

发电技术 ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (6): 1184-1191.DOI: 10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.24071
• 储能 • 上一篇
陈梦东1, 康伟1, 邓占锋1, 赵文强2, 雷国斌2
收稿日期:2024-07-15
修回日期:2024-10-13
出版日期:2025-12-31
发布日期:2025-12-25
通讯作者:
邓占锋
作者简介:基金资助:Mengdong CHEN1, Wei KANG1, Zhanfeng DENG1, Wenqiang ZHAO2, Guobin LEI2
Received:2024-07-15
Revised:2024-10-13
Published:2025-12-31
Online:2025-12-25
Contact:
Zhanfeng DENG
Supported by:摘要:
目的 在高海拔地区应用固体蓄热装置时,空气稀薄会导致其蓄热和释热性能有较大变化,为此,提出了一种测试固体蓄热材料在高海拔地区低气压环境下蓄释热特性的方法。 方法 搭建了由空气环路、水环路及数据采集单元组成的低气压环境模拟实验台,对2块蓄热砖组成的蓄热单元开展了压力范围为40~101 kPa的蓄热和释热实验,通过记录入口空气温度、蓄热砖的温度变化,分析低气压环境下蓄热材料的蓄热速率和释热速率,比较不同气压下空气与蓄热砖的传热性能。 结果 与101 kPa工况相比,80 kPa和40 kPa工况的蓄热时间均有明显增加,且空气压力越低,所需要的蓄热时间越长;同时,80 kPa和40 kPa的环境压力下蓄热砖的平均蓄热速率分别降低约15%和55%;释热时,80 kPa和40 kPa的释热时间分别增加了26.1%和135.4%。 结论 空气压力对蓄热砖的蓄热和释热速率均有重要影响,实验结果可为设计应用于高海拔地区的固体蓄热装置提供指导。
中图分类号:
陈梦东, 康伟, 邓占锋, 赵文强, 雷国斌. 低气压环境下固体蓄热材料的蓄释热特性研究[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(6): 1184-1191.
Mengdong CHEN, Wei KANG, Zhanfeng DENG, Wenqiang ZHAO, Guobin LEI. Research on Heat Storage and Release Characteristics of Solid Heat Storage Materials in Low-Pressure Environments[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2025, 46(6): 1184-1191.
| 序号 | 测量仪表 | 量程与精度 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | K型热电偶 | 测量温度范围:0~600 ℃ 精度:±1 ℃ |
| 2 | 空气流量计 | 流量范围:0~100 m³/h 精度:1.5级 |
| 3 | 真空计 | 绝对压力范围:0~1 bar 精度:1.5级 |
| 4 | PT100热电阻 | 水温度范围:0~100 ℃ 精度:±0.5 ℃ |
| 5 | 水流量计 | 流量范围:0⁓1 m3/h 精度:±1.5% |
表1 实验仪表及精度
Tab. 1 Test instruments and their precision
| 序号 | 测量仪表 | 量程与精度 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | K型热电偶 | 测量温度范围:0~600 ℃ 精度:±1 ℃ |
| 2 | 空气流量计 | 流量范围:0~100 m³/h 精度:1.5级 |
| 3 | 真空计 | 绝对压力范围:0~1 bar 精度:1.5级 |
| 4 | PT100热电阻 | 水温度范围:0~100 ℃ 精度:±0.5 ℃ |
| 5 | 水流量计 | 流量范围:0⁓1 m3/h 精度:±1.5% |
| 工况 | 压力/kPa | 加热丝分阶段加热温度/℃ | 实验起始温度/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 101 | 90~170~250 | 45 |
| 2 | 80 | 90~170~250 | 48 |
| 3 | 40 | 90~170~250 | 49 |
| 4 | 40 | 550 | 45 |
表2 蓄热实验工况
Tab. 2 Operating conditions for heat storage tests
| 工况 | 压力/kPa | 加热丝分阶段加热温度/℃ | 实验起始温度/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 101 | 90~170~250 | 45 |
| 2 | 80 | 90~170~250 | 48 |
| 3 | 40 | 90~170~250 | 49 |
| 4 | 40 | 550 | 45 |
| 工况 | 压力/kPa | 实验起始温度/℃ | 释热空气入口温度/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 101 | 230 | 30 |
| 6 | 80 | 224 | 30 |
| 7 | 40 | 225 | 30 |
| 8 | 40 | 347 | 30 |
| 9 | 40 | 432 | 30 |
表3 释热实验工况
Tab. 3 Operating conditions for heat release tests
| 工况 | 压力/kPa | 实验起始温度/℃ | 释热空气入口温度/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 101 | 230 | 30 |
| 6 | 80 | 224 | 30 |
| 7 | 40 | 225 | 30 |
| 8 | 40 | 347 | 30 |
| 9 | 40 | 432 | 30 |
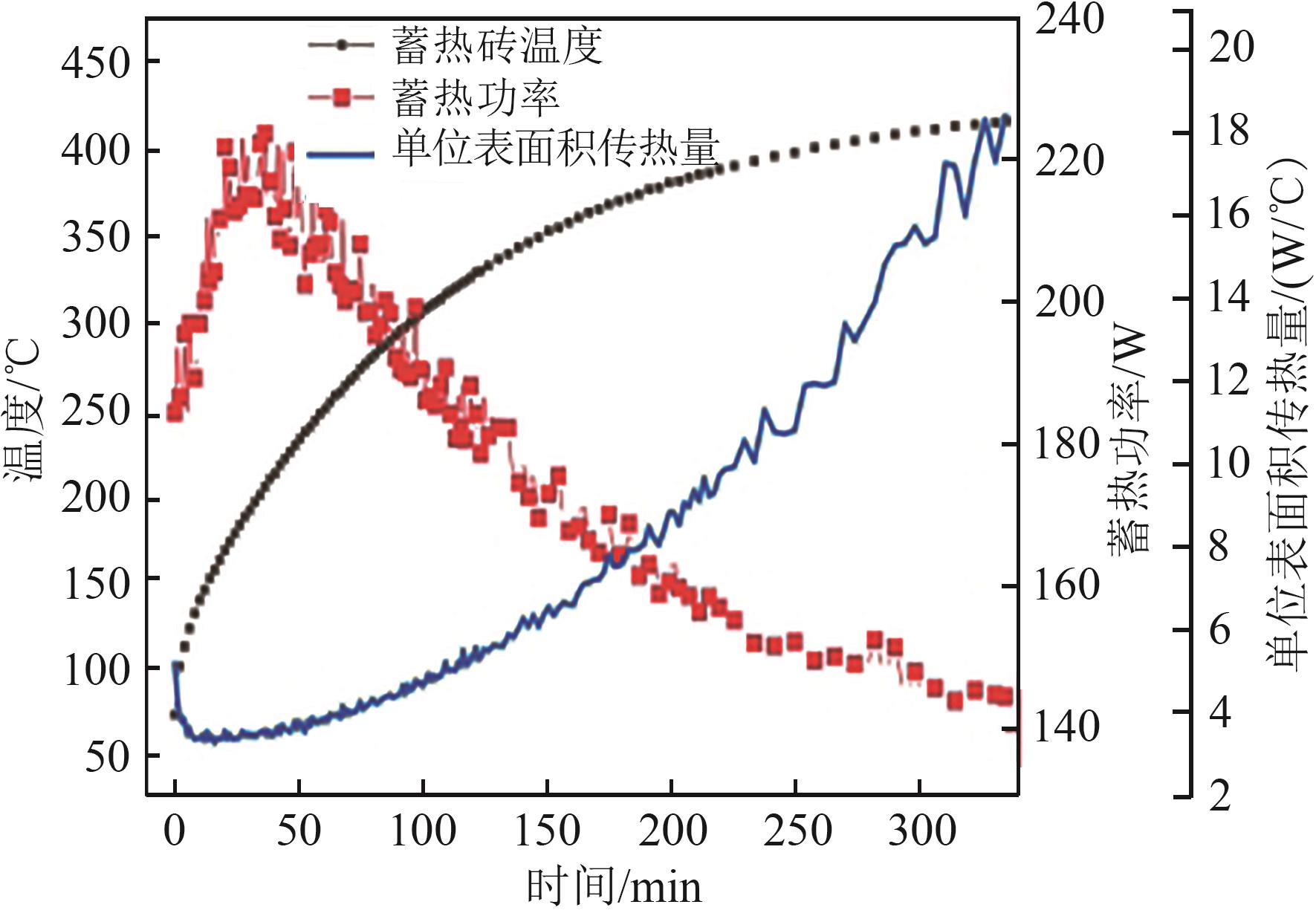
图4 蓄热模式下蓄热砖温度、蓄热功率及单位面积传热量的变化曲线
Fig. 4 Variation curves of heat storage brick temperature, heat storage capacity, and heat transfer per unit area over time in heat storge mode
| [1] | 李建林,张则栋,谭宇良,等 .碳中和目标下储能发展前景综述[J].电气时代,2022(1):61-65. |
| LI J L, ZHANG Z D, TAN Y L,et al .Review of the development prospect of energy storage under the goal of carbon neutrality[J].Electric Age,2022(1):61-65. | |
| [2] | 张力菠,吴一锴,王群伟 .考虑碳中和目标与成本优化的可再生能源大规模发展规划[J].广东电力,2023,36(7):31-39. |
| ZHANG L B, WU Y K, WANG Q W .Large-scale development of renewable energy in consideration of carbon neutrality and cost optimization[J].Guangdong Electric Power,2023,36(7):31-39. | |
| [3] | 杨洁,吴志强,范宏 .基于实时电价的含储能可再生能源系统协同调度策略[J].智慧电力,2023,51(4):46-53. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7598.2023.04.007 |
| YANG J, WU Z Q, FAN H .Collaborative scheduling strategy for renewable energy systemswith energy storage based on real time price[J].Smart Power,2023,51(4):46-53. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7598.2023.04.007 | |
| [4] | 张雷,刘琦,赵晓丽,等 .电力需求增长和负荷灵活性提升视角下的风光资源密集地区可再生能源消纳研究[J].全球能源互联网,2024,7(4):454-462. |
| ZHANG L, LIU Q, ZHAO X L,et al .Research on renewable energy penetration in wind and solar resource-intensive areas from the perspective of power demand growth and load flexibility enhancement[J].Journal of Global Energy Interconnection,2024,7(4):454-462. | |
| [5] | 李文升,刘晓明,曹永吉,等 .考虑电力系统灵活性的网-储联合规划[J].智慧电力,2023,51(4):30-37. |
| LI W S, LIU X M, CAO Y J,et al .Joint planning of energy storage and transmission line considering power system flexibility[J].Smart Power,2023,51(4):30-37. | |
| [6] | 姜竹,邹博杨,丛琳,等 .储热技术研究进展与展望[J].储能科学与技术,2022,11(9):2746-2771. doi:10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2021.0538 |
| JIANG Z, ZOU B Y, CONG L,et al .Recent progress and outlook of thermal energy storage technologies[J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2022,11(9):2746-2771. doi:10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2021.0538 | |
| [7] | KHARE S, DELL'AMICO M, KNIGHT C,et al .Selection of materials for high temperature sensible energy storage[J].Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells,2013,115:114-122. doi:10.1016/j.solmat.2013.03.009 |
| [8] | 吴考阳 .固体蓄热新型换热方式研究[D].张家口:河北建筑工程学院,2021. |
| WU K Y .Research on new heat transfer mode of solid heat storage[D].Zhangjiakou:Hebei University of Architecture,2021. | |
| [9] | MAWIRE A, MCPHERSON M, VAN DEN HEETKAMP R R J,et al .Simulated performance of storage materials for pebble bed thermal energy storage (TES) systems[J].Applied Energy,2009,86(7/8):1246-1252. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2008.09.009 |
| [10] | MAWIRE A, MCPHERSON M .Experimental characterisation of a thermal energy storage system using temperature and power controlled charging[J].Renewable Energy,2008,33(4):682-693. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2007.04.021 |
| [11] | 郑志伟,仇性启,祁风雷,等 .蜂窝陶瓷蓄热体传热和阻力特性实验研究[J].石油化工设备,2013,42(1):9-13. |
| ZHENG Z W, QIU X Q, QI F L,et al .Experimental study of heat transfer and resistance characteristics on honeycomb ceramic regenerator[J].Petro-Chemical Equipment,2013,42(1):9-13. | |
| [12] | XU G Z, HU X, LIAO Z R,et al .Experimental and numerical study of an electrical thermal storage device for space heating[J].Energies,2018,11(9):2180. doi:10.3390/en11092180 |
| [13] | 陈梦东,章康,马美秀,等 .基于Workbench的固体电蓄热装置换热通道参数优化[J].热能动力工程,2023,38(10):64-71. |
| CHEN M D, ZHANG K, MA M X,et al .Optimization of heat exchange channel parameters of solid electric heat storage device based on workbench[J].Journal of Engineering for Thermal Energy and Power,2023,38(10):64-71. | |
| [14] | 毕月虹,吴娟,鲁一涵 .固体蓄热砖孔道结构参数对蓄/释热性能的影响[J].北京工业大学学报,2022,48(5):543-551. |
| BI Y H, WU J, LU Y H .Influence of pore structure parameters of solid thermal storage bricks on the heat storage/release performance[J].Journal of Beijing University of Technology,2022,48(5):543-551. | |
| [15] | 赵頔,王启民 .基于ANSYS分析的蓄热砖蓄热特性数值模拟及实验研究[J].沈阳工程学院学报(自然科学版),2020,16(2):34-38. |
| ZHAO D, WANG Q M .Numerical simulation and experimental study on thermal storage characteristics of thermal storage brick based on ANSYS analysis[J].Journal of Shenyang Institute of Engineering (Natural Science),2020,16(2):34-38. | |
| [16] | 陈贶,刘鹏,刘大玮 .谷电固体蓄热供暖方案的应用与分析[J].有色冶金节能,2020,36(1):41-44. |
| CHEN K, LIU P, LIU D W .Application and analysis of the heating scheme of valley electricity solid heat storage[J].Energy Saving of Nonferrous Metallurgy,2020,36(1):41-44. | |
| [17] | 李传,葛志伟,金翼,等 .基于复合相变材料储热单元的储热特性[J].储能科学与技术,2015,4(2):169-175. |
| LI C, GE Z W, JIN Y,et al .Heat transfer behaviour of thermal energy storage components using composite phase change materials[J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2015,4(2):169-175. | |
| [18] | 胡思科,周林林,邢姣娇 .圆形和椭圆形孔道固体蓄热装置蓄放热特性模拟[J].热力发电,2018,47(1):38-45. |
| HU S K, ZHOU L L, XING J J .Simulation on heat discharge and heat storage performance of solid heat storage device with round and oval pore canals[J].Thermal Power Generation,2018,47(1):38-45. | |
| [19] | 赵思聪,刘云亮,朱瑞,等 .固态储热装置温度场试验研究[J].热能动力工程,2022,37(S1):66-76. |
| ZHAO S C, LIU Y L, ZHU R,et al .Experimental study on temperature field of solid-state heat storage device[J].Journal of Engineering for Thermal Energy and Power,2022,37(S1):66-76. | |
| [20] | 孙德明,马昕霞,朱泊旭,等 .多种固体蓄热装置放热特性的数值模拟研究[J].上海电力大学学报,2022,38(3):227-233. |
| SUN D M, MA X X, ZHU B X,et al .Numerical simulation study on heat dissipation characteristics of multiple solid regenerative devices[J].Journal of Shanghai University of Electric Power,2022,38(3):227-233. | |
| [21] | 邢作霞,赵海川,马士平,等 .电制热固体储热装置关键参数设计研究和经济性评估[J].储能科学与技术,2019,8(6):1211-1216. |
| XING Z X, ZHAO H C, MA S P,et al .Study on key parameters design and economic evaluation of the electric heating and solid sensible heat thermal storage device[J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2019,8(6):1211-1216. |
| [1] | 王志康, 张儒琪, 袁少可, 韩东江, 隋军. 有机朗肯-蒸汽压缩循环系统研究进展[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(6): 1059-1073. |
| [2] | 罗斌, 白小龙, 臧天磊, 黄燕, 张琳, 李萌, 张雪霞, 蒋永龙. 风光水互补发电系统研究综述[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(6): 1097-1111. |
| [3] | 王曦, 陈心怡. 一种基于时序卷积网络-Transformer的海上风电功率预测方法[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(6): 1123-1132. |
| [4] | 陈锋, 路小敏, 沈冰, 王军鹏. 基于消纳-保供博弈的分布式储能双层规划模型[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(6): 1133-1143. |
| [5] | 张萍, 李永强, 杏华良. 基于变分模态分解的平抑风电波动混合储能容量优化配置[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(6): 1144-1153. |
| [6] | 张效伟, 衣振晓, 王凯. 基于改进自适应蜜獾算法优化时间卷积网络的车载锂离子电池健康状态估计[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(6): 1154-1163. |
| [7] | 张静姝, 刘倩, 姚晓乐, 徐超, 巨星. 应用于锂离子电池无源热管理与安全防护的水合盐复合相变材料[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(6): 1164-1175. |
| [8] | 李建林, 彭禹宸, 王茜, 姜晓霞, 王垒. 锂离子电池建模研究现状与展望[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(5): 857-871. |
| [9] | 邹博, 任建地, 许道明, 邓立生, 廖力达, 肖俊兵. 氯化物熔盐储热技术应用于新能源发电的研究进展[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(5): 872-884. |
| [10] | 马宁, 赵攀, 刘艾杰, 许文盼, 王江峰. 纯氢补燃型和天然气补燃型压缩空气储能系统特性与㶲经济性对比[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(5): 885-896. |
| [11] | 董福贵, 张伟. 考虑容量价值的独立新型储能电站运行策略优化研究[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(5): 897-908. |
| [12] | 路诗梦, 孙建林, 曾凡杰, 林小杰, 吴均湛, 马添翼, 钟崴, 谢立坤, 谢伟. 零碳地热能综合利用技术研究进展[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(5): 909-922. |
| [13] | 龙潇, 张晋宾, 陈令特. 未来能源技术展望[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(4): 651-693. |
| [14] | 马浩然, 袁至, 王维庆, 李骥. 考虑数据中心和储能接入的主动配电网经济调度研究[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(4): 748-757. |
| [15] | 王杰, 徐立军, 李笑竹, 樊小朝, 古丽扎提∙海拉提null, 王维庆. 计及灵活性不足风险的配电网智能软开关与多类型共享储能协调优化[J]. 发电技术, 2025, 46(4): 758-767. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||