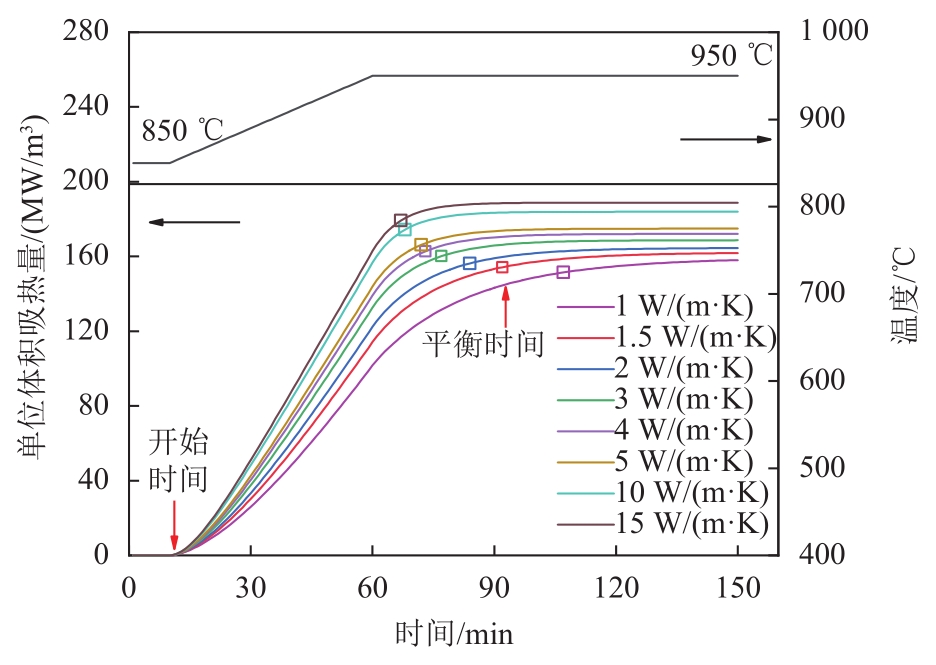
图3 变负荷过程中不同导热系数耐火材料单位体积吸热量
Fig. 3 Heat absorption per unit volume of refractory materials with different thermal conductivity in the process of variable load
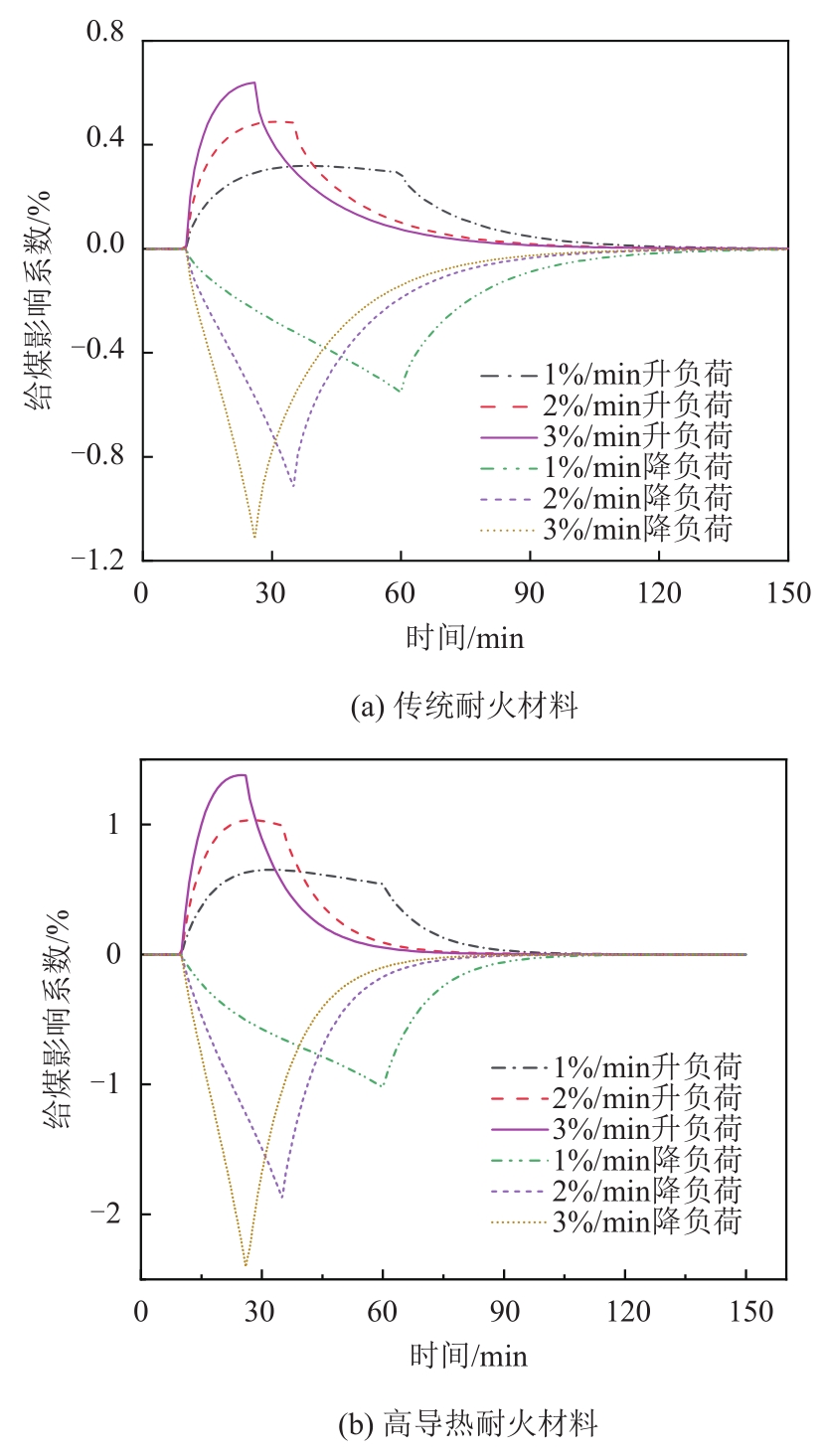
图9 变负荷过程中密相区耐火材料热惯性给煤影响系数随时间变化关系
Fig. 9 Change of influence coefficient of thermal inertia coal feeding of refractory materials in dense phase area with time during variable load process
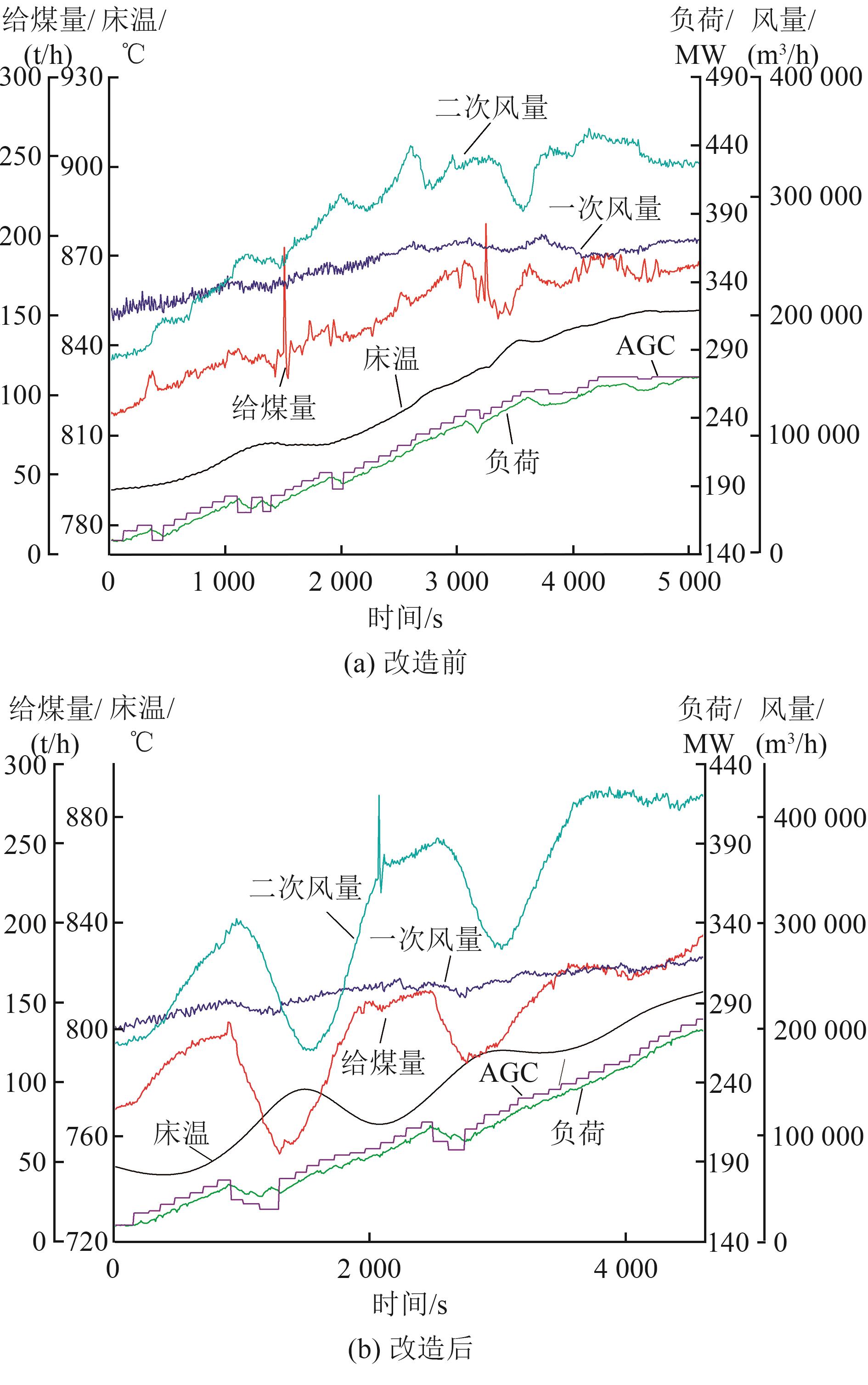
图10 改造前后50%~90%升负荷过程中锅炉运行参数随时间变化曲线
Fig. 10 Variation curves of boiler operating parameters with time in the process of 50%-90% liter load before and after transformation
| 1 | GU Y J, XU J, CHEN D C,et al .Overall review of peak shaving for coal-fired power units in China[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2016,54:723-731. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2015.10.052 |
| 2 | XUE Y S, ZHENG Y Q, RAHMAN S .Proceedings of purple mountain forum 2019-international forum on smart grid protection and control[M].Singapore:Springer,2019. doi:10.1007/978-981-13-9783-7 |
| 3 | 王珏,廖溢文,韩文福,等 .碳达峰背景下抽水蓄能-风电联合系统建模及有功功率控制特性研究[J].水利水电技术,2021,52(9):172-181. doi:10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2021.09.018 |
| WANG Y, LIAO Y W, HAN W F,et al .Modeling and active power control characteristics of pumped storage-wind hybrid power system in the context of peak carbon dioxide emission[J].Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2021,52(9):172-181. doi:10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2021.09.018 | |
| 4 | 王磊,牛耘依,孟娜,等 .考虑调峰与储能特性的抽蓄电站服务电网综合评价[J].电网与清洁能源,2022,38(5):135-142. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3814.2022.05.018 |
| WANG L, NIU Y Y, MENG N,et al .Comprehensive evaluation of pumped storage power plant serving grid considering peak regulation and energy storage[J].Power System and Clean Energy,2022,38(5):135-142. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3814.2022.05.018 | |
| 5 | 魏文,姜飞,戴双凤,等 .计及需求侧储能事故备用风险与火电机组深度调峰的经济优化研究[J].电力系统保护与控制,2022,50(10):153-162. |
| WEI W, JIANG F, DAI S F,et al .Economic optimization of deep peak regulation of thermal power units taking into account the risk of emergency storage on the demand side[J].Power System Protection and Control,2022,50(10):153-162. | |
| 6 | 于国强,刘克天,胡尊民,等 .大规模新能源并网下火电机组深度调峰优化调度[J].电力工程技术,2023,42(1):243-250. doi:10.12158/j.2096-3203.2023.01.029 |
| YU G Q, LIU K T, HU Z M,et al .Optimal scheduling of deep peak regulation for thermal power units in power grid with large-scale new energy[J].Electric Power Engineering Technology,2023,42(1):243-250. doi:10.12158/j.2096-3203.2023.01.029 | |
| 7 | 张松岩,苗世洪,尹斌鑫,等 .考虑火电深度调峰的多类型储能经济性分析[J].电力建设,2022,43(1):132-142. doi:10.12204/j.issn.1000-7229.2022.01.015 |
| ZHANG S Y, MIAO S H, YIN B X,et al .Economic analysis of multi-type energy storages considering the deep peak-regulation of thermal power units[J].Electric Power Construction,2022,43(1):132-142. doi:10.12204/j.issn.1000-7229.2022.01.015 | |
| 8 | 闫修峰,宗珂,何修年,等 .1 000 MW煤电机组调峰中汽温控制策略研究[J].发电技术,2022,43(3):518-522. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.21024 |
| YAN X F, ZONG K, HE X N,et al .Research on steam temperature control strategy in peak regulation of 1 000 MW coal power unit[J].Power Generation Technology,2022,43(3):518-522. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.21024 | |
| 9 | 牛斌,李丽锋,孙倩,等 .超临界循环流化床机组全负荷段深度调峰方法研究[J].发电技术,2021,42(2):273-279. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.20024 |
| NIU B, LI L F, SUN Q,et al .Research on the method of depth peaking at full load of supercritical circulating fluidized bed unit[J].Power Generation Technology,2021,42(2):273-279. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.20024 | |
| 10 | 宋畅,吕俊复,杨海瑞,等 .超临界及超超临界循环流化床锅炉技术研究与应用[J].中国电机工程学报,2018,38(2):338-347. |
| SONG C, LYU J F, YANG H R,et al .Research and application of supercritical and ultra-supercritical circulating fluidized bed boiler technology[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2018,38(2):338-347. | |
| 11 | 蔡晋,单露,王志宁,等 .超临界350 MW循环流化床锅炉变负荷特性[J].热力发电,2020,49(9):98-103. doi:10.19666/j.rlfd.202002012 |
| CAI J, SHAN L, WANG Z N,et al .Variable load characteristics of a supercritical 350 MW circulating fluidized bed boiler[J].Thermal Power Generation,2020,49(9):98-103. doi:10.19666/j.rlfd.202002012 | |
| 12 | 张绪辉,杨兴森,辛刚,等 .燃煤火电机组深度调峰运行试验[J].洁净煤技术,2022,28(4):144-150. |
| ZHANG X H, YANG X S, XIN G,et al .Experimental study on deep peak regulation operation of coal-fired thermal power unit[J].Clean Coal Technology,2022,28(4):144-150. | |
| 13 | 杨中智,卢啸风,角加艺,等 .大型CFB锅炉低负荷再热汽温稳定特性研究[J].洁净煤技术,2023,29(6):32-39. |
| YANG Z Z, LU X F, JIAO J Y,et al .Study on temperature stability characteristics of low load reheat steam in large CFB boiler[J].Clean Coal Technology,2023,29(6):32-39. | |
| 14 | 洪烽 .基于蓄能深度利用的循环流化床机组动态优化控制[D].北京:华北电力大学,2019. |
| HONG F .Dynamic optimal control of criculating fluidized bed unit based on deep utilization of stored energy[D].Beijing:School of Energy Power and Mechanical Engineering,2019. | |
| 15 | 李政,王哲,倪维斗 .循环流化床全工况实时动态数学模型的研究[J].动力工程,2000,20(1):511-514. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7607.2000.01.002 |
| LI Z, WANG Z, NI W D .Study of full working scope dynamic mathematical model for CFBC[J].Power Engineering,2000,20(1):511-514. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7607.2000.01.002 | |
| 16 | GAO M M, HONG F, LIU J Z .Investigation on energy storage and quick load change control of subcritical circulating fluidized bed boiler units[J].Applied Energy,2017,185. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.10.140 |
| 17 | 高明明,岳光溪,雷秀坚,等 .超临界CFB锅炉主蒸汽压力控制系统研究[J].动力工程学报,2015,35(8):625-631. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7607.2015.08.004 |
| GAO M M, YUE G X, LEI X J,et al .Research on main steam pressure control of supercritical CFB boilers[J].Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering,2015,35(8):625-631. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7607.2015.08.004 | |
| 18 | 刘吉臻,洪烽,高明明,等 .循环流化床机组快速变负荷运行控制策略研究[J].中国电机工程学报,2017,37(14):4130-4137. doi:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.161055 |
| LIU J Z, HONG F, GAO M M,et al .Research on the control strategy for quick load change of circulating fluidized bed boiler units[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2017,37(14):4130-4137. doi:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.161055 | |
| 19 | ZHANG H F, GAO M M, FENG H,et al .Control-oriented modelling and investigation on quick load change control of subcritical circulating fluidized bed unit[J].Applied Thermal Engineering,2019,163:1-12. doi:10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.114420 |
| 20 | STEFANITSIS D, NESIADIS A, NIKOLOPOULOS A,et al .Simulation of a circulating fluidized bed power plant integrated with a thermal energy storage system during transient operation[J].Journal of Energy Storage,2021,43:1-17. doi:10.1016/j.est.2021.103239 |
| 21 | DENG B Y, ZHANG M, LYU J F,et al .Analysis on the safety of the water wall in a 350 MW supercritical cfb boiler under electricity failure condition[J].Energy,2019,189:116364. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2019.116364 |
| 22 | 韩小华,黄浩天,闫希晔,等 .大体积混凝土内部温度控制与现场测温差异分析[J].建筑技术,2022,53(8):1094-1097. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-4726.2022.08.035 |
| HAN X H, HUANG H T, YAN X Y,et al .Analysis of difference between internal temperature control and on-site temperature measurement of mass concrete[J].Architecture Technology,2022,53(8):1094-1097. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-4726.2022.08.035 | |
| 23 | 张絮涵 .混凝土埋管式辐射冷顶板室内非稳态换热特性研究[D].长沙:湖南大学,2016. doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2015.11.006 |
| ZHANG X H .Research on the characteristics of non-steady state heat transfer in the room with concrete ceiling radiant cooling panels[D].Changsha:Hunan University,2016. doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2015.11.006 | |
| 24 | RAFIQUE M M, NATHAN G,SAW W .A mathematical model to assess the influence of transients on a refractory-lined solar receiver[J].Renewable Energy,2021,167(C):217-235. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2020.11.077 |
| 25 | RAFIQUE M M, NATHAN G,SAW W .Modelled annual thermal performance of a 50 MW refractory-lined particle-laden solar receiver operating above 1 000 ℃[J].Renewable Energy,2022,197:168-175. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2022.07.111 |
| 26 | RAFIQUE M M, NATHAN G,SAW W .Thermal response of multilayered refractory-lined solar receivers to transient operation[J].Solar Energy,2022,243:352-361. doi:10.1016/j.solener.2022.07.037 |
| 27 | QI G L, LIU X M, WANG Z W,et al .Numerical simulation and optimization of heat-insulation material and structure for CFB boiler[J].Thermal Science and Engineering Progress,2020,20(12):100692. doi:10.1016/j.tsep.2020.100692 |
| 28 | FENG H J, CHEN L G, XIE Z H,et al .Constructal designs for insulation layers of steel rolling reheating furnace wall with convective and radiative boundary conditions[J].Applied Thermal Engineering,2016,100:145-152. doi:10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.02.129 |
| 29 | ZHOU X H, NIU T T, XIN Y F,et al .Experimental and numerical investigation on heat transfer in the vertical upward flow water wall of a 660 MW ultra-supercritical CFB boiler[J].Applied Thermal Engineering,2021,188:169-178. doi:10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2021.116664 |
| 30 | PAN J, WU G, YANG D .Thermal-hydraulic calculation and analysis on water wall system of 600 MW supercritical CFB boiler[J].Applied Thermal Engineering,2015,82:225-236. doi:10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.03.004 |
| 31 | LI J, TUNG Y, KWAUK M .Energy transport and regime transition in particle-fluid two-phase flow[C]//Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Circulating Fluidized Beds,Compiégne,France.1988:75-87. doi:10.1016/b978-0-08-036225-0.50012-5 |
| 32 | 黄永志 .循环流化床锅炉水动力特性研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2016. |
| HUANG Y Z .Research on water circulation characteristics of evaporating system in CFB boiler[D].Shanghai:Shanghai Jiaotong University,2016. | |
| 33 | 张宏涛,徐冰,白玉星,等 .钢混凝土界面接触热阻试验研究[J].土木建筑与环境工程,2015,37(2):34-38. doi:10.11835/j.issn.1674-4764.2015.02.006 |
| ZHANG H T, XU B, BAI Y X,et al .Experiment alanalysis of interface thermal contact resistance between steel and concrete[J].Journal of Civil, Architectural & Environmental Engineering,2015,37(2):34-38. doi:10.11835/j.issn.1674-4764.2015.02.006 |
| [1] | 袁鑫, 刘骏, 陈衡, 潘佩媛, 徐钢, 王修彦. 碳捕集技术应用对燃煤机组调峰能力的影响[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 373-381. |
| [2] | 丁湧. 1 000 MW超超临界燃煤锅炉深度调峰研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 382-391. |
| [3] | 陈晓峰, 左川, 赵宁, 黄凯, 王惠杰. 集成蓄热装置的火电机组调峰特性分析[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 392-400. |
| [4] | 代华松, 浦绍旭, 柴国旭, 金李, 陈为平, 解明亮. 350 MW超临界流化床机组深度调峰研究与应用[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 401-411. |
| [5] | 李军徽, 陈国航, 马腾, 李翠萍, 朱星旭, 贾晨. 高风电渗透率下液流电池储能系统调峰优化控制策略[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 434-447. |
| [6] | 高忠明, 朱德敖, 陈雨佳, 刘三举, 王勤辉. 农林废弃物循环流化床空气气化特性实验研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 535-544. |
| [7] | 张思海, 李超然, 万广亮, 刘印学, 徐海楠, 黄中, 杨海瑞. 330 MW 循环流化床锅炉深度调峰技术[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 199-206. |
| [8] | 郑淇薇, 王华霆, 陈衡, 潘佩媛, 徐钢. 深度调峰背景下火电机组热电解耦技术路径对比分析[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 207-215. |
| [9] | 贾志军, 范伟, 任少君, 魏唐斌. 600 MW亚临界机组长时间深度调峰燃烧稳定性研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 216-225. |
| [10] | 李展, 杨振勇, 刘磊, 陈振山, 季卫鸣, 洪烽. 火电机组深度调峰工况下炉侧蓄热系数对一次调频能力的影响分析[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 226-232. |
| [11] | 杨正, 孙亦鹏, 温志强, 程亮, 李战国. 深度调峰工况下超临界机组的干湿态转换策略研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 233-239. |
| [12] | 邓启刚, 吕卓, 石友, 鲁佳易, 周旭, 王奥宇, 杨冬. 不带外置床的700 MW超超临界循环流化床锅炉失电后水冷壁安全计算分析[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 240-249. |
| [13] | 于松源, 张峻松, 元志伟, 房方. 计及热惯性的热电联产虚拟电厂韧性提升策略[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(6): 758-768. |
| [14] | 郁海彬, 张煜晨, 刘扬洋, 陆增洁, 翁锦德. 碳交易机制下多主体虚拟电厂参与电力市场的优化调度竞标策略[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(5): 634-644. |
| [15] | 楚帅, 王爱华, 葛维春, 李音璇, 崔岱. 电网调控集中式储热降低弃风率分析方法[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(1): 18-24. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||