

发电技术 ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (5): 885-896.DOI: 10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.24136
马宁, 赵攀, 刘艾杰, 许文盼, 王江峰
收稿日期:2024-07-08
修回日期:2024-08-08
出版日期:2025-10-31
发布日期:2025-10-23
作者简介:基金资助:Ning MA, Pan ZHAO, Aijie LIU, Wenpan XU, Jiangfeng WANG
Received:2024-07-08
Revised:2024-08-08
Published:2025-10-31
Online:2025-10-23
Supported by:摘要:
目的 天然气补燃型压缩空气储能(compressed air energy storage,CAES)系统存在环境污染问题,氢气作为替代燃料不会造成温室气体排放,但现阶段对纯氢补燃型CAES系统的技术经济可行性认识不足,因此有必要开展相关研究。 方法 基于㶲和㶲经济分析方法,进行了纯氢补燃型和天然气补燃型CAES系统的对比分析,重点关注其热力学性能、不可逆损失分布、经济性和㶲经济性的影响。此外,探讨了两者参数敏感性。 结果 纯氢补燃型CAES系统在放电时间、储能密度和㶲效率方面均优于天然气补燃型CAES系统;由于氢气成本高于天然气,纯氢补燃型CAES系统的产品平均㶲成本为155.62美元/GJ,显著高于天然气补燃型CAES系统对应的27.57美元/GJ;为使纯氢补燃型CAES系统具备与天然气补燃型CAES系统相同的商用竞争力,推荐售电价格为0.206 2美元/(kW⋅h);此外,纯氢补燃型CAES系统对参数变化更加敏感,在高参数条件下可实现更好的性能提升和成本降低。 结论 研究成果揭示了纯氢补燃型CAES系统的应用潜力,并为其进一步商业推广提供了技术参考。
中图分类号:
马宁, 赵攀, 刘艾杰, 许文盼, 王江峰. 纯氢补燃型和天然气补燃型压缩空气储能系统特性与㶲经济性对比[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(5): 885-896.
Ning MA, Pan ZHAO, Aijie LIU, Wenpan XU, Jiangfeng WANG. Comparison of Characteristics and Exergoeconomic Between Hydrogen and Natural Gas-Fueled Compressed Air Energy Storage Systems[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2025, 46(5): 885-896.
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 高峰电价/[美元/(kW⋅h)] | 0.118 |
| 低谷电价/[美元/(kW⋅h)] | 0.035 |
| 热水价格/[美元/(kW⋅h)] | 0.022 |
| 氢气价格/(美元/GJ) | 30.638 |
| 天然气价格/(美元/GJ) | 6.157 |
| CO2排放成本/(美元/kg) | 0.024 |
| 年工作时间/d | 350 |
| 平均年利率/% | 12 |
| 电厂运行年限/a | 25 |
| 贴现率/% | 10 |
| 通货膨胀率/% | 5 |
| 实际利率/% | 3 |
| 运行维护系数 | 1.06 |
表1 经济分析有关参数
Tab. 1 Parameters related to economic analysis
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 高峰电价/[美元/(kW⋅h)] | 0.118 |
| 低谷电价/[美元/(kW⋅h)] | 0.035 |
| 热水价格/[美元/(kW⋅h)] | 0.022 |
| 氢气价格/(美元/GJ) | 30.638 |
| 天然气价格/(美元/GJ) | 6.157 |
| CO2排放成本/(美元/kg) | 0.024 |
| 年工作时间/d | 350 |
| 平均年利率/% | 12 |
| 电厂运行年限/a | 25 |
| 贴现率/% | 10 |
| 通货膨胀率/% | 5 |
| 实际利率/% | 3 |
| 运行维护系数 | 1.06 |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 理想气体常数/[J/(mol⋅K)] | 8.314 |
| 环境温度/K | 298.15 |
| 环境压力/MPa | 0.1 |
| 透平效率/% | 90 |
| 高压透平入口温度/K | 823 |
| 低压透平入口温度/K | 1 023 |
| 高压透平膨胀比 | 3.82 |
| 低压透平膨胀比 | 10.86 |
| 透平机组额定功率/MW | 290 |
| 压缩机效率/% | 88 |
| 压缩机压比 | 8.43 |
| 压缩机组额定功率/MW | 60 |
| 储气洞穴温度/K | 298.15 |
| 储气洞穴压力/MPa | 4.2~7.2 |
| 储气洞穴容积/m3 | 180 000 |
| 冷却水温/K | 293.15 |
| 机械效率/% | 97 |
| 甲烷热值/(kJ/kg) | 50 179 |
| 氢气热值/(kJ/kg) | 120 994 |
表2 系统参数设置
Tab. 2 System parameter setting
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 理想气体常数/[J/(mol⋅K)] | 8.314 |
| 环境温度/K | 298.15 |
| 环境压力/MPa | 0.1 |
| 透平效率/% | 90 |
| 高压透平入口温度/K | 823 |
| 低压透平入口温度/K | 1 023 |
| 高压透平膨胀比 | 3.82 |
| 低压透平膨胀比 | 10.86 |
| 透平机组额定功率/MW | 290 |
| 压缩机效率/% | 88 |
| 压缩机压比 | 8.43 |
| 压缩机组额定功率/MW | 60 |
| 储气洞穴温度/K | 298.15 |
| 储气洞穴压力/MPa | 4.2~7.2 |
| 储气洞穴容积/m3 | 180 000 |
| 冷却水温/K | 293.15 |
| 机械效率/% | 97 |
| 甲烷热值/(kJ/kg) | 50 179 |
| 氢气热值/(kJ/kg) | 120 994 |
| 性能指标 | 天然气型 | 纯氢型 |
|---|---|---|
| 燃料消耗量/t | 97.23 | 40.21 |
| 充电时间/h | 17.26 | 17.26 |
| 放电时间/h | 4.25 | 4.32 |
| 储能密度/(kW | 6.87 | 6.95 |
| 㶲效率/% | 53.41 | 55.04 |
| 产热平均㶲成本/(美元/GJ) | 20.58 | 20.89 |
| 发电平均㶲成本/(美元/GJ) | 30.64 | 210.69 |
| 产品平均㶲成本/(美元/GJ) | 27.57 | 155.62 |
| CO2排放量/t | 14.08 | 0 |
表3 天然气型和纯氢型CAES系统性能比较
Tab. 3 Performance comparison between natural gas and hydrogen-fueled CAES systems
| 性能指标 | 天然气型 | 纯氢型 |
|---|---|---|
| 燃料消耗量/t | 97.23 | 40.21 |
| 充电时间/h | 17.26 | 17.26 |
| 放电时间/h | 4.25 | 4.32 |
| 储能密度/(kW | 6.87 | 6.95 |
| 㶲效率/% | 53.41 | 55.04 |
| 产热平均㶲成本/(美元/GJ) | 20.58 | 20.89 |
| 发电平均㶲成本/(美元/GJ) | 30.64 | 210.69 |
| 产品平均㶲成本/(美元/GJ) | 27.57 | 155.62 |
| CO2排放量/t | 14.08 | 0 |
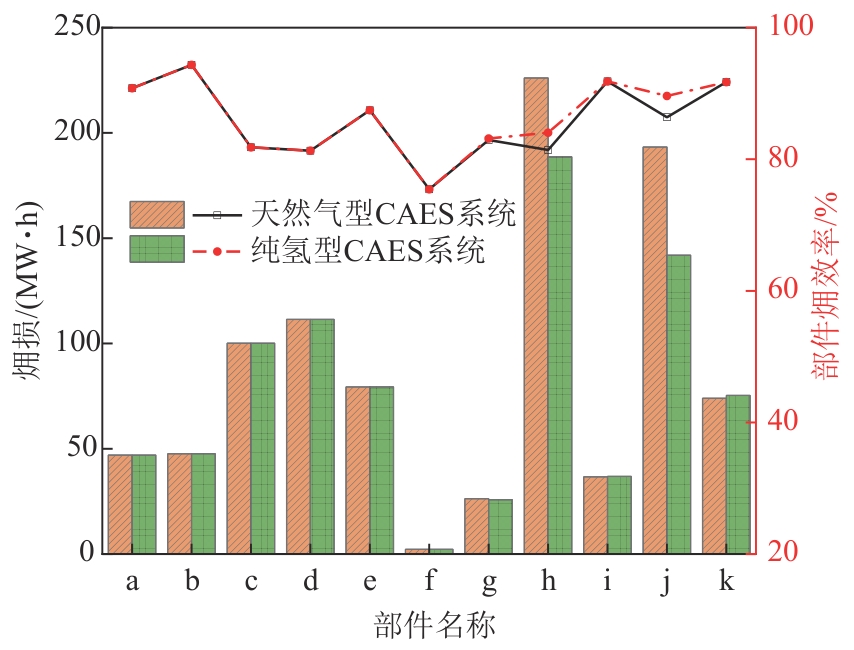
图2 天然气型和纯氢型CAES系统各部件㶲损失和㶲效率情况a—低压压缩机;b—高压压缩机;c—间冷器;d—后冷器;e—节流阀;f—回热器2;g—回热器1;h—燃烧室1;i—高压透平;j—燃烧室2;k—低压透平。
Fig. 2 Exergy destruction and exergy efficiency of each component of natural gas and hydrogen-fueled CAES systems
| 参数 | 天然气型 | 纯氢型 |
|---|---|---|
| 总投资成本/万美元 | 1 380 | 1 375 |
| 运行维护成本/万美元 | 2 071 | 2 063 |
| 购电成本/万美元 | 3 172 | 3 172 |
| 燃料成本/万美元 | 2 628 | 13 044 |
| 环境惩罚成本/万美元 | 564 | 0 |
| 生命周期总成本/万美元 | 9 815 | 19 654 |
表4 天然气型和纯氢型CAES系统各项投资成本
Tab. 4 The investment costs for natural gas and hydrogen-fueled CAES systems
| 参数 | 天然气型 | 纯氢型 |
|---|---|---|
| 总投资成本/万美元 | 1 380 | 1 375 |
| 运行维护成本/万美元 | 2 071 | 2 063 |
| 购电成本/万美元 | 3 172 | 3 172 |
| 燃料成本/万美元 | 2 628 | 13 044 |
| 环境惩罚成本/万美元 | 564 | 0 |
| 生命周期总成本/万美元 | 9 815 | 19 654 |
| 部件 | cf, i /(美元/GJ) | cp, i /(美元/GJ) | fi | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低压压缩机 | 9.72 | 13.81 | 95.25 | 300.03 | 395.28 | 75.90 |
| 高压压缩机 | 11.26 | 13.75 | 111.90 | 300.03 | 411.93 | 72.84 |
| 间冷器 | 13.81 | 17.70 | 288.38 | 6.67 | 295.04 | 2.26 |
| 后冷器 | 13.75 | 16.00 | 319.50 | 6.51 | 326.01 | 2.00 |
| 空气洞穴 | 13.75 | 5.79 | 0 | 1 286.39 | 1 286.39 | 100 |
| 热水罐 | 46.33 | 22.78 | 0 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 100 |
| 冷水罐 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 100 |
| 节流阀 | 5.79 | 6.63 | 389.22 | 5.61 | 394.84 | 1.42 |
| 回热器1 | 7.21 | 7.62 | 160.50 | 133.64 | 294.14 | 45.43 |
| 回热器2 | 6.56 | 6.73 | 12.48 | 66.82 | 79.30 | 84.26 |
| 燃烧室1 | 6.94 | 8.43 | 1 329.15 | 3.78 | 1 332.93 | 0.28 |
| 燃烧室2 | 7.03 | 8.09 | 1 151.23 | 3.80 | 1 155.03 | 0.33 |
| 高压透平 | 8.43 | 10.50 | 261.96 | 1 393.11 | 1 655.07 | 84.17 |
| 低压透平 | 8.09 | 11.73 | 506.56 | 790.28 | 1 296.83 | 60.94 |
表5 天然气型CAES系统各部件的㶲经济性分析
Tab. 5 Exergoeconomic analysis of various components in natural gas-fueled CAES system
| 部件 | cf, i /(美元/GJ) | cp, i /(美元/GJ) | fi | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低压压缩机 | 9.72 | 13.81 | 95.25 | 300.03 | 395.28 | 75.90 |
| 高压压缩机 | 11.26 | 13.75 | 111.90 | 300.03 | 411.93 | 72.84 |
| 间冷器 | 13.81 | 17.70 | 288.38 | 6.67 | 295.04 | 2.26 |
| 后冷器 | 13.75 | 16.00 | 319.50 | 6.51 | 326.01 | 2.00 |
| 空气洞穴 | 13.75 | 5.79 | 0 | 1 286.39 | 1 286.39 | 100 |
| 热水罐 | 46.33 | 22.78 | 0 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 100 |
| 冷水罐 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 100 |
| 节流阀 | 5.79 | 6.63 | 389.22 | 5.61 | 394.84 | 1.42 |
| 回热器1 | 7.21 | 7.62 | 160.50 | 133.64 | 294.14 | 45.43 |
| 回热器2 | 6.56 | 6.73 | 12.48 | 66.82 | 79.30 | 84.26 |
| 燃烧室1 | 6.94 | 8.43 | 1 329.15 | 3.78 | 1 332.93 | 0.28 |
| 燃烧室2 | 7.03 | 8.09 | 1 151.23 | 3.80 | 1 155.03 | 0.33 |
| 高压透平 | 8.43 | 10.50 | 261.96 | 1 393.11 | 1 655.07 | 84.17 |
| 低压透平 | 8.09 | 11.73 | 506.56 | 790.28 | 1 296.83 | 60.94 |
| 部件 | cf, i /(美元/GJ) | cp, i /(美元/GJ) | fi | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低压压缩机 | 9.72 | 13.81 | 95.25 | 300.03 | 395.28 | 75.90 |
| 高压压缩机 | 11.26 | 13.75 | 111.90 | 300.03 | 411.93 | 72.84 |
| 间冷器 | 13.81 | 17.70 | 288.38 | 6.67 | 295.04 | 2.26 |
| 后冷器 | 13.75 | 16.00 | 319.50 | 6.51 | 326.01 | 2.00 |
| 空气洞穴 | 13.75 | 5.87 | 0 | 1 282.61 | 1 282.61 | 100 |
| 热水罐 | 46.33 | 23.12 | 0 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 100 |
| 冷水罐 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 100 |
| 节流阀 | 5.87 | 6.72 | 388.75 | 5.45 | 394.20 | 1.38 |
| 回热器1 | 15.71 | 16.39 | 337.80 | 134.31 | 472.11 | 28.45 |
| 回热器2 | 6.65 | 6.82 | 12.46 | 65.56 | 78.02 | 84.03 |
| 燃烧室1 | 20.45 | 24.62 | 3 218.92 | 3.67 | 3 222.58 | 0.11 |
| 燃烧室2 | 28.32 | 32.47 | 3 352.87 | 3.68 | 3 356.54 | 0.11 |
| 高压透平 | 24.62 | 27.28 | 758.53 | 1 347.88 | 2 106.41 | 63.99 |
| 低压透平 | 32.47 | 46.24 | 2 041.47 | 760.32 | 2 801.79 | 27.14 |
表6 纯氢型CAES系统各部件的㶲经济性分析
Tab. 6 Exergoeconomic analysis of various components in hydrogen-fueled CAES system
| 部件 | cf, i /(美元/GJ) | cp, i /(美元/GJ) | fi | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低压压缩机 | 9.72 | 13.81 | 95.25 | 300.03 | 395.28 | 75.90 |
| 高压压缩机 | 11.26 | 13.75 | 111.90 | 300.03 | 411.93 | 72.84 |
| 间冷器 | 13.81 | 17.70 | 288.38 | 6.67 | 295.04 | 2.26 |
| 后冷器 | 13.75 | 16.00 | 319.50 | 6.51 | 326.01 | 2.00 |
| 空气洞穴 | 13.75 | 5.87 | 0 | 1 282.61 | 1 282.61 | 100 |
| 热水罐 | 46.33 | 23.12 | 0 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 100 |
| 冷水罐 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 100 |
| 节流阀 | 5.87 | 6.72 | 388.75 | 5.45 | 394.20 | 1.38 |
| 回热器1 | 15.71 | 16.39 | 337.80 | 134.31 | 472.11 | 28.45 |
| 回热器2 | 6.65 | 6.82 | 12.46 | 65.56 | 78.02 | 84.03 |
| 燃烧室1 | 20.45 | 24.62 | 3 218.92 | 3.67 | 3 222.58 | 0.11 |
| 燃烧室2 | 28.32 | 32.47 | 3 352.87 | 3.68 | 3 356.54 | 0.11 |
| 高压透平 | 24.62 | 27.28 | 758.53 | 1 347.88 | 2 106.41 | 63.99 |
| 低压透平 | 32.47 | 46.24 | 2 041.47 | 760.32 | 2 801.79 | 27.14 |
| [1] | 许洪华,邵桂萍,鄂春良,等 .我国未来能源系统及能源转型现实路径研究[J].发电技术,2023,44(4):484-491. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.23002 |
| XU H H, SHAO G P, E C L,et al .Research on China’s future energy system and the realistic path of energy transformation[J].Power Generation Technology,2023,44(4):484-491. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.23002 | |
| [2] | 陈灏,田琳,盛剑胜,等 .考虑风险规避和需求响应的电力市场可再生能源综合交易决策研究[J].电力科学与技术学报,2023,38(1):27-34. |
| CHEN H, TIAN L, SHENG J S,et al .Research on comprehensive trading decision of renewable energy in power market considering the risk aversion and demand response[J].Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology,2023,38(1):27-34. | |
| [3] | 张力菠,吴一锴,王群伟 .考虑碳中和目标与成本优化的可再生能源大规模发展规划[J].广东电力,2023,36(7):31-39. |
| ZHANG L B, WU Y K, WANG Q W .Large-scale development of renewable energy in consideration of carbon neutrality and cost optimization[J].Guangdong Electric Power,2023,36(7):31-39. | |
| [4] | 蔡浩,施凯,唐静,等 .基于改进蚁狮优化算法的可再生能源分布式电源优化配置[J].电测与仪表,2022,59(11):88-95. |
| CAI H, SHI K, TANG J,et al .Optimal configuration of renewable energy distributed power generation based on improved ant-lion optimization algorithm[J].Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation,2022,59(11):88-95. | |
| [5] | International Energy Agency .Renewables 2023:Analysis and forecasts to 2028[R].Paris:IEA,2023. |
| [6] | 黎立丰,刘春晓,朱浩骏,等 .考虑网络安全约束的可再生能源消纳能力评估方法[J].电力科学与技术学报,2023,38(4):162-168. |
| LI L F, LIU C X, ZHU H J,et al .Absorptive capability evaluation method of renewable energy considering security constraints of power grid[J].Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology,2023,38(4):162-168. | |
| [7] | 梅书凡,檀勤良,代美 .考虑风光出力季节性波动的储能容量配置[J].电力工程技术,2022,41(4):51-57. doi:10.12158/j.2096-3203.2022.04.007 |
| MEI S F, TAN Q L, DAI M .Energy storage capacity configuration considering seasonal fluctuation of wind and photovoltaic output[J].Electric Power Engineering Technology,2022,41(4):51-57. doi:10.12158/j.2096-3203.2022.04.007 | |
| [8] | 夏晨阳,杨子健,周娟,等 .基于新型电力系统的储能技术研究[J].内蒙古电力技术,2022,40(4):3-12. |
| XIA C Y, YANG Z J, ZHOU J,et al .Research of energy storage technology based on new power system[J].Inner Mongolia Electric Power,2022,40(4):3-12. | |
| [9] | 唐健,李浩志,谢小荣 .计及需求响应和储能技术发展的未来区间电力流规模分析[J].智慧电力,2022,50(7):58-64. |
| TANG J, LI H Z, XIE X R .Analysis of future interregional electricity flow model considering development of demand response and energy storage[J].Smart Power,2022,50(7):58-64. | |
| [10] | 张程翔,丁宁,尹峰,等 .新型储能应用场景与商业模式综述[J].分布式能源,2022,7(1):54-62. |
| ZHANG C X, DING N, YIN F,et al .Overview of new energy storage application scenarios and business models[J].Distributed Energy,2022,7(1):54-62. | |
| [11] | 霍龙,张誉宝,陈欣 .人工智能在分布式储能技术中的应用[J].发电技术,2022,43(5):707-717. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.22109 |
| HUO L, ZHANG Y B, CHEN X .Artificial intelligence applications in distributed energy storage technologies[J].Power Generation Technology,2022,43(5):707-717. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.22109 | |
| [12] | 井浩然,李佳,赵红生,等 .双馈变速抽水蓄能全工况转换过程建模与仿真[J].电力建设,2023,44(10):41-50. |
| JING H R, LI J, ZHAO H S,et al .Modeling and simulation of operating condition conversion of doubly-fed variable speed pumped storage[J].Electric Power Construction,2023,44(10):41-50. | |
| [13] | 邵磊,多增森,柴嘉启,等 .抽蓄-风-光-火联合系统日前优化调度研究[J].电网与清洁能源,2023,39(6):108-114. |
| SHAO L, DUO Z S, CHAI J Q,et al .A study on the day-ahead optimal scheduling of the pumped storage-wind-solar-thermal combined system[J].Power System and Clean Energy,2023,39(6):108-114. | |
| [14] | HE W, WANG J .Optimal selection of air expansion machine in compressed air energy storage:a review[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2018,87:77-95. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2018.01.013 |
| [15] | 赵攀,王佩姿,许文盼,等 .两级填充床蓄热器式绝热压缩空气储能系统变工况特性研究[J].太阳能学报,2022,43(1):294-299. |
| ZHAO P, WANG P Z, XU W P,et al .Off-design performance analysis of a CAES system with two-stage packed bed heat storage unit[J].Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica,2022,43(1):294-299. | |
| [16] | RAJU M, KUMAR KHAITAN S .Modeling and simulation of compressed air storage in Caverns:a case study of the huntorf plant[J].Applied Energy,2012,89(1):474-481. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.08.019 |
| [17] | CAVALLO A .Controllable and affordable utility-scale electricity from intermittent wind resources and compressed air energy storage (CAES)[J].Energy,2007,32(2):120-127. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2006.03.018 |
| [18] | WU S, ZHOU C, DOROODCHI E,et al .Thermodynamic analysis of a novel hybrid thermochemical-compressed air energy storage system powered by wind,solar and/or off-peak electricity[J].Energy Conversion and Management,2019,180:1268-1280. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2018.11.063 |
| [19] | YANG Z, WANG Z, RAN P,et al .Thermodynamic analysis of a hybrid thermal-compressed air energy storage system for the integration of wind power[J].Applied Thermal Engineering,2014,66(1/2):519-527. doi:10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.02.043 |
| [20] | WANG P, ZHAO P, XU W,et al .Performance analysis of a combined heat and compressed air energy storage system with packed bed unit and electrical heater[J].Applied Thermal Engineering,2019,162:114321. doi:10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.114321 |
| [21] | 雷超,李韬 .碳中和背景下氢能利用关键技术及发展现状[J].发电技术,2021,42(2):207-217. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.20015 |
| LEI C, LI T .Key technologies and development status of hydrogen energy utilization under the background of carbon neutrality[J].Power Generation Technology,2021,42(2):207-217. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.20015 | |
| [22] | 王宇飞 .集成储氢的氢燃料压缩空气储能系统性能评估与成本分析[D].吉林:东北电力大学,2023. |
| WANG Y F .Performance evaluation and cost analysis of hydrogen fuel compressed air energy storage system with integrated hydrogen storage[D].Jilin:Northeast Dianli University,2023. | |
| [23] | ZHAO P, XU W, LIU A,et al .Assessment the hydrogen-electric coupled energy storage system based on hydrogen-fueled CAES and power-to-gas-to-power device considering multiple time-scale effect and actual operation constraints[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2023,48(25):9198-9218. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.12.097 |
| [24] | ALIRAHMI S M, RAZMI A R, ARABKOOHSAR A .Comprehensive assessment and multi-objective optimization of a green concept based on a combination of hydrogen and compressed air energy storage (CAES) systems[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2021,142:110850. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2021.110850 |
| [25] | MIGLIARI L, MICHELETTO D, COCCO D .A hydrogen-fuelled compressed air energy storage system for flexibility reinforcement and variable renewable energy integration in grids with high generation curtailment[J].Energy Conversion and Management,2024,306:118308. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2024.118308 |
| [26] | 李延兵,贾树旺,张军亮,等 .汽轮机高位布置超超临界燃煤发电系统变工况(火用)经济性分析[J].发电技术,2024,45(1):69-78. |
| LI Y B, JIA S W, ZHANG J L,et al .Exergy economic analysis of ultra-supercritical coal-fired power plants with high-level layout of turbine under load-cycling conditions[J].Power Generation Technology,2024,45(1):69-78. | |
| [27] | KOTAS T J .The exergy method of thermal plant analysis[M].London:Butterworths,1985:37-51. doi:10.1016/b978-0-408-01350-5.50009-x |
| [28] | BEJAN A, TSATSARONIS G, MORAN M .Thermal design and optimization[M].New York:Wiley,1996:143-150. |
| [29] | China Entrepreneur Investment Club (CEIC) .China hydrogen energy:price[EB/OL].(2024-04-01)[2024-06-10].. |
| [30] | 国网陕西省电力有限公司 .国网陕西省电力有限公司关于 2024年4月份代理购电工商业用户购电价格的公告[EB/OL].(2024-03-28)[2024-06-10].. |
| State Grid Shaanxi Electric Power Co., Ltd .Announcement of State Grid Shaanxi Electric Power Co., Ltd. on the purchase price of electricity for commercial users through proxy purchase of electricians in April 2024.(2024-03-28)[2024-06-10].. | |
| [31] | ASSAREH E, ASL S S M, AGARWAL N,et al .A cogeneration-coupled energy storage system utilizing hydrogen and methane-fueled CAES and ORC with ambient temperature consideration enhanced by artificial neural network,and multi-objective optimization[J].Thermal Science and Engineering Progress,2023,46:102161. doi:10.1016/j.tsep.2023.102161 |
| [32] | XU X, YE Z, QIAN Q .Economic,exergoeconomic analyses of a novel compressed air energy storage-based cogeneration[J].Journal of Energy Storage,2022,51:104333. doi:10.1016/j.est.2022.104333 |
| [33] | DARABADI ZAREH A, KHOSHBAKHTI SARAY R, MIRMASOUMI S,et al .Extensive thermodynamic and economic analysis of the cogeneration of heat and power system fueled by the blend of natural gas and biogas[J].Energy Conversion and Management,2018,164:329-343. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2018.03.003 |
| [34] | ZARE V, MAHMOUDI S M S, YARI M,et al .Thermoeconomic analysis and optimization of an ammonia-water power/cooling cogeneration cycle[J].Energy,2012,47(1):271-283. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2012.09.002 |
| [35] | HOUSSAINY S, JANBOZORGI M, KAVEHPOUR P .Thermodynamic performance and cost optimization of a novel hybrid thermal-compressed air energy storage system design[J].Journal of Energy Storage,2018,18:206-217. doi:10.1016/j.est.2018.05.004 |
| [36] | MORANDIN M, MERCANGÖZ M, HEMRLE J,et al .Thermoeconomic design optimization of a thermo-electric energy storage system based on transcritical CO2 cycles[J].Energy,2013,58:571-587. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2013.05.038 |
| [37] | 胡珊,刘畅,徐玉杰,等 .基于峰谷分时电价的压缩空气储能系统热经济性分析[J].储能科学与技术,2021,10(5):1607-1613. |
| HU S, LIU C, XU Y J,et al .Thermo-economic analysis of compressed air energy storage under peak load shaving condition[J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2021,10(5):1607-1613. | |
| [38] | WU J, SHANG L, PAN Z,et al .Energy,exergy,economic,exergoeconomic,and exergoenvironmental (5E) analyses and optimization of a novel three-stage cascade system based on liquefied natural gas cold energy[J].Energy Technology,2022,10(7):2200228. doi:10.1002/ente.202200228 |
| [1] | 李建林, 彭禹宸, 王茜, 姜晓霞, 王垒. 锂离子电池建模研究现状与展望[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(5): 857-871. |
| [2] | 邹博, 任建地, 许道明, 邓立生, 廖力达, 肖俊兵. 氯化物熔盐储热技术应用于新能源发电的研究进展[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(5): 872-884. |
| [3] | 张杰, 王瑞川. 氢燃料电池钛双极板液压成形机理研究[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(4): 727-736. |
| [4] | 马浩然, 袁至, 王维庆, 李骥. 考虑数据中心和储能接入的主动配电网经济调度研究[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(4): 748-757. |
| [5] | 王杰, 徐立军, 李笑竹, 樊小朝, 古丽扎提∙海拉提null, 王维庆. 计及灵活性不足风险的配电网智能软开关与多类型共享储能协调优化[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(4): 758-767. |
| [6] | 卫广宇, 应笑冬, 姚延军, 杨小芳, 翁楚迪, 彭勇刚, 李海龙. 计及荷电状态的并网型直流微电网功率协同控制策略[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(4): 788-796. |
| [7] | 刘佳佳, 巨星. 弃电热储能光伏-光热复合发电系统技术经济性分析[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(4): 807-817. |
| [8] | 刘宿城, 栾李, 李龙, 洪涛, 刘晓东. 基于人工智能的直流微电网大信号稳定性评估方法研究[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(3): 496-507. |
| [9] | 王驰中, 高鑫, 陈衡, 张国强, 张锴. 分布式光伏电站投资决策及经济性分析[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(3): 607-616. |
| [10] | 刘忠, 黄彦铭, 朱光明, 邹淑云. 含风-光-电氢混合储能的多微电网系统容量优化配置方法[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(2): 240-251. |
| [11] | 雷基林, 余林兴, 别玉, 徐稚博, 肖雨寒. 孤岛微电网能量管理系统研究综述[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(2): 370-385. |
| [12] | 李亚楼, 赵飞, 樊雪君. 构网型储能及其应用综述[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(2): 386-398. |
| [13] | 张杰, 宋科, 张瀚, 曾云, 郑鹏. 车载供氢系统发展现状及展望[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(1): 58-71. |
| [14] | 王婷, 王银顺, 郭丽宁, 卞雨妍, 连占英, 李乐依, 毛承鹏. 稀土钡铜氧化物闭环超导葫芦形环片堆叠磁体的机械特性分析[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(6): 1039-1047. |
| [15] | 李文, 卜凡鹏, 张潇桐, 杨创东, 张静. 基于典型商业运营模式的含电-氢混合储能微电网系统优化运行方法[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(6): 1186-1200. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||