

发电技术 ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 600-610.DOI: 10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.23162
罗勇军1, 李建波2, 朱红燕2
收稿日期:2023-12-04
修回日期:2024-03-07
出版日期:2024-08-31
发布日期:2024-08-27
通讯作者:
李建波
作者简介:基金资助:Yongjun LUO1, Jianbo LI2, Hongyan ZHU2
Received:2023-12-04
Revised:2024-03-07
Published:2024-08-31
Online:2024-08-27
Contact:
Jianbo LI
Supported by:摘要:
目的 研究生物质在流化床燃烧过程的结焦问题,分析钾盐形式和含量对生物质灰烧结熔融特性的影响。 方法 借助扫描电子显微镜耦合能谱仪、X射线衍射仪、X射线荧光分析仪和FactSage热力学计算软件,通过实验分析了生物质合成灰的烧结熔融特性和矿物转变规律。 结果 在流化床的典型运行温度750~950 ℃范围内,合成灰的烧结熔融程度随温度以及钾盐质量分数的增加而加剧。此外,钾盐形式不同,其对生物质合成灰的烧结熔融特性的影响也有显著差异:钾盐为K2CO3时,合成灰中液相比例最高可达34.36%,合成灰由此发生严重烧结;钾盐为KCl时,大部分K和Cl元素在750~850 ℃逃逸,合成灰的烧结程度较K2CO3有所减弱;钾盐为K2SO4时,合成灰中液相含量最少,烧结熔融程度也最弱。 结论 改变钾盐的存在形式并控制床温,有望缓解生物质在流化床燃烧过程的结焦问题。
中图分类号:
罗勇军, 李建波, 朱红燕. 生物质合成灰的烧结熔融特性和矿物转变规律实验研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(4): 600-610.
Yongjun LUO, Jianbo LI, Hongyan ZHU. Experimental Study on Sintering and Melting Characteristics and Mineral Transformation Law of Synthetic Biomass Ash[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2024, 45(4): 600-610.
| 样品 | 化学成分质量分数/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | CaO | MgO | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | Na2SO4 | |
| 1 | 7.50 | 69.16 | 6.78 | 2.50 | 2.03 | 4.65 |
| 2 | 7.50 | 60.50 | 5.94 | 2.50 | 1.78 | 4.08 |
| 3 | 7.50 | 43.22 | 4.24 | 2.50 | 1.27 | 3.96 |
| 4 | 7.50 | 69.16 | 6.78 | 2.50 | 2.03 | 4.65 |
| 5 | 7.50 | 60.50 | 5.94 | 2.50 | 1.78 | 4.08 |
| 6 | 7.50 | 43.22 | 4.24 | 2.50 | 1.27 | 3.96 |
| 7 | 7.50 | 69.16 | 6.78 | 2.50 | 2.03 | 4.65 |
| 8 | 7.50 | 60.50 | 5.94 | 2.50 | 1.78 | 4.08 |
| 9 | 7.50 | 43.22 | 4.24 | 2.50 | 1.27 | 3.96 |
| 10 | 37.50 | 34.58 | 3.39 | 12.50 | 1.02 | 2.34 |
| 11 | 37.50 | 25.94 | 2.54 | 12.50 | 0.76 | 1.74 |
| 12 | 37.50 | 8.65 | 0.85 | 12.50 | 0.25 | 0.57 |
| 13 | 37.50 | 34.58 | 3.39 | 12.50 | 1.02 | 2.34 |
| 14 | 37.50 | 25.94 | 2.54 | 12.50 | 0.76 | 1.74 |
| 15 | 37.50 | 8.65 | 0.85 | 12.50 | 0.25 | 0.57 |
| 16 | 37.50 | 34.58 | 3.39 | 12.50 | 1.02 | 2.34 |
| 17 | 37.50 | 25.94 | 2.54 | 12.50 | 0.76 | 1.74 |
| 18 | 37.50 | 8.65 | 0.85 | 12.50 | 0.25 | 0.57 |
表1 生物质合成灰的化学成分组成
Tab. 1 Chemical composition of synthetic biomass ash
| 样品 | 化学成分质量分数/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | CaO | MgO | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | Na2SO4 | |
| 1 | 7.50 | 69.16 | 6.78 | 2.50 | 2.03 | 4.65 |
| 2 | 7.50 | 60.50 | 5.94 | 2.50 | 1.78 | 4.08 |
| 3 | 7.50 | 43.22 | 4.24 | 2.50 | 1.27 | 3.96 |
| 4 | 7.50 | 69.16 | 6.78 | 2.50 | 2.03 | 4.65 |
| 5 | 7.50 | 60.50 | 5.94 | 2.50 | 1.78 | 4.08 |
| 6 | 7.50 | 43.22 | 4.24 | 2.50 | 1.27 | 3.96 |
| 7 | 7.50 | 69.16 | 6.78 | 2.50 | 2.03 | 4.65 |
| 8 | 7.50 | 60.50 | 5.94 | 2.50 | 1.78 | 4.08 |
| 9 | 7.50 | 43.22 | 4.24 | 2.50 | 1.27 | 3.96 |
| 10 | 37.50 | 34.58 | 3.39 | 12.50 | 1.02 | 2.34 |
| 11 | 37.50 | 25.94 | 2.54 | 12.50 | 0.76 | 1.74 |
| 12 | 37.50 | 8.65 | 0.85 | 12.50 | 0.25 | 0.57 |
| 13 | 37.50 | 34.58 | 3.39 | 12.50 | 1.02 | 2.34 |
| 14 | 37.50 | 25.94 | 2.54 | 12.50 | 0.76 | 1.74 |
| 15 | 37.50 | 8.65 | 0.85 | 12.50 | 0.25 | 0.57 |
| 16 | 37.50 | 34.58 | 3.39 | 12.50 | 1.02 | 2.34 |
| 17 | 37.50 | 25.94 | 2.54 | 12.50 | 0.76 | 1.74 |
| 18 | 37.50 | 8.65 | 0.85 | 12.50 | 0.25 | 0.57 |
| 等级 | 类别 | 特征 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 附着灰 | 无黏聚特征,灰粒间呈松散堆积状 |
| 1 | 微黏聚灰渣 | 已有灰粒的黏聚特征,易刮除,呈疏松状 |
| 2 | 弱黏聚灰渣 | 有一定的黏聚特征,较易刮除,有一定硬度 |
| 3 | 黏聚灰渣 | 黏聚在一起,硬度比强黏聚灰渣弱,较难刮除 |
| 4 | 强黏聚灰渣 | 硬度较大,无法完全刮除,不规则地黏聚硬渣 |
| 5 | 黏熔灰渣 | 由全熔融和半熔融渣组成,二者之间无法分开 |
| 6 | 熔融灰渣 | 全熔融,残灰表面被流渣覆盖,内部泡状结构 |
表2 合成灰烧结和熔融等级划分
Tab. 2 Sintering and melting grade division of synthetic ash
| 等级 | 类别 | 特征 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 附着灰 | 无黏聚特征,灰粒间呈松散堆积状 |
| 1 | 微黏聚灰渣 | 已有灰粒的黏聚特征,易刮除,呈疏松状 |
| 2 | 弱黏聚灰渣 | 有一定的黏聚特征,较易刮除,有一定硬度 |
| 3 | 黏聚灰渣 | 黏聚在一起,硬度比强黏聚灰渣弱,较难刮除 |
| 4 | 强黏聚灰渣 | 硬度较大,无法完全刮除,不规则地黏聚硬渣 |
| 5 | 黏熔灰渣 | 由全熔融和半熔融渣组成,二者之间无法分开 |
| 6 | 熔融灰渣 | 全熔融,残灰表面被流渣覆盖,内部泡状结构 |
| A/B | 钾盐 | 质量分数/% | 烧结等级 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 750 ℃ | 850 ℃ | 950 ℃ | |||
| 0.1 | K2CO3 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 20 | 2 | 2 | 3 | ||
| 40 | 2 | 4 | 5 | ||
| KCl | 10 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| 20 | 2 | 2 | 3 | ||
| 40 | 2 | 2 | 4 | ||
| K2SO4 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| 20 | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| 40 | 2 | 2 | 4 | ||
| 1.0 | K2CO3 | 10 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| 20 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 40 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| KCl | 10 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 20 | 3 | 3 | 4 | ||
| 40 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| K2SO4 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 4 | |
| 20 | 2 | 2 | 4 | ||
| 40 | 3 | 3 | 4 | ||
表3 合成灰在750~950 ℃的烧结熔融等级
Tab. 3 Sintering and melting degree of synthetic ash at 750-950 ℃
| A/B | 钾盐 | 质量分数/% | 烧结等级 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 750 ℃ | 850 ℃ | 950 ℃ | |||
| 0.1 | K2CO3 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 20 | 2 | 2 | 3 | ||
| 40 | 2 | 4 | 5 | ||
| KCl | 10 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| 20 | 2 | 2 | 3 | ||
| 40 | 2 | 2 | 4 | ||
| K2SO4 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| 20 | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| 40 | 2 | 2 | 4 | ||
| 1.0 | K2CO3 | 10 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| 20 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 40 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| KCl | 10 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 20 | 3 | 3 | 4 | ||
| 40 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| K2SO4 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 4 | |
| 20 | 2 | 2 | 4 | ||
| 40 | 3 | 3 | 4 | ||
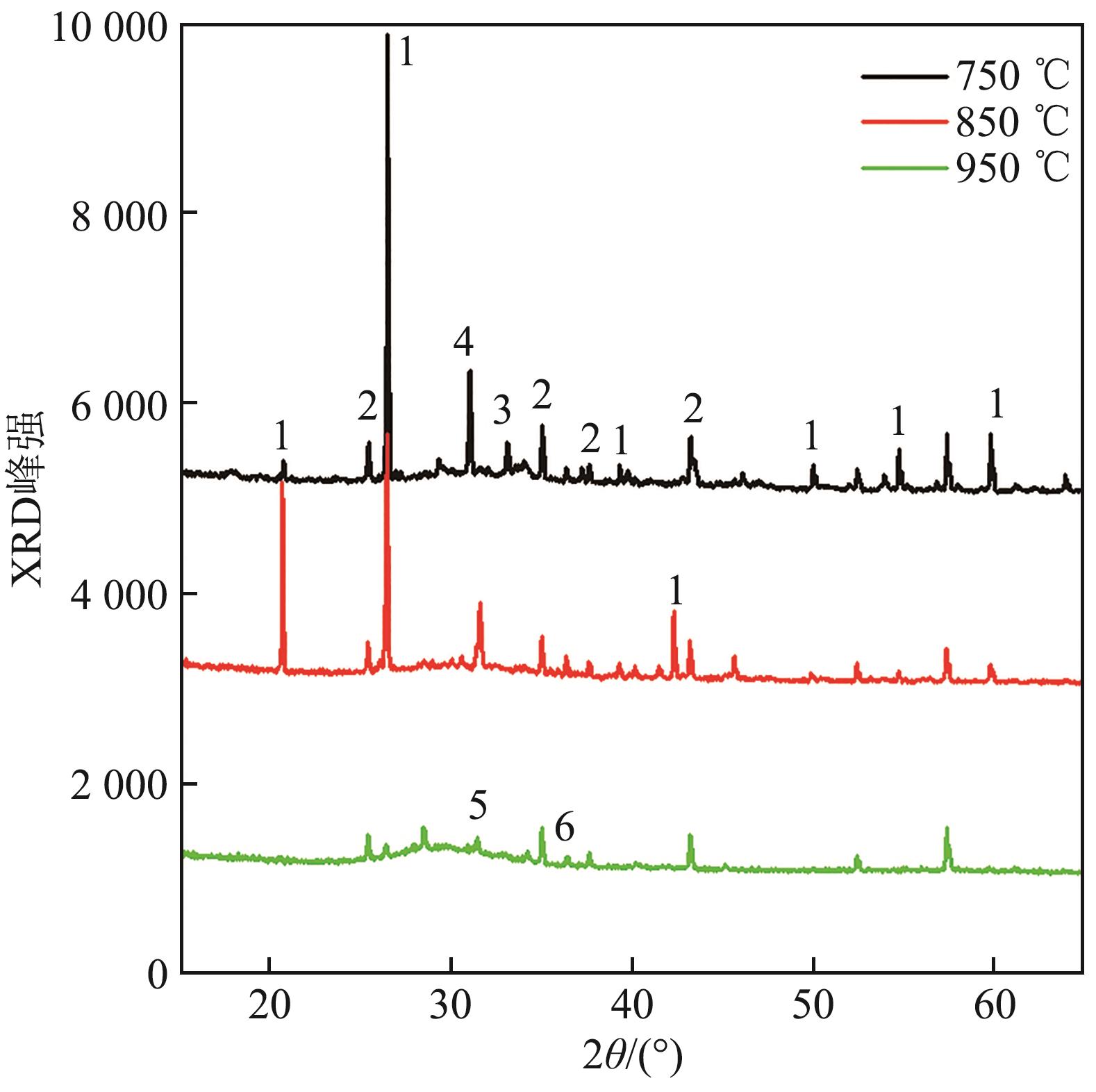
图15 钾盐为K2CO3、A/B=1.0的合成灰矿物组成1—SiO2;2—Al2O3;3—Ca3Al2O6; 4—K4Al2Si2O9;5—Ca2Al2SiO7;6—CaSiO3。
Fig. 15 Mineral composition of synthetic ash with potassium salt of K2CO3 and A/B=1.0
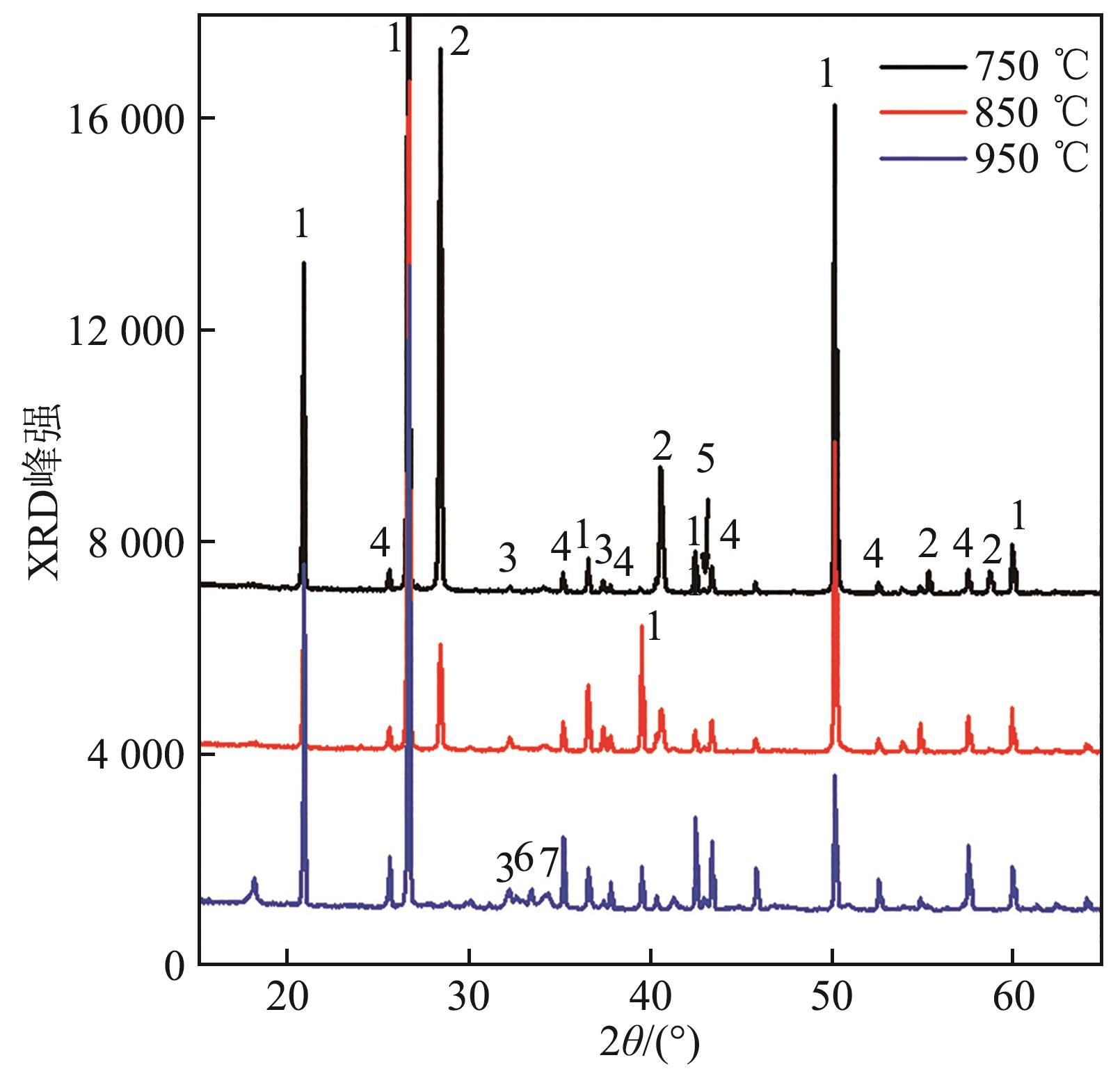
图16 钾盐为KCl、A/B=1.0的合成灰矿物组成1—SiO2;2—KCl;3—CaO;4—Al2O3;5—MgO;6—Ca11.3Al14O32.3;7—Ca54MgAl2Si16O90。
Fig. 16 Mineral composition of synthetic ash with potassium salt of KCl and A/B=1.0
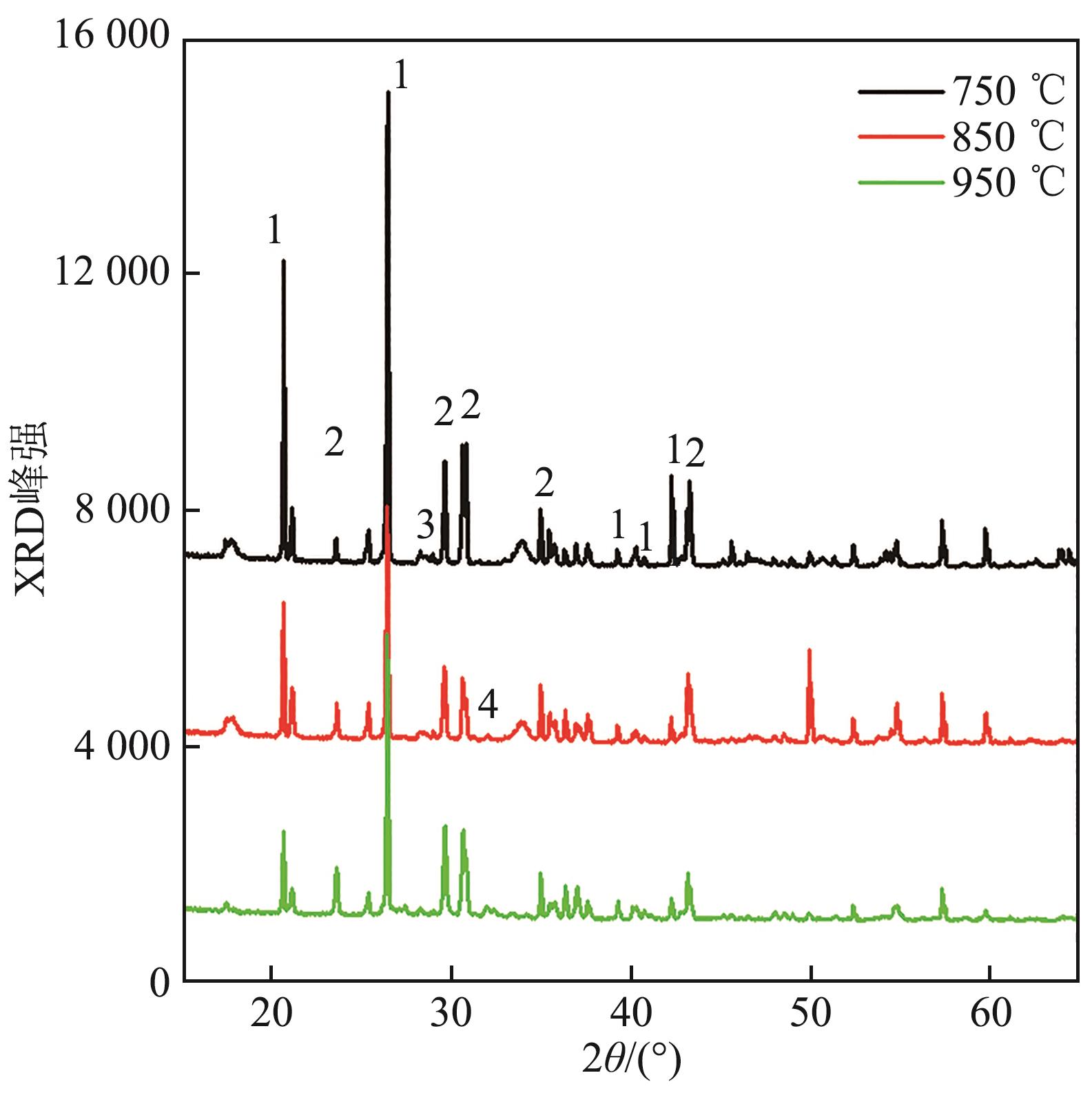
图17 钾盐为K2SO4、A/B=1.0的合成灰矿物组成1—SiO2;2—K2SO4;3—K6Ca(SO4)4;4—Ca2SiO4。
Fig. 17 Mineral composition of synthetic ash with potassium salt of K2SO4 and A/B=1.0
| 温度/℃ | 矿物质量分数/% | 熔融相比例/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KAlSiO4-HT | (Na, K)2Si2O5 | 菱硅钙钠石(Na4Ca4Si6O18) | K2Ca2Si2O7 | K2Ca6Si4O15 | 钙铁榴石(Ca3Fe2Si3O12) | ||
| 750 | 52.40 | 21.02 | 1.14 | 19.13 | 5.40 | 0.92 | 0 |
| 850 | 50.71 | 0 | 2.06 | 18.66 | 5.13 | 0.88 | 22.55 |
| 950 | 47.42 | 0 | 0 | 17.40 | 0 | 0.82 | 34.36 |
表4 钾盐为K2CO3、A/B=1.0的合成灰矿物组分FactSage计算结果
Tab. 4 FactSage calculation results of synthetic ash mineral components with potassium salt of K2CO3 and A/B=1.0
| 温度/℃ | 矿物质量分数/% | 熔融相比例/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KAlSiO4-HT | (Na, K)2Si2O5 | 菱硅钙钠石(Na4Ca4Si6O18) | K2Ca2Si2O7 | K2Ca6Si4O15 | 钙铁榴石(Ca3Fe2Si3O12) | ||
| 750 | 52.40 | 21.02 | 1.14 | 19.13 | 5.40 | 0.92 | 0 |
| 850 | 50.71 | 0 | 2.06 | 18.66 | 5.13 | 0.88 | 22.55 |
| 950 | 47.42 | 0 | 0 | 17.40 | 0 | 0.82 | 34.36 |
| 温度/℃ | 矿物质量分数/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白榴石(K2Al2Si4O12) | 硅灰石(CaSiO3) | 单斜辉石(CaMgSi2O6) | 长石(KAlSi3O8, CaAl2Si2O8) | 钙铁榴石(Ca3Fe2Si3O12) | |
| 750 | 69.74 | 18.51 | 7.33 | 3.87 | 0.55 |
| 850 | 67.99 | 18.66 | 7.24 | 5.68 | 0.27 |
| 950 | 27.21 | 15.04 | 6.97 | 47.18 | 0 |
表5 钾盐为KCl、A/B=1.0的合成灰矿物组分FactSage计算结果
Tab. 5 FactSage calculation results of synthetic ash mineral components with potassium salt of KCl and A/B=1.0
| 温度/℃ | 矿物质量分数/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白榴石(K2Al2Si4O12) | 硅灰石(CaSiO3) | 单斜辉石(CaMgSi2O6) | 长石(KAlSi3O8, CaAl2Si2O8) | 钙铁榴石(Ca3Fe2Si3O12) | |
| 750 | 69.74 | 18.51 | 7.33 | 3.87 | 0.55 |
| 850 | 67.99 | 18.66 | 7.24 | 5.68 | 0.27 |
| 950 | 27.21 | 15.04 | 6.97 | 47.18 | 0 |
| 温度/℃ | 矿物质量分数/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白榴石(K2Al2Si4O12) | 硅灰石(CaSiO3) | 黄长石(Ca2MgSi2O7) | 霞石((Na, K)AlSiO4) | 钙铁榴石(Ca3Fe2Si3O12) | KAlSiO4-HT | |
| 750 | 69.88 | 17.45 | 8.70 | 3.39 | 0.58 | 0 |
| 850 | 69.99 | 17.64 | 8.99 | 3.37 | 0.05 | 0 |
| 950 | 64.67 | 19.55 | 6.81 | 0 | 0 | 9.76 |
表6 钾盐为K2SO4、A/B=1.0的合成灰矿物组分FactSage计算结果
Tab. 6 FactSage calculation results of synthetic ash mineral components with potassium salt of K2SO4 and A/B=1.0
| 温度/℃ | 矿物质量分数/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白榴石(K2Al2Si4O12) | 硅灰石(CaSiO3) | 黄长石(Ca2MgSi2O7) | 霞石((Na, K)AlSiO4) | 钙铁榴石(Ca3Fe2Si3O12) | KAlSiO4-HT | |
| 750 | 69.88 | 17.45 | 8.70 | 3.39 | 0.58 | 0 |
| 850 | 69.99 | 17.64 | 8.99 | 3.37 | 0.05 | 0 |
| 950 | 64.67 | 19.55 | 6.81 | 0 | 0 | 9.76 |
| 1 | 郑妍,姚宣,陈训强 .生物质气化耦合发电体系的合成气组分与能量分析[J].发电技术,2023,44(6):859-864. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.22164 |
| ZHENG Y, YAO X, CHEN X Q .Analysis of syngas components and energy in biomass gasification coupled power generation system[J].Power Generation Technology,2023,44(6):859-864. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.22164 | |
| 2 | 张政林,张惠娟,孙文治,等 .基于改进旗鱼算法的综合能源系统能量管理[J].电力系统保护与控制,2022,20(22):142-151. |
| ZHENG Z L, ZHANG H J, SUN W Z,et al .Energy management of an integrated energy system based on an improved sailed fish optimizer algorithm[J].Power System Protection and Control,2022,20(22):142-151. | |
| 3 | LV Y, NIU Y, LIANG Y,et al .Experiment and kinetics studies on ash fusion characteristics of biomass/coal mixtures during combustion[J].Energy & Fuels,2019,33(10):10317-10323. doi:10.1021/acs.energyfuels.9b02563 |
| 4 | SAIDUR R, ABDELAZIZ E A, DEMIRBAS A,et al .A review on biomass as a fuel for boilers[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2011,15(5):2262-2289. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2011.02.015 |
| 5 | 臧海祥,马铭欣,周亦洲,等 .电力市场环境下风电-光热-生物质混合电站鲁棒优化调度模型[J].电力系统保护与控制,2022,50(5):1-11. |
| ZANG H X, MA M X, ZHOU Y Z,et al .Robust optimal scheduling model for a ‘wind power-concentrating solar power-biomass’ hybrid power plant in the electricity market[J].Power System Protection and Control,2023,44(3):1-14. | |
| 6 | 王永利,韩煦,刘晨,等 .基于生-光耦合利用的乡村电-热综合能源系统规划[J].电力建设,2023,44(3):1-14. |
| WANG Y L, HAN X, LIU C,et al .Rural electricity-heat integrated energy system planning based on coupling utilization of biomass and solar resources[J].Electric Power Construction,2023,44(3):1-14. | |
| 7 | 薛凯,王义函,陈衡,等 .槽式太阳能辅助生物质热电联产系统热力学性能分析[J].发电技术,2021,42(6):653-664. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.21044 |
| XUE K, WANG Y H, CHEN H,et al .Thermodynamic performance analysis of a parabolic trough solar-assisted Biomass-fired cogeneration system[J].Power Generation Technology,2021,42(6):653-664. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.21044 | |
| 8 | 朱骏杰,管俊豪,岳子尧,等 .燃煤机组直接耦合生物质的模型构建与碳减排分析[J].内蒙古电力技术,2023,41(6):17-25. |
| ZHU J J, GUAN J H, YUE Z Y,et al .Model construction and carbon emission reduction analysis of direct coupling of biomass in coal-fired unit[J].Inner Mongolia Electric Power,2023,41(6):17-25. | |
| 9 | LI Q H, ZHANG Y G, MENG A H,et al .Study on ash fusion temperature using original and simulated biomass ashes[J].Fuel Processing Technology,2013,107:107-112. doi:10.1016/j.fuproc.2012.08.012 |
| 10 | VASSILEV S V, BAXTER D, VASSILEVA C G .An overview of the behaviour of biomass during combustion:part II.Ash fusion and ash formation mechanisms of biomass types[J].Fuel,2014,117:152-183. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2013.09.024 |
| 11 | MA T, FAN C, HAO L,et al .Fusion characterization of biomass ash[J].Thermochimica Acta,2016,638:1-9. doi:10.1016/j.tca.2016.06.008 |
| 12 | SHAO Y, WANG J, PRETO F,et al .Ash deposition in biomass combustion or co-firing for power/heat generation[J].Energies,2012,5(12):5171-5189. doi:10.3390/en5125171 |
| 13 | LI G, LI S, XU X,et al .Dynamic behavior of biomass ash deposition in a 25 kW one-dimensional down-fired combustor[J].Energy & Fuels,2014,28(1):219-227. doi:10.1021/ef401530a |
| 14 | NIU Y, ZHU Y, TAN H,et al .Investigations on biomass slagging in utility boiler:criterion numbers and slagging growth mechanisms[J].Fuel Processing Technology,2014,128:499-508. doi:10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.07.038 |
| 15 | NIU Y, TAN H, HUI S E .Ash-related issues during biomass combustion:alkali-induced slagging,silicate melt-induced slagging (ash fusion),agglomeration,corrosion,ash utilization,and related countermeasures[J].Progress in Energy and Combustion Science,2016,52:1-61. doi:10.1016/j.pecs.2015.09.003 |
| 16 | 李定青,王鹏,姜春光,等 .采用添加剂抑制生物质锅炉受热面沉积试验分析[J].内蒙古电力技术,2023,41(1):87-92. |
| LI D Q, WANG P, JIANG C G,et al .Experimental analysis of using additive to inhibit heating surface deposition in biomass-fired boiler[J].Inner Mongolia Electric Power,2023,41(1):87-92. | |
| 17 | 马隆龙 .生物质能利用技术的研究及发展[J].化学工业,2007,25(8):9-14. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-9647.2007.08.002 |
| MA L L .Process technology of bio-energy utilization and its development[J].Chemical Industry,2007,25(8):9-14. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-9647.2007.08.002 | |
| 18 | 王朝华 .对我国生物质能源发展现状和趋势的分析[J].农业经济,2011(10):12-14. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-6139.2011.10.004 |
| WANG Z H .Analysis on the present situation and trend of biomass energy development in China[J].Agricultural Economy,2011(10):12-14. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-6139.2011.10.004 | |
| 19 | EASTERLY J L, BURNHAM M .Overview of biomass and waste fuel resources for power production[J].Biomass and Bioenergy,1996,10(2/3):79-92. doi:10.1016/0961-9534(95)00063-1 |
| 20 | VASSILEV S V, VASSILEVA C G, VASSILEV V S .Advantages and disadvantages of composition and properties of biomass in comparison with coal:an overview[J].Fuel,2015,158:330-350. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2015.05.050 |
| 21 | VASSILEV S V, BAXTER D, ANDERSEN L K,et al .An overview of the composition and application of biomass ash:potential utilisation,technological and ecological advantages and challenges[J].Fuel,2013,105:19-39. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2012.10.001 |
| 22 | LANE D J, VAN EYK P J, ASHMAN P J,et al .Release of Cl,S,P,K,and Na during thermal conversion of algal biomass[J].Energy & Fuels,2015,29(4):2542-2554. doi:10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b00279 |
| 23 | 方江涛,廖艳芬,黄泽浩,等 .中国南方典型农业生物质结渣特性实验研究[J].新能源进展,2014,2(4):275-281. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-560X.2014.04.006 |
| FANG J T, LIAO Y F, HUANG Z H,et al .Experimental study on slagging characteristics of typical agricultural biomass in South China[J].Advances in New and Renewable Energy,2014,2(4):275-281. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-560X.2014.04.006 | |
| 24 | DU S, YANG H, QIAN K,et al .Fusion and transformation properties of the inorganic components in biomass ash[J].Fuel,2014,117:1281-1287. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2013.07.085 |
| 25 | NÄZELIUS I L, FAGERSTRÖM J, BOMAN C,et al .Slagging in fixed-bed combustion of phosphorus-poor biomass:critical ash-forming processes and compositions[J].Energy & Fuels,2015,29(2):894-908. doi:10.1021/ef502531m |
| 26 | WU Y, WU S, LI Y,et al .Physico-chemical characteristics and mineral transformation behavior of ashes from crop straw[J].Energy & Fuels,2009,23(10):5144-5150. doi:10.1021/ef900496b |
| 27 | JIANG J,TIE Y, DENG L,et al .Influence of water-washing pretreatment on ash fusibility of biomass[J].Renewable Energy,2022,200:125-135. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2022.09.121 |
| 28 | CHEN X D, KONG L-X, BAI J,et al .Study on fusibility of coal ash rich in sodium and sulfur by synthetic ash under different atmospheres[J].Fuel,2017,202:175-183. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2017.04.001 |
| 29 | 岑可法 .锅炉和热交换器的积灰、结渣、磨损和腐蚀的防止原理与计算[M].北京:科学出版社,1994. |
| CEN K F .Prevention principle and calculation of ash accumulation,slagging,wear and corrosion of boilers and heat exchangers[M].Beijing:Science Press,1994. | |
| 30 | KNUDSEN J N, JENSEN P A, DAM-JOHANSEN K .Transformation and release to the gas phase of Cl,K,and S during combustion of annual biomass[J].Energy & Fuels,2004,18(5):1385-1399. doi:10.1021/ef049944q |
| 31 | SEVONIUS C, YRJAS P, HUPA M .Defluidization of a quartz bed-Laboratory experiments with potassium salts[J].Fuel,2014,127:161-168. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2013.10.047 |
| 32 | 刘卓,李建波,龙潇飞,等 .循环流化床燃烧高钠准东煤的床料颗粒聚团特性[J].中国电机工程学报,2022,42(6):2248-2258. |
| LIU Z, LI J B, LONG X F,et al .Bed particle agglomeration in circulating fluidized bed burning high-sodium Zhundong coal[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2022,42(6):2248-2258. |
| [1] | 代华松, 浦绍旭, 柴国旭, 金李, 陈为平, 解明亮. 350 MW超临界流化床机组深度调峰研究与应用[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 401-411. |
| [2] | 高忠明, 朱德敖, 陈雨佳, 刘三举, 王勤辉. 农林废弃物循环流化床空气气化特性实验研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 535-544. |
| [3] | 张思海, 李超然, 万广亮, 刘印学, 徐海楠, 黄中, 杨海瑞. 330 MW 循环流化床锅炉深度调峰技术[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 199-206. |
| [4] | 邓启刚, 吕卓, 石友, 鲁佳易, 周旭, 王奥宇, 杨冬. 不带外置床的700 MW超超临界循环流化床锅炉失电后水冷壁安全计算分析[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 240-249. |
| [5] | 蒋海威, 高明明, 李杰, 于浩洋, 岳光溪, 黄中. 生物质振动炉排炉燃烧过程建模及动态特性分析[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 250-259. |
| [6] | 邓飞龙, 叶垚, 李阳, 王巧丽, 张俊霞. CO2气氛下杜氏盐藻热解特性的数值研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(1): 113-119. |
| [7] | 郑妍, 姚宣, 陈训强. 生物质气化耦合发电体系的合成气组分与能量分析[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(6): 859-864. |
| [8] | 董中豪, 卢啸风, 史丽超, 杨增增, 孔繁盛, 王鹏, 林国强, 赵鹏. 炉膛耐火材料热惯性对循环流化床锅炉调峰速率的影响[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(4): 514-524. |
| [9] | 王洪健, 王海洋, 孔皓, 周托, 张缦, 杨海瑞. 135 MW循环流化床锅炉纯燃准东煤改造策略与运行技术研究[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43(6): 918-926. |
| [10] | 李振山, 陈虎, 李维成, 刘磊, 蔡宁生. 化学链燃烧中试系统的研究进展与展望[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43(4): 544-561. |
| [11] | 薛凯, 王义函, 陈衡, 徐钢, 雷兢. 槽式太阳能辅助生物质热电联产系统热力学性能分析[J]. 发电技术, 2021, 42(6): 653-664. |
| [12] | 韩峰, 丛堃林, 向杰, 李清海, 张衍国, 马静. 基于Kolmogorov熵的气固鼓泡流化床中空隙率波动信号分析[J]. 发电技术, 2021, 42(3): 322-328. |
| [13] | 牛斌, 李丽锋, 孙倩, 张培华. 超临界循环流化床机组全负荷段深度调峰方法研究[J]. 发电技术, 2021, 42(2): 273-279. |
| [14] | 邱国华, 徐鹏志. 掺烧固废燃料的循环流化床锅炉引风机叶片腐蚀原因分析[J]. 发电技术, 2020, 41(6): 681-688. |
| [15] | 任少辉,胡晓炜,胡灿,赵渊,李跃峰. 生物质直燃电厂余热在农业中的应用[J]. 发电技术, 2020, 41(2): 206-209. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||