

发电技术 ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 910-918.DOI: 10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.24030
• 储能 • 上一篇
姬海民1, 薛磊2, 周方盛3, 王电2, 陈诚3, 李靖2, 刘辉1,4, 薛宁1, 张知翔1, 徐党旗1
收稿日期:2024-04-01
修回日期:2024-05-01
出版日期:2024-10-31
发布日期:2024-10-29
作者简介:基金资助:Haimin JI1, Lei XUE2, Fangsheng ZHOU3, Dian WANG2, Cheng CHEN3, Jing LI2, Hui LIU1,4, Ning XUE1, Zhixiang ZHANG1, Dangqi XU1
Received:2024-04-01
Revised:2024-05-01
Published:2024-10-31
Online:2024-10-29
Supported by:摘要:
目的 压缩空气储能是大容量、长周期、低成本、高效率的一种储能技术,由于气态压缩空气储能受制于储气室的苛刻要求,无法多场景、规模化推广应用,因此提出一种非补燃液态压缩空气储能系统。 方法 构建了系统理论计算模型,对系统内压缩机级间温度、压缩机级数、透平入口温度等关键参数进行了敏感性分析,同时与非补燃气态压缩空气储能系统进行了对比。 结果 压缩机级间温度过低或过高都会制约系统电-电转化效率的提升;压缩机级数与压缩机耗功呈现正相关趋势,与透平发电功率呈现负相关趋势;在入口压力相同的条件下,透平入口温度越高,发电功率越大,电-电转化效率越高;与非补燃气态储能系统相比,非补燃液态储能密度增加了3.7倍,储气室容积缩小了9/10。 结论 非补燃液态压缩空气储能系统有效解决了储气室的难题,使压缩空气储能技术能够在多场景、规模化推广应用,对火电机组深度调峰及电网大容量储能具有重要意义。
中图分类号:
姬海民, 薛磊, 周方盛, 王电, 陈诚, 李靖, 刘辉, 薛宁, 张知翔, 徐党旗. 非补燃液态压缩空气储能系统性能模拟研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(5): 910-918.
Haimin JI, Lei XUE, Fangsheng ZHOU, Dian WANG, Cheng CHEN, Jing LI, Hui LIU, Ning XUE, Zhixiang ZHANG, Dangqi XU. System Simulation Study on Performance of Non-Supplementary Combustion Liquid Compressed Air Energy Storage System[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2024, 45(5): 910-918.
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 第一级压缩机入口空气温度/℃ | 20 |
| 第一级压缩机入口空气压力/MPa | 0.1 |
| 储能压缩压力等级/MPa | 8.1 |
| 压缩机等熵效率/% | 85 |
| 压缩机机械效率/% | 98 |
| 蓄热器能量利用率/% | 85 |
| 换热器端差/℃ | 20 |
| 导热油初始温度/℃ | 20 |
| 储能液态空气量/kg | 15 500 |
| 储罐液态空气压力/MPa | 2 |
| 储罐液态空气温度/℃ | -155 |
| 液态空气密度/(kg/m3) | 821 |
| 储罐尺寸/m | Φ4×5 |
| 液泵效率/% | 80 |
| 液泵驱动效率/% | 98 |
| 液泵出口压力等级/MPa | 8.1 |
| 蓄冷器能量利用率/% | 85 |
| 膨胀机级数 | 3 |
| 膨胀比 | 4 |
| 膨胀机等熵效率/% | 85 |
| 膨胀机机械效率/% | 98 |
表1 非补燃压缩空气储能系统边界参数
Tab. 1 Boundary parameters of non-supplementary combustion compressed air energy storage system
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 第一级压缩机入口空气温度/℃ | 20 |
| 第一级压缩机入口空气压力/MPa | 0.1 |
| 储能压缩压力等级/MPa | 8.1 |
| 压缩机等熵效率/% | 85 |
| 压缩机机械效率/% | 98 |
| 蓄热器能量利用率/% | 85 |
| 换热器端差/℃ | 20 |
| 导热油初始温度/℃ | 20 |
| 储能液态空气量/kg | 15 500 |
| 储罐液态空气压力/MPa | 2 |
| 储罐液态空气温度/℃ | -155 |
| 液态空气密度/(kg/m3) | 821 |
| 储罐尺寸/m | Φ4×5 |
| 液泵效率/% | 80 |
| 液泵驱动效率/% | 98 |
| 液泵出口压力等级/MPa | 8.1 |
| 蓄冷器能量利用率/% | 85 |
| 膨胀机级数 | 3 |
| 膨胀比 | 4 |
| 膨胀机等熵效率/% | 85 |
| 膨胀机机械效率/% | 98 |
| 参数 | 工况1 | 工况2 | 工况3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 压缩级数 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 压缩机级间温度/℃ | 45 | 65 | 85 |
表2 不同压缩机级间温度参数
Tab. 2 Temperature parameters of different compressor interstages
| 参数 | 工况1 | 工况2 | 工况3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 压缩级数 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 压缩机级间温度/℃ | 45 | 65 | 85 |
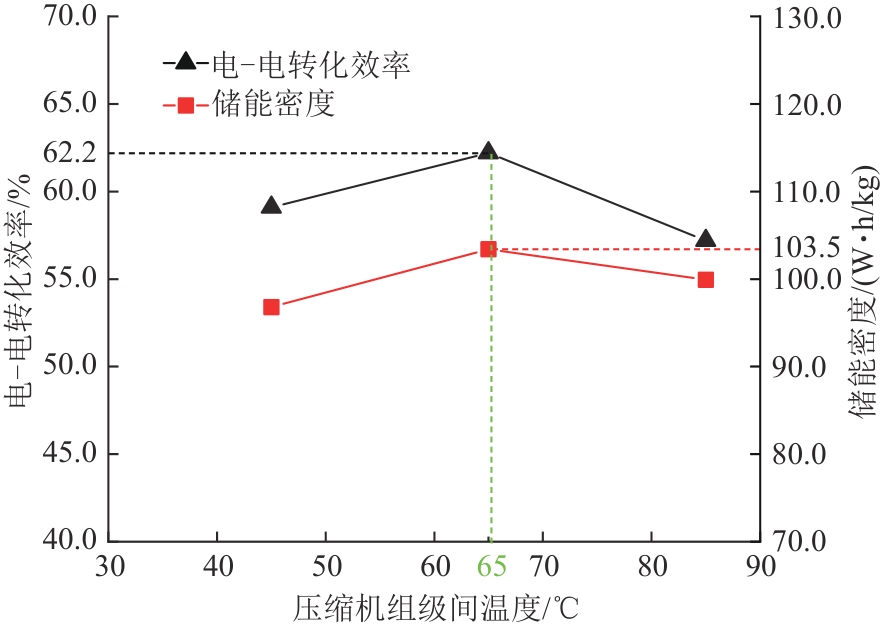
图5 压缩机级间温度与电-电转化效率、储能密度关系
Fig. 5 Relationship between compressor interstage temperature and electric-electric conversion efficiency and energy storage density
| 参数 | 工况4 | 工况5 | 工况6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 压缩级数 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| 压缩机级间温度/℃ | 65 | 65 | 65 |
| 液泵消耗的电功率/kW | 53 | 53 | 53 |
表3 不同压缩机级数工况参数
Tab. 3 Operating parameters of different compressor stages
| 参数 | 工况4 | 工况5 | 工况6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 压缩级数 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| 压缩机级间温度/℃ | 65 | 65 | 65 |
| 液泵消耗的电功率/kW | 53 | 53 | 53 |
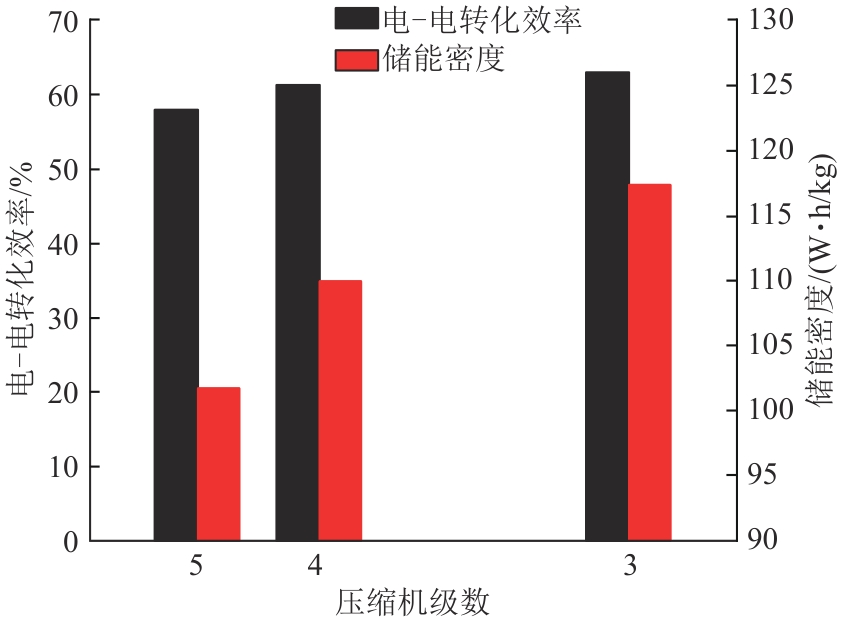
图8 压缩机级数与电-电转化效率、储能密度的关系
Fig. 8 Relationship between number of compressor stages and electric-electric conversion efficiency and energy storage density
| 参数 | 工况6 | 工况7 | 工况8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 压缩级数 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 压缩机级间温度/℃ | 65 | 65 | 65 |
| 液泵消耗电功率/kW | 53 | 53 | 53 |
| 一级透平入口温度/℃ | 301 | 351 | 401 |
| 二级透平入口温度/℃ | 279 | 329 | 379 |
| 三级透平入口温度/℃ | 196 | 246 | 296 |
| 外界输入热量/kW | 0 | 342 | 689 |
表4 不同透平入口温度参数
Tab. 4 Different turbine inlet temperature parameters
| 参数 | 工况6 | 工况7 | 工况8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 压缩级数 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 压缩机级间温度/℃ | 65 | 65 | 65 |
| 液泵消耗电功率/kW | 53 | 53 | 53 |
| 一级透平入口温度/℃ | 301 | 351 | 401 |
| 二级透平入口温度/℃ | 279 | 329 | 379 |
| 三级透平入口温度/℃ | 196 | 246 | 296 |
| 外界输入热量/kW | 0 | 342 | 689 |
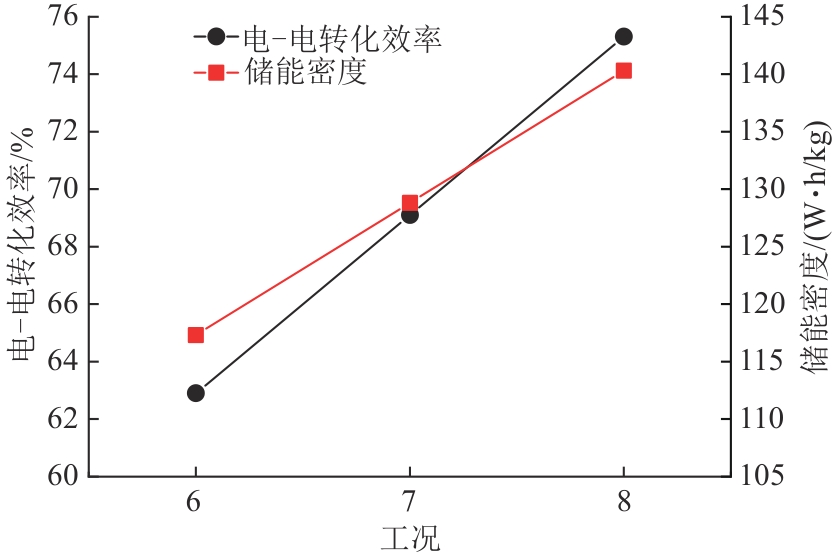
图10 透平入口温度与电-电转化效率、储能密度的关系
Fig. 10 Relationship between turbine inlet air temperature and electric-electric conversion efficiency and energy storage density
| 参数 | 非补燃液态 | 非补燃气态 |
|---|---|---|
| 压缩压力等级/MPa | 8.1 | 8.1 |
| 压缩级数 | 3 | 3 |
| 压缩机级间温度/℃ | 65 | 65 |
| 储存物质状态 | 液态 | 气态 |
| 储存温度/℃ | -155 | 20 |
| 储存压力/MPa | 2 | 8.1 |
| 储存物质密度/(kg/m3) | 821 | 87 |
| 储存质量/kg | 15 500 | 15 500 |
| 液泵消耗电功率/kW | 53 | 0 |
表5 2种储能系统边界参数
Tab. 5 Boundary parameters of two types of energy storage systems
| 参数 | 非补燃液态 | 非补燃气态 |
|---|---|---|
| 压缩压力等级/MPa | 8.1 | 8.1 |
| 压缩级数 | 3 | 3 |
| 压缩机级间温度/℃ | 65 | 65 |
| 储存物质状态 | 液态 | 气态 |
| 储存温度/℃ | -155 | 20 |
| 储存压力/MPa | 2 | 8.1 |
| 储存物质密度/(kg/m3) | 821 | 87 |
| 储存质量/kg | 15 500 | 15 500 |
| 液泵消耗电功率/kW | 53 | 0 |
| 1 | 张松岩,苗世洪,尹斌鑫,等 .考虑火电深度调峰的多类型储能经济性分析[J].电力建设,2022,43(1):132-142. doi:10.12204/j.issn.1000-7229.2022.01.015 |
| ZHANG S Y, MIAO S H, YIN B X,et al .Economic analysis of multi-type energy storages considering the deep peak-regulation of thermal power units[J].Electric Power Construction,2022,43(1):132-142. doi:10.12204/j.issn.1000-7229.2022.01.015 | |
| 2 | 陈宏,贺悝,谭庄熙,等 .考虑SOC均衡的储能电站一次调频协同控制方法[J].电力科学与技术学报,2023,38(6):105-114. |
| CHEN H, HE L, TAN Z X,et al .Coordinated control method of primary frequency regulation for energy storage power station considering SOC balance[J].Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology,2023,38(6):105-114. | |
| 3 | 刘红 .基于改进粒子群算法的储能调峰容量优化配置研究[J].广东电力,2023,36(1):68-76. |
| LIU H .Research on optimal configuration of energy storage peak shaving capacity based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm[J].Guangdong Electric Power,2023,36(1):68-76. | |
| 4 | 吴盛军,李强,彭维馨,等 .考虑平抑直流故障后功率波动的储能系统选址配置方法[J].电力科学与技术学报,2023,38(1):35-42. |
| WU S J, LI Q, PENG W X,et al .Site selection and configuration method of energy storage system for suppressing power fluctuation after DC fault[J].Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology,2023, | |
| 38(1):35-42. | |
| 5 | 姜红丽,刘羽茜,冯一铭,等 .碳达峰、碳中和背景下“十四五”时期发电技术趋势分析[J].发电技术,2022,43(1):54-64. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.21030 |
| JIANG H L, LIU Y X, FENG Y M,et al .Analysis of power generation technology trend in 14th Five-Year Plan under the background of carbon peak and carbon neutrality[J].Power Generation Technology,2022,. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.21030 | |
| 43(1):54-64. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.21030 | |
| 6 | 德格吉日夫,田雪沁,王新雷,等 .计及运行成本与排放量的风光火储联合外送调度多目标优化模型研究[J].电网与清洁能源,2022,38(6):121-128. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3814.2022.06.016 |
| DE G R, TIAN X Q, WANG X L,et al .Research on multi-objective optimization model of the combined outward transmission dispatching of wind,solar,thermal-power and storage considering operation cost and emission[J].Power System and Clean Energy,2022,38(6):121-128. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3814.2022.06.016 | |
| 7 | 李泽航,周浩,李浩秒,等 .面向电力系统的液态金属电池储能技术[J].发电技术,2022,43(5):760-774. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.22154 |
| LI Z H, ZHOU H, LI H M,et al .Liquid metal battery energy storage technology for power system[J].Power Generation Technology,2022,43(5):760-774. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.22154 | |
| 8 | 韩晓娟,牟志国,魏梓轩 .基于云模型的电化学储能工况适应性综合评估[J].电力工程技术,2022,41(4):213-219. |
| HAN X J, MU Z G, WEI Z X .Comprehensive evaluation for the adaptability of electrochemical energy storage conditions based on cloud model[J].Electric Power Engineering Technology,2022,41(4):213-219. | |
| 9 | 郑明辉,宋民航,王金星 .“双碳”目标下燃煤机组转型目标与技术分析[J].广东电力,2022,35(7):14-22. |
| ZHENG M H, SONG M H, WANG J X .Objective and technical analysis of coal-fired unit transformation under dual carbon goals[J].Guangdong Electric Power,2022,35(7):14-22. | |
| 10 | 陈海生,刘金超,郭欢,等 .压缩空气储能技术原理[J].储能科学与技术,2013,2(2):146-151. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-4239.2013.02.008 |
| CHEN H S, LIU J C, GUO H,et al .Technical principle of compressed air energy storage system[J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2013,2(2):146-151. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-4239.2013.02.008 | |
| 11 | 张杰,陈洁,孙晗喆,等 .基于碳捕集与液态CO2储能的综合能源系统优化调度[J].智慧电力,2023,51(3):1-8. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7598.2023.03.002 |
| ZHANG J, CHEN J, SUN H Z,et al .Optimal scheduling of integrated energy systems based on carbon capture and liquid CO2 energy storage[J].Smart Power,2023,51(3):1-8. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7598.2023.03.002 | |
| 12 | 吴金龙,李峻,邢泰高,等 .绝热压缩空气储能系统的热力性能与经济性分析[J].热力发电,2024,53(2):27-36. |
| WU J L, LI J, XING T G,et al .Thermodynamics and economic analysis of adiabatic compressed air energy storage system[J].Thermal Power Generation,2024,53(2):27-36. | |
| 13 | 何青,贾明祥,康浩强,等 .绝热压缩空气储能系统Aspen Plus软件自定义蓄热器模块设计及应用[J].热力发电,2018,47(2):114-119. |
| HE Q, JIA M X, KANG H Q,et al .Design and application of custom regenerator module in Aspen Plus for adiabatic compressed air energy storage system[J].Thermal Power Generation,2018,47(2):114-119. | |
| 14 | 马兴民 .深冷液化空气储能系统设计及分析[D].北京:华北电力大学,2021. |
| MA X M .Design and analysis of cryogenic liquefied air energy storage system[D].Beijing:North China Electric Power University,2021. | |
| 15 | 苏要港,吴晓南,廖柏睿,等 .耦合LNG冷能及ORC的新型液化空气储能系统分析[J].储能科学与技术,2022,11(6):1996-2006. |
| SU Y G, WU X N, LIAO B R,et al .Analysis of novel liquefied-air energy-storage system coupled with LNG cold energy and ORC[J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2022,11(6):1996-2006. | |
| 16 | 薛皓白,张新敬,陈海生,等 .微型压缩空气储能系统释能过程分析[J].工程热物理学报,2014,35(10):1923-1929. |
| XUE H B, ZHANG X J, CHEN H S,et al .Analysis of energy release process of micro-compressed air energy storage systems[J].Journal of Engineering Thermophysics,2014,35(10):1923-1929. | |
| 17 | 刘烨,魏高升,由文江,等 .空气压缩系统深度节能技术[J].发电技术,2018,39(1):70-76. |
| LIU Y, WEI G S, YOU W J,et al .Deep energy saving technology in air compression system[J].Power Generation Technology,2018,39(1):70-76. | |
| 18 | 李姚旺,苗世洪,尹斌鑫,等 .含先进绝热压缩空气储能电站的电力系统实时调度模型[J].电工技术学报,2019,34(2):387-397. |
| LI Y W, MIAO S H, YIN B X,et al .Real-time dispatch model for power system with advanced adiabatic compressed air energy storage[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society,2019,34(2):387-397. | |
| 19 | 李丞宸,李宇峰,张严,等 .一种新型蒸汽恒压抽水压缩空气储能系统及其热力学分析[J].西安交通大学学报,2021,55(6):84-91. doi:10.7652/xjtuxb202106011 |
| LI C C, LI Y F, ZHANG Y,et al .Novel steam constant-pressure pumped hydro with compressed air energy storage system and thermodynamic analysis[J].Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University,2021,55(6):84-91. doi:10.7652/xjtuxb202106011 | |
| 20 | 姚尔人,王焕然,席光,等 .等一种压缩空气储能与内燃机技术耦合的冷热电联产系统[J].西安交通大学学报,2016,50(1):22-27. |
| YAO E R, WANG H R, XI G,et al .A novel combined cooling heating and power system with coupled compressed air energy storage and combustion engine[J].Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University,2016,50(1):22-27. | |
| 21 | 文贤馗,张世海,邓彤天,等 .大容量电力储能调峰调频性能综述[J].发电技术,2018,39(6):487-492. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.18214 |
| WEN X K, ZHAGN S H, DENG T T,et al .A summary of large capacity power energy storage peak regulation and frequency adjustment performance[J].Power Generation Technology,2018,39(6):487-492. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.18214 | |
| 22 | YAO E, WANG H, WANG L,et al .Thermo-economic optimization of a combined cooling,heating and power system based on small-scale compressed air energy storage[J].Energy Conversion and Management,2016,118:377-386. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2016.03.087 |
| 23 | 姜云涛,付林,胡鹏,等 .电厂及工业废热利用新途径[J].石油石化节能与减排,2011(S1):29-32. |
| JIANG Y T, FU L, HU P,et al .New ways of waste heat utilization in power plants and industries[J].Green Petroleum & Petrochemicals,2011(S1):29-32. | |
| 24 | 梅生伟,李瑞,陈来军,等 .先进绝热压缩空气储能技术研究进展及展望[J].中国电机工程学报,2018,38(10):2893-2907. |
| MEI S W, LI R, CHEN L J,et al .An overview and outlook on advanced adiabatic compressed air energy storage technique[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2018,38(10):2893-2907. |
| [1] | 赵星源, 谢芳毅, 刘乙学, 陈昉, 崔建华, 韩少峰, 何青. 压气储能电站智能建造体系及其关键技术[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(5): 899-909. |
| [2] | 胡程平, 范明, 刘艾旺, 施云辉. 考虑云储能的多区互联综合能源系统规划[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(4): 641-650. |
| [3] | 张崇, 李博, 李笑宇, 刘洪波, 刘永发. 基于虚拟同步机控制参数自适应调节的储能系统调频方法[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(4): 772-780. |
| [4] | 袁鑫, 刘骏, 陈衡, 潘佩媛, 徐钢, 王修彦. 碳捕集技术应用对燃煤机组调峰能力的影响[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 373-381. |
| [5] | 丁湧. 1 000 MW超超临界燃煤锅炉深度调峰研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 382-391. |
| [6] | 陈晓峰, 左川, 赵宁, 黄凯, 王惠杰. 集成蓄热装置的火电机组调峰特性分析[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 392-400. |
| [7] | 代华松, 浦绍旭, 柴国旭, 金李, 陈为平, 解明亮. 350 MW超临界流化床机组深度调峰研究与应用[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 401-411. |
| [8] | 周丹, 袁至, 李骥, 范玮. 考虑平抑未来时刻风电波动的混合储能系统超前模糊控制策略[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 412-422. |
| [9] | 赵斌, 梁告, 姜孟浩, 邹港, 王力. 光储系统并网功率波动平抑及储能优化配置[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 423-433. |
| [10] | 李军徽, 陈国航, 马腾, 李翠萍, 朱星旭, 贾晨. 高风电渗透率下液流电池储能系统调峰优化控制策略[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 434-447. |
| [11] | 韩秀秀, 魏少鑫, 汪剑, 崔超婕, 骞伟中. 高性能锂离子电容器正极材料石墨烯-介孔炭复合物的制备及性能分析[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 494-507. |
| [12] | 张思海, 李超然, 万广亮, 刘印学, 徐海楠, 黄中, 杨海瑞. 330 MW 循环流化床锅炉深度调峰技术[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 199-206. |
| [13] | 郑淇薇, 王华霆, 陈衡, 潘佩媛, 徐钢. 深度调峰背景下火电机组热电解耦技术路径对比分析[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 207-215. |
| [14] | 贾志军, 范伟, 任少君, 魏唐斌. 600 MW亚临界机组长时间深度调峰燃烧稳定性研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 216-225. |
| [15] | 李展, 杨振勇, 刘磊, 陈振山, 季卫鸣, 洪烽. 火电机组深度调峰工况下炉侧蓄热系数对一次调频能力的影响分析[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 226-232. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||