

发电技术 ›› 2026, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 157-167.DOI: 10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.260114
• 发电及环境保护 • 上一篇
陈禄1,2, 王波1,3, 王登亮1, 陈伟雄1, 刘继平4
收稿日期:2025-05-06
修回日期:2025-08-31
出版日期:2026-02-28
发布日期:2026-02-12
通讯作者:
陈伟雄
作者简介:基金资助:Lu CHEN1,2, Bo WANG1,3, Dengliang WANG1, Weixiong CHEN1, Jiping LIU4
Received:2025-05-06
Revised:2025-08-31
Published:2026-02-28
Online:2026-02-12
Contact:
Weixiong CHEN
Supported by:摘要:
目的 随着可再生能源发电装机量快速攀升,对燃煤发电机组运行灵活性要求愈发严苛。在此背景下,机组关键热力参数控制难度增大,瞬态变负荷时系统能效降低,为此,需开发多参数协同调控策略,以平衡变负荷速率与能效水平。 方法 基于GSE仿真平台,构建并验证了350 MW超临界燃煤机组动态模型,同时建立了包含锅炉内工质及管道金属蓄热的锅炉系统蓄热模型。在采用高压加热器抽汽节流的基础上,提出考虑锅炉系统内部蓄热变化规律的优化控制策略。 结果 在30%~50%热耗率验收(turbine heat acceptance,THA)工况升负荷过程中,高压加热器抽汽节流使机组最大升负荷速率从1.5%Pe/min (Pe为额定负荷)提至2.5%Pe/min,瞬态过程平均标准煤耗率达314.81 g⋅(kW⋅h)-1。而在满足电力标准前提下,通过优化控制策略实现了瞬态过程平均节煤量达0.67 g⋅(kW⋅h)-1。 结论 该优化控制策略既能显著提升机组升负荷速率,又可高效改善系统能效,为燃煤机组的高效、稳定运行提供了有力支撑。
中图分类号:
陈禄, 王波, 王登亮, 陈伟雄, 刘继平. 燃煤发电机组瞬态变负荷过程性能优化研究[J]. 发电技术, 2026, 47(1): 157-167.
Lu CHEN, Bo WANG, Dengliang WANG, Weixiong CHEN, Jiping LIU. Research on Performance Optimization of Transient Load Change Process in Coal-Fired Power Units[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2026, 47(1): 157-167.
| 参数 | 数值/% |
|---|---|
| 收到基碳质量分数Car | 53.08 |
| 收到基氢质量分数Har | 3.22 |
| 收到基氮质量分数Nar | 9.18 |
| 收到基氧质量分数Oar | 9.18 |
| 收到基硫质量分数Sar | 0.64 |
| 收到基灰分质量分数Aar | 18.10 |
| 收到基水分质量分数Mar | 15.00 |
表1 锅炉设计煤质元素分析
Tab. 1 Elemental analysis of coal in boiler design
| 参数 | 数值/% |
|---|---|
| 收到基碳质量分数Car | 53.08 |
| 收到基氢质量分数Har | 3.22 |
| 收到基氮质量分数Nar | 9.18 |
| 收到基氧质量分数Oar | 9.18 |
| 收到基硫质量分数Sar | 0.64 |
| 收到基灰分质量分数Aar | 18.10 |
| 收到基水分质量分数Mar | 15.00 |
| 类型 | 热力参数 | 100%THA | 75%THA | 50%THA | 30%THA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 主蒸汽温度 | 设计值/℃ | 574.0 | 574.0 | 574.0 | 574.0 |
| 模拟值/℃ | 574.2 | 573.2 | 574.3 | 574.6 | |
| 相对误差/% | 0.01 | -0.01 | 0.05 | 0.11 | |
| 主蒸汽压力 | 设计值/MPa | 25.40 | 18.25 | 12.02 | 10.10 |
| 模拟值/MPa | 25.14 | 18.34 | 11.86 | 9.99 | |
| 相对误差/% | -1.02 | 0.49 | -1.35 | -1.09 | |
| 再热蒸汽温度 | 设计值/℃ | 572.0 | 572.0 | 572.0 | 572.0 |
| 模拟值/℃ | 572.1 | 572.4 | 572.2 | 572.2 | |
| 相对误差/% | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.03 | |
| 再热蒸汽压力 | 设计值/MPa | 4.61 | 3.42 | 2.26 | 1.85 |
| 模拟值/MPa | 4.62 | 3.41 | 2.24 | 1.87 | |
| 相对误差/% | 0.22 | -0.29 | -0.88 | 1.08 | |
| 给水温度 | 设计值/℃ | 306.4 | 292.6 | 266.9 | 239.1 |
| 模拟值/℃ | 310.7 | 290.9 | 265.1 | 236.5 | |
| 相对误差/% | 1.41 | -0.57 | -0.66 | -1.07 | |
| 给水压力 | 设计值/MPa | 28.96 | 20.78 | 14.35 | 9.76 |
| 模拟值/MPa | 29.21 | 21.05 | 14.55 | 9.92 | |
| 相对误差/% | 0.86 | 1.29 | 1.39 | 1.64 |
表2 仿真模拟结果与机组设计参数对比
Tab. 2 Comparison between simulation results and unit design parameters
| 类型 | 热力参数 | 100%THA | 75%THA | 50%THA | 30%THA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 主蒸汽温度 | 设计值/℃ | 574.0 | 574.0 | 574.0 | 574.0 |
| 模拟值/℃ | 574.2 | 573.2 | 574.3 | 574.6 | |
| 相对误差/% | 0.01 | -0.01 | 0.05 | 0.11 | |
| 主蒸汽压力 | 设计值/MPa | 25.40 | 18.25 | 12.02 | 10.10 |
| 模拟值/MPa | 25.14 | 18.34 | 11.86 | 9.99 | |
| 相对误差/% | -1.02 | 0.49 | -1.35 | -1.09 | |
| 再热蒸汽温度 | 设计值/℃ | 572.0 | 572.0 | 572.0 | 572.0 |
| 模拟值/℃ | 572.1 | 572.4 | 572.2 | 572.2 | |
| 相对误差/% | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.03 | |
| 再热蒸汽压力 | 设计值/MPa | 4.61 | 3.42 | 2.26 | 1.85 |
| 模拟值/MPa | 4.62 | 3.41 | 2.24 | 1.87 | |
| 相对误差/% | 0.22 | -0.29 | -0.88 | 1.08 | |
| 给水温度 | 设计值/℃ | 306.4 | 292.6 | 266.9 | 239.1 |
| 模拟值/℃ | 310.7 | 290.9 | 265.1 | 236.5 | |
| 相对误差/% | 1.41 | -0.57 | -0.66 | -1.07 | |
| 给水压力 | 设计值/MPa | 28.96 | 20.78 | 14.35 | 9.76 |
| 模拟值/MPa | 29.21 | 21.05 | 14.55 | 9.92 | |
| 相对误差/% | 0.86 | 1.29 | 1.39 | 1.64 |
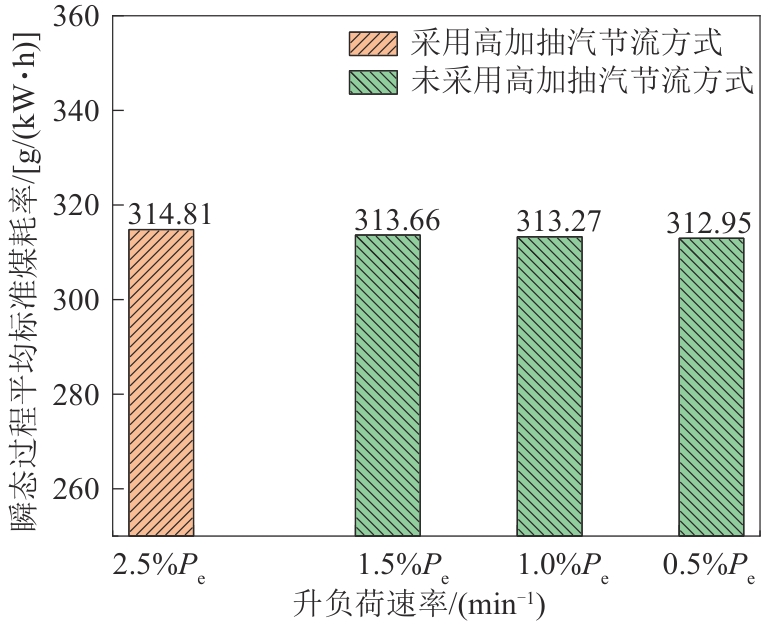
图6 不同升负荷速率下机组瞬态过程平均标准煤耗率对比
Fig. 6 Comparison of average standard coal consumption rate of unit during transient process under different load increase rates
| [1] | 龙潇,张晋宾,陈令特 .未来能源技术展望[J].发电技术,2025,46(4):651-693. |
| LONG X, ZHANG J B, CHEN L T .Prospects for future energy technologies[J].Power Generation Technology,2025,46(4):651-693. | |
| [2] | 崔茗莉,冯天天,刘利利 .双碳目标下区块链与可再生能源的融合发展研究[J].智慧电力,2024,52(2):17-24. |
| CUI M L, FENG T T, LIU L L .Integration and development of blockchain and renewable energy under double carbon target[J].Smart Power,2024,52(2):17-24. | |
| [3] | 邵天铭,王利宁,高鑫,等 .“双碳”目标下中国建筑部门能源转型模拟[J].全球能源互联网,2024,7(6):640-649. |
| SHAO T M, WANG L N, GAO X,et al .Modelling energy transition of China’s building sector under the dual-carbon goal[J].Journal of Global Energy Interconnection,2024,7(6):640-649. | |
| [4] | 周勤勇,郝绍煦,董武,等 .“十五五”电网规划安全稳定分析关键问题[J].中国电力,2025,58(9):138-147. |
| ZHOU Q Y, HAO S X, DONG W,et al .Key issues in security and stability analysis for the “15 th five-year”power grid planning[J].Electric Power,2025,58(9):138-147. | |
| [5] | 张文博,邢海军,聂立君,等 .考虑高渗透率可再生能源的新型电力系统可靠性评估综述[J].电测与仪表,2025,62(9):51-61. |
| ZHANG W B, XING H J, NIE L J,et al .Review of the novel power system reliability assessment with high penetration renewable energy[J].Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation,2025,62(9):51-61. | |
| [6] | 汤明润,李若旸,刘慕然,等 .电力系统稳态下可再生能源大规模接入量预测[J].中国电力,2025,58(2):126-132. |
| TANG M R, LI R Y, LIU M R,et al .Prediction of large-scale renewable energy access under steady state of electric power system[J].Electric Power,2025,58(2):126-132. | |
| [7] | 朱继忠,高美云,肖鹏飞,等 .大规模海上风电并网与运行技术综述[J].电力工程技术,2025,44(5):2-24. |
| ZHU J Z, GAO M Y, XIAO P F,et al .Review of grid integration and operation technologies for large-scale offshore wind power[J].Electric Power Engineering Technology,2025,44(5):2-24. | |
| [8] | 周倩,樊宇姣,张艳丽,等 .考虑大规模可再生能源接入的电力系统多目标无功优化方法[J].电网与清洁能源,2025,41(4):97-103. |
| ZHOU Q, FAN Y J, ZHANG Y L,et al .The multi-objective reactive power optimization of power systems considering large-scale renewable integration[J].Power System and Clean Energy,2025,41(4):97-103. | |
| [9] | 骆国铭,黄小耘,范心明 .考虑可再生能源特性的实时电力调度优化研究[J].电力科学与技术学报,2025,40(3):163-173. |
| LUO G M, HUANG X Y, FAN X M .Research on real-time power scheduling optimization considering renewable energy characteristics[J].Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology,2025,40(3):163-173. | |
| [10] | 严新荣,胡志勇,张鹏威,等 .煤电机组运行灵活性提升技术研究与应用[J].发电技术,2024,45(6):1074-1086. |
| YAN X R, HU Z Y, ZHANG P W,et al .Research and application of operation flexibility improvement technology for coal-fired power unit[J].Power Generation Technology,2024,45(6):1074-1086. | |
| [11] | CHEN C, LIU M, LI M J,et al .Digital twin modeling and operation optimization of the steam turbine system of thermal power plants[J].Energy,2024,290:129969. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2023.129969 |
| [12] | 樊梦阳,赵永亮,张成宇,等 .高低位分轴布置燃煤发电机组不同抽汽节流方案的运行灵活性研究[J].工程热物理学报,2023,44(11):2991-2998. |
| FAN M Y, ZHAO Y L, ZHANG C Y,et al .Research on the operational flexibility of different extraction steam throttling schemes for coal-fired generating units arranged by high-low position axis[J].Journal of Engineering Thermophysics,2023,44(11):2991-2998. | |
| [13] | 丁湧 .1 000 MW超超临界燃煤锅炉深度调峰研究[J].发电技术,2024,45(3):382-391. |
| DING Y .Research on deep peak shaving performance of 1 000 MW ultra-supercritical coal-fired boiler[J].Power Generation Technology,2024,45(3):382-391. | |
| [14] | 窦文雷,张娜,胡旌伟,等 .寒地新能源与灵活供热煤电改造协同规划模型[J].电力建设,2024,45(9):13-25. |
| DOU W L, ZHANG N, HU J W,et al .Cooperative planning model for renewable energy and flexible coal-fired CHP in cold regions[J].Electric Power Construction,2024,45(9):13-25. | |
| [15] | DENG B Y, ZHANG M, SHAN L,et al .Modeling study on the dynamic characteristics in the full-loop of a 350 MW supercritical CFB boiler under load regulation[J].Journal of the Energy Institute,2021,97:117-130. doi:10.1016/j.joei.2021.04.014 |
| [16] | 王志轩,张晶杰,董博,等 .“双碳”目标下燃煤电厂灵活性改造及政策建议[J].电力科技与环保,2024,40(3):213-220. |
| WANG Z X, ZHANG J J, DONG B,et al .Research on technology and policy of flexibility renovation for coal-fired power plants under carbon peaking and carbon neutrality goal[J].Electric Power Technology and Environmental Protection,2024,40(3):213-220. | |
| [17] | 杨正,孙亦鹏,温志强,等 .深度调峰工况下超临界机组的干湿态转换策略研究[J].发电技术,2024,45(2):233-239. |
| YANG Z, SUN Y P, WEN Z Q,et al .Research on dry-wet conversion strategy of supercritical thermal power units under deep peaking condition[J].Power Generation Technology,2024,45(2):233-239. | |
| [18] | 刘志强,李建锋,潘荔,等 .中国煤电机组改造升级效果分析与展望[J].中国电力,2024,57(7):1-11. |
| LIU Z Q, LI J F, PAN L,et al .Analysis and prospect of transformation and upgrading effects of coal-fired power units in China[J].Electric Power,2024,57(7):1-11. | |
| [19] | 丁天阳,陈辉,张超群,等 .熔盐储热用于煤电机组灵活性改造的研究进展[J].电力科技与环保,2025,41(4):528-541. |
| DING T Y, CHEN H, ZHANG C Q,et al .Research progress on molten salt thermal energy storage for flexibility retrofit of tcoal-fired power units[J].Electric Power Technology and Environmental Protection,2025,41(4):528-541. | |
| [20] | WANG C Y, LIU M, LI B X,et al .Thermodynamic analysis on the transient cycling of coal-fired power plants:Simulation study of a 660 MW supercritical unit[J].Energy,2017,122:505-527. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2017.01.123 |
| [21] | WANG Z, LIU M, ZHAO Y L,et al .Flexibility and efficiency enhancement for double-reheat coal-fired power plants by control optimization considering boiler heat storage[J].Energy,2020,201:117594. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2020.117594 |
| [22] | LIU Z F, WANG C Y, FAN J L,et al .Enhancing the flexibility and stability of coal-fired power plants by optimizing control schemes of throttling high-pressure extraction steam[J].Energy,2024,288:129756. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2023.129756 |
| [23] | ZHAO Y L, LIU M, WANG C Y,et al .Increasing operational flexibility of supercritical coal-fired power plants by regulating thermal system configuration during transient processes[J].Applied Energy,2018,228:2375-2386. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.07.070 |
| [24] | ZHAO Y L, WANG C Y, LIU M,et al .Improving operational flexibility by regulating extraction steam of high-pressure heaters on a 660 MW supercritical coal-fired power plant:a dynamic simulation[J].Applied Energy,2018,212:1295-1309. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.01.017 |
| [25] | 叶青,王朝阳,易广宙,等 .超超临界二次再热尾部三烟道锅炉汽温动态特性及协同优化控制[J].动力工程学报,2023,43(2):117-125. |
| YE Q, WANG C Y, YI G Z,et al .Dynamic characteristics of steam temperature and collaborative optimization control of ultra-supercritical secondary reheat tail three-flue boiler[J].Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering,2023,43(2):117-125. | |
| [26] | 侯国莲,黄婷,郭志强,等 .适应大型燃煤机组全工况灵活性运行的快速变负荷控制策略[J].热力发电,2024,53(12):93-101. |
| HOU G L, HUANG T, GUO Z Q,et al .A rapid load varying control strategy for flexible operation of large scale coal-fired power unit under full operating conditions[J].Thermal Power Generation,2024,53(12):93-101. | |
| [27] | WANG Z, LIU M, YAN H,et al .Improving flexibility of thermal power plant through control strategy optimization based on orderly utilization of energy storage[J].Applied Thermal Engineering,2024,240:122231. doi:10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2023.122231 |
| [28] | 赵征,孙赫宇,陈江丽 .基于AGC负荷指令优化分解的火电机组蓄能综合利用[J].动力工程学报,2023,43(5):575-581. |
| ZHAO Z, SUN H Y, CHEN J L .Optimized decomposition of AGC load command for comprehensive utilization of energy storage in the thermal power unit[J].Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering,2023,43(5):575-581. | |
| [29] | 马良玉,赵晶璇,马进 .高压加热器抽汽切除及灵活调节仿真试验研究[J].热能动力工程,2021,36(8):114-120. |
| MA L Y, ZHAO J X, MA J .Simulation study on cutting-off and flexible regulation of the extraction steam to high-pressure heaters[J].Journal of Engineering for Thermal Energy and Power,2021,36(8):114-120. | |
| [30] | 王唯铧,高明明,王勇权,等 .350 MW热电联产循环流化床机组负荷响应特性[J].洁净煤技术,2024,30(9):102-110. |
| WANG W H, GAO M M, WANG Y Q,et al .Load response characteristics of 350 MW cogeneration CFB unit[J].Clean Coal Technology,2024,30(9):102-110. | |
| [31] | WANG Z, LIU M, YAN J J .Flexibility and efficiency co-enhancement of thermal power plant by control strategy improvement considering time varying and detailed boiler heat storage characteristics[J].Energy,2021,232:121048. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2021.121048 |
| [32] | YAN H, LIU M, WANG Z,et al .Flexibility enhancement of solar-aided coal-fired power plant under different direct normal irradiance conditions[J].Energy,2023,262:125349. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2022.125349 |
| [33] | 国家能源局 . 火力发电厂模拟量控制系统验收测试规程: [S].北京:中国电力出版社,2015. |
| National Energy Administration . Code for acceptance test of modulating control system in fossil fuel power plant: [S].Beijing:China Electric Power Press,2015. | |
| [34] | 赵永亮,许朋江,居文平,等 .燃煤发电机组瞬态过程灵活高效协同运行的理论与技术研究综述[J].中国电机工程学报,2023,43(6):2080-2100. |
| ZHAO Y L, XU P J, JU W P,et al .Overview of theoretical and technical research on flexible and efficient synergistic operation of coal-fired power units during transient processes[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2023,43(6):2080-2100. |
| [1] | 徐义巍, 洪岩, 赵晓鹏, 隋炳伟. 煤氨混燃对燃煤锅炉受热面传热特性影响分析[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(5): 1022-1031. |
| [2] | 罗晟, 王磊, 李杨, 孟庆明, 张贵彬, 赵元宾. 变流量配水对湿冷塔冷却特性的影响及其优化[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(5): 1041-1049. |
| [3] | 陈璟, 刘辉, 朱萌, 王灿, 陈磊, 周敬, 许凯, 江龙, 胡松, 向军. 125 MW超临界CO2燃煤发电机组烟气再循环对锅炉热力性能及经济性的影响分析[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(5): 986-995. |
| [4] | 张帅柠, 高明明, 王勇权, 王唯铧, 于浩洋, 黄中. 循环流化床锅炉宽负荷一体化脱硫建模研究[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(4): 849-856. |
| [5] | 汪义财, 喻鑫, 于敦喜. 能源植物芦竹燃烧利用研究进展[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(3): 570-578. |
| [6] | 张鹏新, 高明明, 解沛然, 于浩洋, 张洪福, 黄中. 基于数据驱动的循环流化床机组深度调峰NO x 预测[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(3): 627-636. |
| [7] | 赵海宝, 何毓忠, 刘含笑, 梁江. 燃煤电厂电除尘脉冲电源改进及工程应用[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(1): 154-160. |
| [8] | 严新荣, 胡志勇, 张鹏威, 郑成航, 向军, 唐郭安, 刘金亮, 郭剑雄, 黄一博, 于鹏峰, 高翔. 煤电机组运行灵活性提升技术研究与应用[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(6): 1074-1086. |
| [9] | 郑淇薇, 赵欣悦, 卢荻, 陈衡, 潘佩媛, 刘彤. 多类型小容量火电机组热电解耦潜力与经济性对比评估[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(5): 929-940. |
| [10] | 王轶男, 吕佳阳, 陈衡, 张国强, 徐钢, 翟融融. 基于Aspen Plus的气流床煤气化炉建模及其变工况特性研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(5): 951-958. |
| [11] | 季恩昌, 杨冬, 孙佰仲. 高水分褐煤流动性实验研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(4): 633-640. |
| [12] | 丁湧. 1 000 MW超超临界燃煤锅炉深度调峰研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 382-391. |
| [13] | 代华松, 浦绍旭, 柴国旭, 金李, 陈为平, 解明亮. 350 MW超临界流化床机组深度调峰研究与应用[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 401-411. |
| [14] | 张思海, 李超然, 万广亮, 刘印学, 徐海楠, 黄中, 杨海瑞. 330 MW 循环流化床锅炉深度调峰技术[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 199-206. |
| [15] | 郑淇薇, 王华霆, 陈衡, 潘佩媛, 徐钢. 深度调峰背景下火电机组热电解耦技术路径对比分析[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 207-215. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||