

发电技术 ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 908-917.DOI: 10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.22088
朱京冀1, 徐义书1, 徐静颖1, 王华坤1, 刘小伟1, 于敦喜1, 马晶晶2, 徐明厚1
收稿日期:2022-04-27
出版日期:2022-12-31
发布日期:2023-01-03
作者简介:基金资助:Jingji ZHU1, Yishu XU1, Jingying XU1, Huakun WANG1, Xiaowei LIU1, Dunxi YU1, Jingjing MA2, Minghou XU1
Received:2022-04-27
Published:2022-12-31
Online:2023-01-03
Supported by:摘要:
掺烧“零碳、富氢、高氮”的氨气(NH3)燃料是实现燃煤电站CO2减排的重要技术路径。为探究氨燃料的引入对煤燃烧及污染物生成行为的影响,基于McKenna平面火焰燃烧系统开展了煤掺氨燃烧实验,结合可见光相机、烟气分析仪及热泳探针取样分析系统,探究了掺烧氨燃料对煤挥发分火焰形态与温度特征、气态污染物及碳烟等细颗粒物生成的影响。研究结果表明:氨燃料先于煤着火,并加热促进煤热解及挥发分的生成与释放,促使挥发分着火燃烧,导致挥发分火焰长度和温度增加。掺烧的NH3在挥发分火焰中部分转化为NO,导致火焰中NO浓度显著升高。掺烧NH3提升了气相燃料当量比,促进了挥发分向碳烟的转化,促使碳烟颗粒生成量增加。
中图分类号:
朱京冀, 徐义书, 徐静颖, 王华坤, 刘小伟, 于敦喜, 马晶晶, 徐明厚. 掺烧氨燃料对煤挥发分火焰特性及颗粒物生成的影响[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43(6): 908-917.
Jingji ZHU, Yishu XU, Jingying XU, Huakun WANG, Xiaowei LIU, Dunxi YU, Jingjing MA, Minghou XU. Effect of Co-firing Ammonia on Coal Volatile Flame Characteristics and Particulate Matter Formation Behaviours[J]. Power Generation Technology, 2022, 43(6): 908-917.
| 工业分析 | 元素分析 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCad | Vad | Aad | Mad | Cad | Had | Nad | Sad | Oad |
| 55.4 | 30.8 | 7.5 | 6.3 | 68.4 | 5.4 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 11.0 |
表1 煤的工业分析和元素分析 (%)
Tab. 1 Proximate and ultimate analysis of coal
| 工业分析 | 元素分析 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCad | Vad | Aad | Mad | Cad | Had | Nad | Sad | Oad |
| 55.4 | 30.8 | 7.5 | 6.3 | 68.4 | 5.4 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 11.0 |
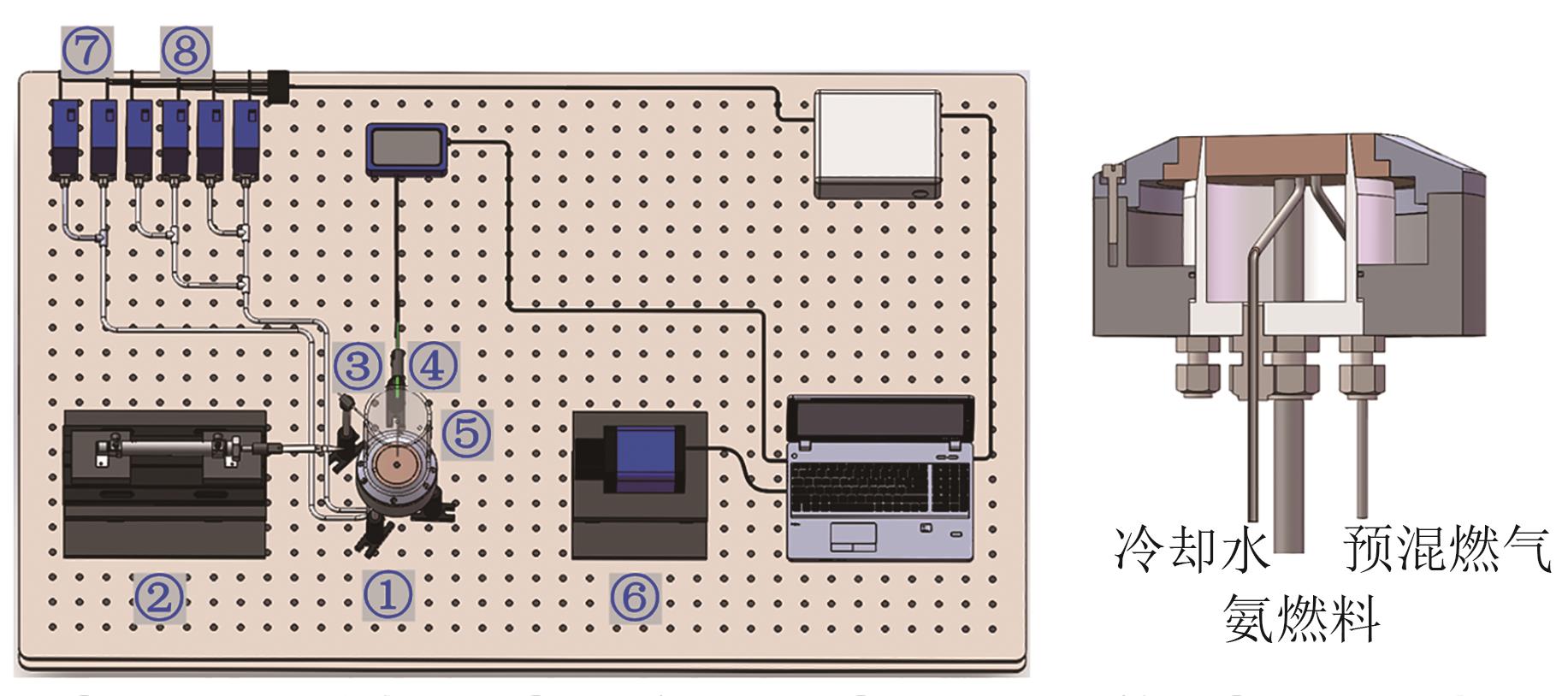
图1 燃烧实验系统示意图①—McKenna燃烧器;②—热泳取样;③—石英取样管;④—细丝热电偶;⑤—石英罩;⑥—相机;⑦—中心燃料管给气(NH3/Ar、N2);⑧—预混燃气(N2、O2、CO、CH4)。
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of combustion experimental system
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 过量空气系数 | 1.15 |
| CO流量/(L/min) | 1.17 |
| CH4流量/(L/min) | 0.43 |
| O2流量/(L/min) | 1.65 |
| N2流量/(L/min) | 8.00 |
| 总流量/(L/min) | 11.25 |
表2 预混气态燃料流参数设置 (fuel flow)
Tab. 2 Parameter setting of premixed gaseous
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 过量空气系数 | 1.15 |
| CO流量/(L/min) | 1.17 |
| CH4流量/(L/min) | 0.43 |
| O2流量/(L/min) | 1.65 |
| N2流量/(L/min) | 8.00 |
| 总流量/(L/min) | 11.25 |
| 参数 | 无氨 | 低掺氨 | 高掺氨 |
|---|---|---|---|
| NH3体积分数/% | 0 | 25 | 50 |
| NH3流量/(L/min) | 0 | 0.05 | 0.10 |
| N2流量/(L/min) | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0 |
| Ar流量/(L/min) | 0 | 0.05 | 0.10 |
| 总流量/(L/min) | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
表3 携氨气流参数设置 (gas flow)
Tab. 3 Parameter setting of ammonia carrying
| 参数 | 无氨 | 低掺氨 | 高掺氨 |
|---|---|---|---|
| NH3体积分数/% | 0 | 25 | 50 |
| NH3流量/(L/min) | 0 | 0.05 | 0.10 |
| N2流量/(L/min) | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0 |
| Ar流量/(L/min) | 0 | 0.05 | 0.10 |
| 总流量/(L/min) | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| 1 | TONG D, ZHANG Q, LIU F,et al .Current emissions and future mitigation pathways of coal-fired power plants in China from 2010 to 2030[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2018,52(21):12905-12914. |
| 2 | 赵春生,杨君君,王婧,等 .燃煤发电行业低碳发展路径研究[J].发电技术,2021,42(5):547-553. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.21054 |
| ZHAO C S, YANG J J, WANG J,et al .Research on low-carbon development path of coal-fired power industry[J].Power Generation Technology,2021,. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.21054 | |
| 42(5):547-553. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.21054 | |
| 3 | 姜红丽,刘羽茜,冯一铭,等 .碳达峰、碳中和背景下“十四五”时期发电技术趋势分析[J].发电技术,2022,43(1):54-64. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.21030 |
| JIANG H L, LIU Y X, FENG Y M,et al .Analysis of power generation technology trend in 14th Five-Year Plan under the background of carbon peak and carbon neutrality[J].Power Generation Technology,2022,43(1):54-64. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.21030 | |
| 4 | 冯伟忠,李励 .“双碳”目标下煤电机组低碳、零碳和负碳化转型发展路径研究与实践[J].发电技术,2022,43(3):452-461. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.22061 |
| FENG W Z, LI L .Research and practice on development path of low-carbon, zero-carbon and negative carbon transformation of coal-fired power units under “double carbon”targets[J].Power Generation Technology,2022,43(3):452-461. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.22061 | |
| 5 | 徐静颖,朱鸿玮,徐义书,等 .燃煤电站锅炉氨燃烧研究进展及展望[J].华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(7):55-65. |
| XU J Y, ZHU H W, XU Y S,et al .Research progress and prospect of ammonia cofiring in utility coalfired boiler[J].Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2022,50(7):55-65. | |
| 6 | CHAI W S, BAO Y, JIN P,et al .A review on ammonia,ammonia-hydrogen and ammonia-methane fuels[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2021,147:111254. |
| 7 | VALERA-MEDINA A, XIAO H, OWEN-JONES M,et al .Ammonia for power[J].Progress in Energy and Combustion Science,2018,69:63-102. |
| 8 | KOBAYASHI H, HAYAKAWA A, SOMARATHNE K D K A,et al .Science and technology of ammonia combustion[J].Proceedings of the Combustion Institute,2019,37(1):109-133. |
| 9 | 高虎,刘凡,李海 .碳中和目标下氨燃料的机遇、挑战及应用前景[J].发电技术,2022,43(3):462-467. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.22059 |
| GAO H, LIU F, LI H .Opportunities,Challenges and Application Prospects of Ammonia Fuel Under the Target of Carbon Neutrality[J].Power Generation Technology,2022,43(3):462-467. doi:10.12096/j.2096-4528.pgt.22059 | |
| 10 | 周上坤,杨文俊,谭厚章,等 .氨燃烧研究进展[J].中国电机工程学报,2021,41(12):4164-4182. doi:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.201476 |
| ZHOU S K, YANG W J, TAN H Z,et al .Research progress of ammonia combustion[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2021,41(12):4164-4182. doi:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.201476 | |
| 11 | 高正平,涂安琪,李天新,等 .面向零碳电力的氨燃烧技术研究进展[J].洁净煤技术,2022,28(3):173-184. |
| GAO Z P, TU A Q, LI T X,et al .Recent advances on ammonia combustion technology for zero-carbon power[J].Clean Coal Technology,2022,28(3):173-184. | |
| 12 | 王智化,余作超,陈晨霖,等 .新型零碳氨燃料的燃烧特性研究进展[J].华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(7):24-40. |
| WANG Z H, YU Z C, CHEN C L,et al .Research progress on combustion characteristics of zero-carbon ammonia fuel[J].Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2022,50(7):24-40. | |
| 13 | TAMURA M, GOTOU T, ISHII H,et al .Experimental investigation of ammonia combustion in a bench scale 1.2 MW-thermal pulverised coal firing furnace[J].Applied Energy,2020,277:115580. |
| 14 | 牛涛,张文振,刘欣,等 .燃煤锅炉氨煤混合燃烧工业尺度试验研究[J].洁净煤技术,2022,28(3):193-200. |
| NIU T, ZHANG W Z, LIU X,et al .Industrial-scale experimental investigation of ammonia-coal cofiring in coal-fired boiler[J].Clean Coal Technology,2022,28(3):193-200. | |
| 15 | 马仑,方庆艳,张成,等 .深度空气分级下煤粉耦合氨燃烧及NO生成特性数值模拟研究[J/OL].洁净煤技术:1-13[2022-03-28].DOI:10.13226/j.issn.1006-6772.CC21101401. |
| MA L, FANG Q Y, ZHANG C,et al .Numerical study on combustion and NO formation characteristics of pulverized coal co-firing with ammonia in a deep-air staging condition[J/OL].Clean Coal Technology:1-13[2022-03-28].DOI:10.13226/j.issn.1006-6772.CC21101401. | |
| 16 | MURAI R, OMORI R, KANO R,et al .The radiative characteristics of NH3/N2/O2 non-premixed flame on a 10 kW test furnace[J].Energy Procedia,2017,120:325-332. |
| 17 | HADI K, ICHIMURA R, HASHIMOTO G,et al .Effect of fuel ratio of coal on the turbulent flame speed of ammonia/coal particle cloud co-combustion at atmospheric pressure[J].Proceedings of the Combustion Institute,2021,38(3):4131-4139. |
| 18 | XIA Y, HADI K, HASHIMOTO G,et al .Effect of ammonia/oxygen/nitrogen equivalence ratio on spherical turbulent flame propagation of pulverized coal/ammonia co-combustion[J].Proceedings of the Combustion Institute,2021,38(3):4043-4052. |
| 19 | 熊刚,李水清,宋蔷,等 .燃煤碳烟生成的实验研究[J].工程热物理学报,2011,32(11):1965-1968. |
| XIONG G, LI S Q, SONG Q,et al .Experimental study of coot formation in coal combustion process[J].Clean Coal Technology,2011,32(11):1965-1968. | |
| 20 | XU Y, ZHU J, LIU X,et al .Insight into soot formed in coal combustion flame:evolution of physiochemical structure,oxidation reactivity[J].Fuel,2022,312:122948. |
| 21 | CHENG X, LI Y, XU Y,et al .Study of effects of ammonia addition on soot formation characteristics in n-heptane co-flow laminar diffusion flames[J].Combustion and Flame,2022,235:111683. |
| 22 | LIU Y, CHENG X, LI Y,et al .Effects of ammonia addition on soot formation in ethylene laminar diffusion flames[J].Fuel,2021,292:120416. |
| [1] | 袁鑫, 刘骏, 陈衡, 潘佩媛, 徐钢, 王修彦. 碳捕集技术应用对燃煤机组调峰能力的影响[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 373-381. |
| [2] | 袁家海, 胡玥琳, 张健. 基于改进三阶段松弛测量-数据包络模型的火电上市公司碳排放效率评估研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 458-467. |
| [3] | 张宏伟, 张永生, 汪涛, 王家伟. 电厂燃煤飞灰固化脱硫污泥重金属铅特性研究[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(3): 527-534. |
| [4] | 龚思琦, 云再鹏, 许明, 敖乐, 李初福, 黄凯, 孙晨. 基于三元催化剂的固体氧化物燃料电池尾气催化燃烧数值模拟[J]. 发电技术, 2024, 45(2): 331-340. |
| [5] | 汪丽, 张欢, 叶舣, 赵兴雷. N-氨乙基哌嗪与甘氨酸钠CO2吸收剂配方研究[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(5): 674-684. |
| [6] | 刘含笑. 双碳背景下电除尘器的节能减碳分析[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(5): 738-744. |
| [7] | 罗志刚, 何成兵, 孟浩然, 刘国栋, 沈鹏, 张军, 张浩亮. 燃煤电厂SCR脱硝系统精准控氨优化方法研究[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(4): 525-533. |
| [8] | 高志刚, 陈福春, 王家伟, 汪涛, 张永生. 600 MW褐煤机组烟气汞排放及灰特性研究[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(4): 543-549. |
| [9] | 尹桃柱, 张永生, 汪涛, 王家伟. 硫掺杂多孔碳材料的制备及其对脱硫废水中重金属的电吸附性能研究[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(3): 382-391. |
| [10] | 吉攀. 燃煤电厂烟气中氨脱除及分布机理研究[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(3): 392-398. |
| [11] | 刘含笑, 郭高飞. 袋式除尘器脱Hg特性研究[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(2): 193-200. |
| [12] | 陈思勤, 朱伊囡, 李晓辰, 王学海. 基于双层规划的碳减排配煤优化方法研究[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(2): 155-162. |
| [13] | 刘含笑, 郭高飞, 陈招妹. 超低排放机组湿式电除尘器多污染物减排及能效测试研究[J]. 发电技术, 2023, 44(1): 94-99. |
| [14] | 董瑞, 高林, 何松, 杨东泰. CCUS技术对我国电力行业低碳转型的意义与挑战[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43(4): 523-532. |
| [15] | 高虎, 刘凡, 李海. 碳中和目标下氨燃料的机遇、挑战及应用前景[J]. 发电技术, 2022, 43(3): 462-467. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||