

发电技术 ›› 2021, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 682-689.DOI: 10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.21096
收稿日期:2021-07-30
出版日期:2021-12-31
发布日期:2021-12-23
通讯作者:
张燕平
作者简介:王鼎(1997), 男, 硕士研究生, 研究方向为太阳能吸热器传热特性数值模拟, 741099174@qq.com基金资助:
Ding WANG( ), Yuxuan CHEN(
), Yuxuan CHEN( ), Hu XIAO(
), Hu XIAO( ), Yanping ZHANG(
), Yanping ZHANG( )
)
Received:2021-07-30
Published:2021-12-31
Online:2021-12-23
Contact:
Yanping ZHANG
Supported by:摘要:
为探究传热工质对太阳能吸热器传热特性的影响,利用光线追踪和计算流体动力学方法,对采用超临界CO2和压缩空气作为传热工质的锥形腔体吸热器的传热特性进行对比分析。基于数值模拟讨论了吸热器锥角、工质进口流量和进口温度对吸热器传热性能的影响规律。结果表明:相同工况下,压缩空气的出口温度比超临界CO2高,但相应的吸热器热效率和系统光热转化效率却较低。对于2种传热工质,系统光热转化效率均在锥角为4.12°时取得最优值。在研究的运行参数范围内,传热工质的出口温度随进口温度的增加呈线性增长;当流量超过0.04 kg/s时,继续增大流量对提高系统光热转化效率作用较小。
中图分类号:
王鼎, 陈宇轩, 肖虎, 张燕平. 采用不同传热工质的锥形腔式吸热器传热特性对比分析[J]. 发电技术, 2021, 42(6): 682-689.
Ding WANG, Yuxuan CHEN, Hu XIAO, Yanping ZHANG. Comparative Analysis of Heat Transfer Characteristics of Conical Cavity Receivers With Different Heat Transfer Fluids[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2021, 42(6): 682-689.
| 网格数量 | 出口温度/K | 绝对误差/% |
| 2 423 370 | 860.40 | 0.24 |
| 3 598 505 | 861.09 | 0.16 |
| 4 442 491 | 862.60 | 0.00 |
| 5 630 989 | 862.52 | — |
表1 网格无关性验证
Tab. 1 Grid independence check
| 网格数量 | 出口温度/K | 绝对误差/% |
| 2 423 370 | 860.40 | 0.24 |
| 3 598 505 | 861.09 | 0.16 |
| 4 442 491 | 862.60 | 0.00 |
| 5 630 989 | 862.52 | — |
| ϕ/(°) | Qab/W | ηop/% |
| 0 | 10 387 | 88.21 |
| 4.12 | 10 347 | 87.88 |
| 8.23 | 10 318 | 87.62 |
| 12.35 | 10 308 | 87.54 |
| 16.46 | 10 293 | 87.42 |
表2 不同锥角下腔内吸收总能量和光学效率
Tab. 2 Total energy absorbed by the cavity and optical efficiency under different cone angles
| ϕ/(°) | Qab/W | ηop/% |
| 0 | 10 387 | 88.21 |
| 4.12 | 10 347 | 87.88 |
| 8.23 | 10 318 | 87.62 |
| 12.35 | 10 308 | 87.54 |
| 16.46 | 10 293 | 87.42 |
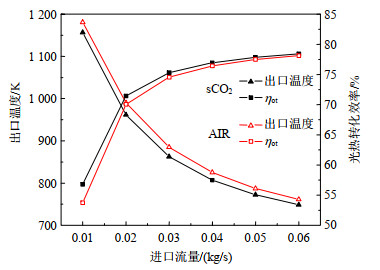
图9 HTF出口温度和系统光热转化效率随进口流量的变化
Fig.9 Variations of HTF outlet temperature and system photothermal conversion efficiency with different inlet mass flow rates
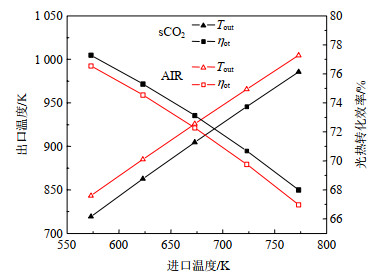
图11 HTF出口温度和系统光热转化效率随进口温度的变化情况
Fig.11 Variations of HTF outlet temperature and system photothermal conversion efficiency with different inlet temperatures
| 1 | 史洁, 刘晓飞. 新能源功率预测算法优化研究[J]. 发电技术, 2019, 40 (1): 78- 82. |
| SHI J , LIU X F . The optimization research approaches for renewable energy output forecasting[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2019, 40 (1): 78- 82. | |
| 2 | 童家麟, 吕洪坤, 李汝萍, 等. 国内光热发电现状及应用前景综述[J]. 浙江电力, 2019, 38 (12): 25- 30. |
| TONG J L , LYU H K , LI R P , et al. Review on status and application prospect of domestic CSP generation[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2019, 38 (12): 25- 30. | |
| 3 | 佟锴, 杨立军, 宋记锋, 等. 聚光太阳能集热场先进技术综述[J]. 发电技术, 2019, 40 (5): 413- 425. |
| TONG K , YANG L J , SONG J F , et al. Review on advanced technology of concentrated solar power concentrators[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2019, 40 (5): 413- 425. | |
| 4 | KASAEIAN A , KOURAVAND A , RAD M , et al. Cavity receivers in solar dish collectors: a geometric overview[J]. Renewable Energy, 2020, 169 (14): 53- 79. |
| 5 |
ZOU C Z , ZHANG Y P , FALCOZ Q , et al. Design and optimization of a high-temperature cavity receiver for a solar energy cascade utilization system[J]. Renewable Energy, 2017, 103, 478- 489.
DOI |
| 6 |
TAN Y , ZHAO L , BAO J , et al. Experimental investigation on heat loss of semi-spherical cavity receiver[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2014, 87, 576- 583.
DOI |
| 7 |
PAVLOVIC S , LONI R , BELLOS E , et al. Comparative study of spiral and conical cavity receivers for a solar dish collector[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 178, 111- 122.
DOI |
| 8 | DAABO A M , MAHMOUD S , AL-DADAH R K , et al. Numerical investigation of pitch value on thermal performance of solar receiver for solar powered Brayton cycle application[J]. Energy, 2017, 119 (15): 523- 539. |
| 9 | QIU K , YAN L , NI M , et al. Simulation and experimental study of an air tube-cavity solar receiver[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2015, 103 (10): 847- 858. |
| 10 | 郭缝伟. 基于MCRT和FVM方法的碟式太阳能聚光集热系统的光热转换特性数值研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2019. |
| GUO F W. Numerical study on the light-to-heat conversion characteristics of the dish-type solar energy concentrating and collecting system based on MCRT and FVM methods[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2019. | |
| 11 |
BENOIT H , SPREAFICO L , GAUTHIER D , et al. Review of heat transfer fluids in tube-receivers used in concentrating solar thermal systems: properties and heat transfer coefficients[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 55, 298- 315.
DOI |
| 12 |
LONI R , ASKARI A , SLI-ARDEH E , et al. Numerical comparison of a solar dish concentrator with different cavity receivers and working fluids[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 198, 1013- 30.
DOI |
| 13 | 陶文铨. 数值传热学[M]. 西安: 西安交通大学出版社, 2001: 128- 129. |
| TAO W Q . Numerical heat transfer[M]. Xi'an: Xi'an Jiaotong University Press, 2001: 128- 129. | |
| 14 |
CHU S , BAI F , ZHANG X , et al. Experimental study and thermal analysis of a tubular pressurized air receiver[J]. Renewable Energy, 2018, 125, 413- 424.
DOI |
| 15 |
ZOU C Z , FENG H Y , ZHANG Y P , et al. Geometric optimization model for the solar cavity receiver with helical pipe at different solar radiation[J]. Frontiers in Energy, 2019, 13 (2): 1- 12.
DOI |
| 16 |
ZHANG Y P , XIAO H , ZOU C Z , et al. Combined optics and heat transfer numerical model of a solar conical receiver with built-in helical pipe[J]. Energy, 2020, 193, 116775.
DOI |
| 17 |
ZHANG Y P , Chen Y X , ZOU C Z , et al. Experimental investigation on heat-transfer characteristics of a cylindrical cavity receiver with pressurized air in helical pipe[J]. Renewable Energy, 2021, 163, 320- 330.
DOI |
| 18 |
BELLOS E , BOUSI E , TZIVANIDIS C , et al. Optical and thermal analysis of different cavity receiver designs for solar dish concentrators[J]. Energy Conversion and Management X, 2019, 2, 100013.
DOI |
| [1] | 屠楠, 刘家琛, 徐静, 方嘉宾, 马彦花. 管壳式相变蓄热器的蓄释热过程性能分析[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 508-516. |
| [2] | 董军, 汤建方, 臧春城, 徐立, 王志峰. 抛物面槽式太阳能集热器球形接头测试系统的研制与应用[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 291-298. |
| [3] | 徐立, 孙飞虎, 李钧, 张强强. 抛物面槽式太阳能集热器热损失因素研究[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(2): 229-234. |
| [4] | 王晓文, 屠楠, 方嘉宾, 刘晓群, 王驰宇, 刘家琛. 布置螺旋管的太阳能腔式吸热器光学性能模拟[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(2): 221-228. |
| [5] | Mohamed ABD-HAMID, 夏龙禹, 魏高升, 崔柳, 徐超, 杜小泽. 集成相变储热材料的光伏/热复合系统性能分析[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(1): 53-62. |
| [6] | 岳晓鹏, 赵兴, 闫慧琳, 樊冰冰, 黄浩, 闫路遥, 崔鹏, 马峻峰, 李美成. 基于SnO2电子传输层的n-i-p型钙钛矿太阳能电池关键技术研究[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(1): 63-77. |
| [7] | 徐运飞, 吴水木, 李英杰. 面向太阳能热发电的CaO-CO2热化学储热技术研究进展[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43(5): 740-747. |
| [8] | 徐立, 孙飞虎, 李志, 张强强. 一种太阳能集热器流体平均温度计算方法[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43(3): 405-412. |
| [9] | 李英峰, 张涛, 张衡, 崔鹏, 付在国, 高中亮, 耿奇, 柳志晗, 朱群志, 李和兴, 李美成. 太阳能光伏光热高效综合利用技术[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43(3): 373-391. |
| [10] | 肖瑶, 钮文泽, 魏高升, 崔柳, 杜小泽. 太阳能光伏/光热技术研究现状与发展趋势综述[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43(3): 392-404. |
| [11] | 郑开云. 低温场景超临界CO2循环燃煤发电系统研究[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43(1): 126-130. |
| [12] | 廖志荣, 李朋达, 田紫芊, 徐超, 魏高升. 非均匀翅片对级联相变储热系统热性能强化的研究[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43(1): 83-91. |
| [13] | 张沧洪, 屠楠, 方嘉宾. 单侧非均匀热流边界下水/蒸汽太阳能吸热管热应力研究[J]. 发电技术, 2021, 42(6): 699-706. |
| [14] | 薛凯, 王义函, 陈衡, 徐钢, 雷兢. 槽式太阳能辅助生物质热电联产系统热力学性能分析[J]. 发电技术, 2021, 42(6): 653-664. |
| [15] | 徐立, 孙飞虎, 李钧, 张强强. 流量对抛物面槽式太阳能集热器传热特性影响的实验分析[J]. 发电技术, 2021, 42(6): 665-672. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||