0 引言
1 EDEM数值计算理论基础
1.1 离散元素法与EDEM软件基本原理
1.1.1 离散元素法基本原理
1.1.2 EDEM软件基本原理
1.2 EDEM模型建立
1.2.1 设置全局变量
表2 材料接触属性
Tab. 2
| 接触材料 | 恢复系数 | 静摩擦因数 | 动摩擦因数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 煤-煤 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.05 |
| 煤-钢 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.05 |
1.2.2 定义颗粒体
在设置完基础参数后,建立颗粒模型。由于实际生活中煤颗粒的形状多变,在软件中建立模型十分繁琐。为了简化计算,采用球形颗粒模拟煤散料颗粒。原型颗粒是由1个或多个球面来定义颗粒的几何特征。本模型把煤颗粒近似为球体,添加多个球体组成新形态,之后可以根据第一步中所设置的颗粒密度计算出各颗粒的质量、体积以及惯性矩,最后在该基础模型的外部生成大的轮廓后,通过向轮廓模型中添加颗粒,使颗粒充满该模型内部,这样通过EDEM软件自身的计算功能可以得出相关的数据与参数。
1.2.3 定义几何体
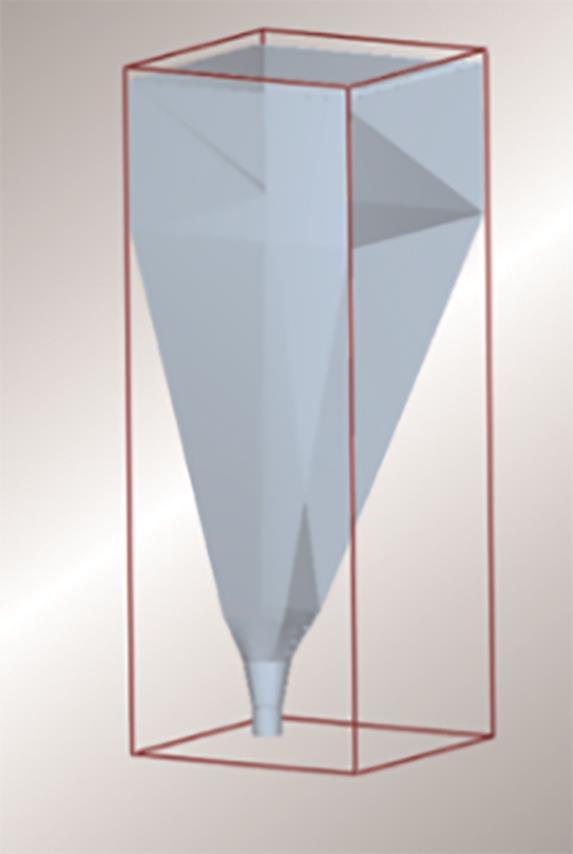
图1
图1
煤仓三维模型示意图
Fig. 1
Schematic diagram of three-dimensional model of coal bunker
1.2.4 创建颗粒工厂
颗粒工厂动态产生颗粒的计数方式有无限个颗粒、颗粒总数量和颗粒总质量3种。本文设置生成的颗粒粒径呈正态分布,半径均值为50 mm。
1.2.5 仿真计算
设定时间步长为14.174 2%,仿真总时间为8 s,其数据每0.01 s输出1次。仿真计算是将仿真区域划分为许多小网格进行的,定义仿真网格尺寸为3倍的颗粒半径,通过输入具体数据为接下来的仿真计算进行铺垫,方便进行数据的计算与提取。
2 结果及堵塞机理分析
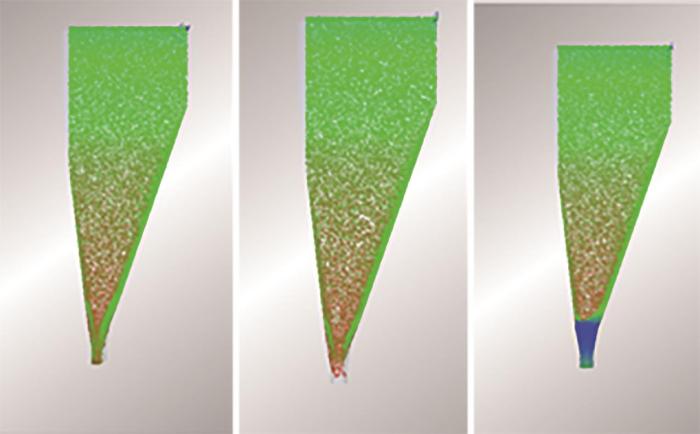
通过建立模型、数据输入对其进行仿真计算后,得到煤在流动中的相关规律。如图2所示,仓体内部颗粒的流动状态大致分为2种:一种表现出整体流动状态;另一种表现为中心流动状态。整体流主要体现在下落的过程中,仓内无静止的颗粒,所有煤粒同时向下移动,颗粒与仓壁间也存在相对运动,越靠近仓口的颗粒越早流出,因此,这种整体流动方式的优点就是没有颗粒在煤仓内停留过长时间,但是这样流动容易引起壁面的压力值急剧增加,对仓壁磨损较严重。
图2
图3
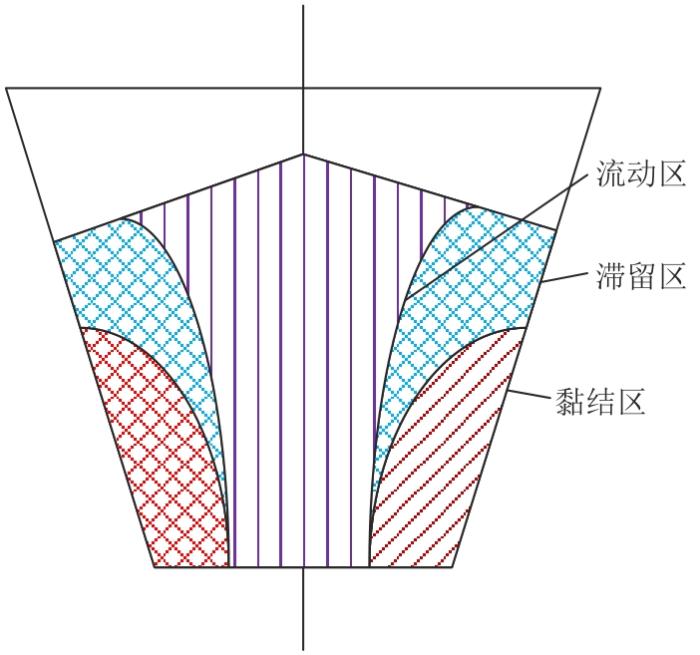
1)细粒物料表现出黏结性,并容易形成黏结性料拱,所以可以利用流动函数来表示其流动性能。通过数值模拟分析,当流动函数(flow function,FF)<2时,颗粒散料表现为不易流动;当2<FF<4时为散料,主要体现出黏性的影响;当FF>10时散料的黏性影响较小,表现出自由流动。电厂中的原煤颗粒较细碎,在模拟过程中设置粒径也相对较小,所以当小尺寸颗粒增多时,会使颗粒与颗粒之间的流动性能降低,而靠近仓体表面的一侧更容易发生黏结,如图4所示,所以这也是形成结拱的主要原因。
图4
图5
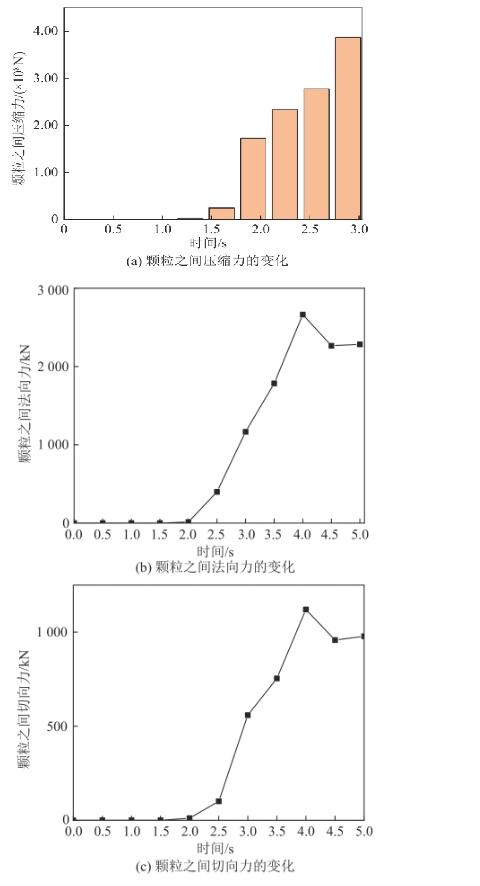
图5
颗粒流动过程中颗粒之间力的变化
Fig. 5
Variation of force between particles during particle flow
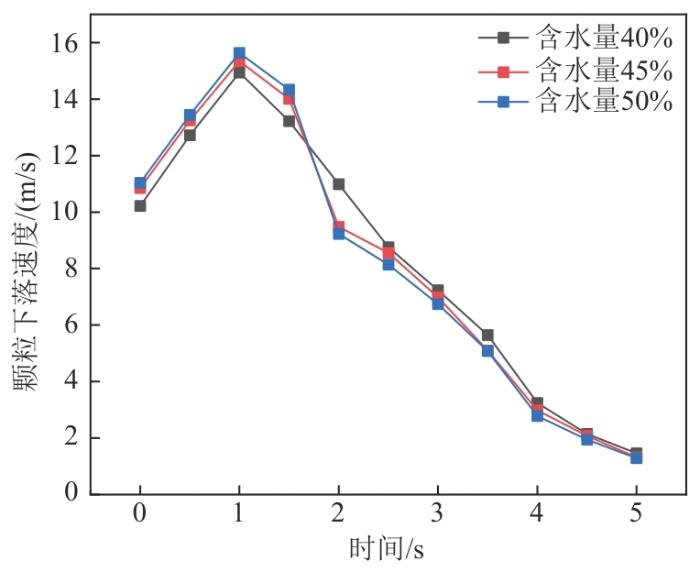
3)相比于普通煤来说,本文所研究煤种为高水分褐煤,通过对实际的原煤进行水分测定,原煤含水量约为46.7%,所以为了方便研究,将含水量设置为40%、45%、50%三个组别进行对照分析,其余条件均不变。如图6所示,通过数值模拟可以看出,在刚进行下落时水分含量较高的颗粒相对速度较快,这是由于水分含量高的颗粒质量较大,在刚开始下落时还未产生大面积接触挤压。随后在颗粒逐渐下落发生聚集后,会有一个明显降速的过程,这主要是由于颗粒之间发生挤压产生的摩擦以及与壁面的摩擦导致降速,但是由于水分对其黏结性的影响迫使降速的效果不一样,所以,在水分含量较高的情况下,其速度减慢的程度也相对较大,也会使颗粒自身重力加大。水分对流动状态的影响主要体现在:1)含水量的提高导致颗粒黏结性发生变化;2)含水量较高的颗粒自身质量也很大,导致压力增大。因此,含水量既可直接导致堵塞,也可以间接导致堵塞。
图6
图6
不同含水量颗粒下落中速度的变化
Fig. 6
Changes in velocity of particles falling with different water contents
3 结论
根据离散元法,利用EDEM软件,通过构建煤仓的3D模型对煤仓中煤颗粒流动性进行研究,得出以下结论:
1)由于颗粒粒径过小或者过大,导致在仓体流动过程中其自身颗粒与颗粒之间发生相对作用,产生结拱现象进而影响流动。
2)颗粒在仓体流动过程中,颗粒间的压缩力随时间增加,这也是堵塞的重要原因之一。
3)不同含水量对煤黏附性影响较大,加上含水量高也会使煤的自身重力加大,所以在高水分褐煤下落状态下极易发生堵塞现象。
参考文献
中心给料机在煤仓治堵中的应用与研究
[D].
Application and research of central feeder in coal bunker blocking
[D].
粉煤流动性及其影响因素探究
[D].
Study on the fluidity of pulverized coal and its influencing factors
[D].
Some factors influencing the fluidity of coal blends:particle size,blend ratio and inherent oxygen species
[J].
电厂原煤仓堵煤机理试验研究
[D].
Experimental study on coal blocking mechanism of raw coal bunker in power plant
[D] .
An empirical model for coal fluidity based on a macromolecular network pyrolysis model
[J].
基于离散元法的玉米种子建模及播种过程的仿真分析与试验研究
[D].
Modeling of corn seeds based on discrete element method and simulation analysis and experimental study of sowing process
[D].
岩石拉压实验的颗粒离散元模拟
[D].
Particle discrete element simulation of rock tensile and compressive experiment
[D].
颗粒离散元法工程应用的三大问题探讨
[J].
Discussion on three major problems in engineering application of particle discrete element method
[J].
煤灰及铁矿石熔融与流动特性实验研究
[D].
Experimental study on melting and flowing characteristics of coal ash and iron ore
[D].
下行床热解器中高温高通量半焦/煤流动-传热-反应过程数值计算研究
[D].
Numerical calculation of the flow-heat transfer-reaction process of high-temperature and high-flux semi-coke/coal in the down-bed pyrolyzer
[D].
Deciphering the differential influence of organic additives on coal fluidity development:a first-principles investigation
[J].
Investigators from JFE steel corporation release new data on metals research (addition effect of aromatic amines on coal fluidity and coke strength)
[J].
Recent studies from china university of mining and technology add new data to Geoscience Engineering (An analysis of the layered failure of coal:new insights into the flow process of outburst coal)
[J].
离散元软件EDEM在矿冶工程中的应用与研究
[J].
Application and research of edem in mining and metallurgy engineering
[J].
基于EDEM模拟振动参数对计量斗矿物粘附的影响
[J].
Simulation study on vibration parameters of metering bucket based on EDEM
[J].
基于EDEM软件的肥料调配装置关键部件参数优化与试验
[J].
Parameter optimization and test of key components of fertilizer mixing device based on EDEM software
[J].