0 引言
随着新型电力系统建设的不断推进,对火电机组调节支撑能力提出了更高要求,深度调峰等极端工况下的调频能力更需加强[1]。
近年来,大量学者对常规工况下火电机组调频建模问题开展深入研究。文献[2]创新性地提出了高压缸功率自然过调系数的概念,大大提高了再热式汽轮机仿真模型的精确度。文献[3]依据最小二乘法对机组实际调频数据进行辨识,进而分析了调频死区和不等率对机组一次调频能力的影响。文献[4]将汽轮机阀门流量特性、主汽压力等机组调频关键因素融入新模型,修正后的模型能更好地反映机组实际的一次调频功率响应特性。文献[5]为消除人为选取稳态值造成的调频建模误差,提出一种改进的群智能算法,解除了常规阶跃响应辨识要求初始与结束状态必须在稳态的限制。文献[6]建立了考虑流动与传热的锅炉-汽机耦合调频模型,并验证了耦合模型的正确性。文献[7]对超超临界百万机组深度调峰进行相关的试验研究,为其他机组深度调峰提供了参考。文献[8]对某超临界流化床机组进行控制策略优化,保证机组深度调峰运行的稳定性。文献[9]分析机组汽水侧蓄热系数随负荷变化所呈现的规律,提出汽水侧蓄热系数的定量计算方法。
随着火电机组深度调峰工况运行时间增长,机组炉侧参数不稳定性持续增加,加深了炉侧蓄热系数等相关参数对机组调频能力的影响,若套用现有常规高度简化的调频模型,仿真效果将不尽如人意[10]。本文考虑机组在深度调峰工况下相关炉侧参数的影响,按照机组实际协调方式控制策略,搭建了深度调峰工况下的精细化一次调频模型,并对炉侧蒸发段及过热段蓄热系数对机组一次调频能力的影响进行定量分析,有利于更准确地分析、预测机组的一次调频能力。
1 深度调峰工况一次调频精细化模型搭建
1.1 模型概述
图1
图1
深度调峰工况下一次调频精细化模型示意图
Fig. 1
Refined model of primary frequency regulation under deep regulation condition
1.2 锅炉制粉系统模型
由于锅炉制粉系统需要经过原煤的长距离输送、研磨、分离、一次风机输送等环节,导致系统延迟性较大,可将制粉系统简化为一阶惯性纯延迟环节[14]:
式中:
1.3 锅炉汽水系统模型
工程上常将锅炉给水在水冷壁的加热过程分解成多个微小的加热扰动过程,根据质量守恒、动量守恒、能量守恒等定律,锅炉蒸发段蓄热系数表示为
式中:
若忽略各过热器受热面减温水及蒸汽少量泄漏,根据各过热器受热面管内工质质量守恒、动量守恒及能量守恒定律得出:
式中:
图2
图3
图4
为表征仿真模型的精确度大小,引进系数
式中:
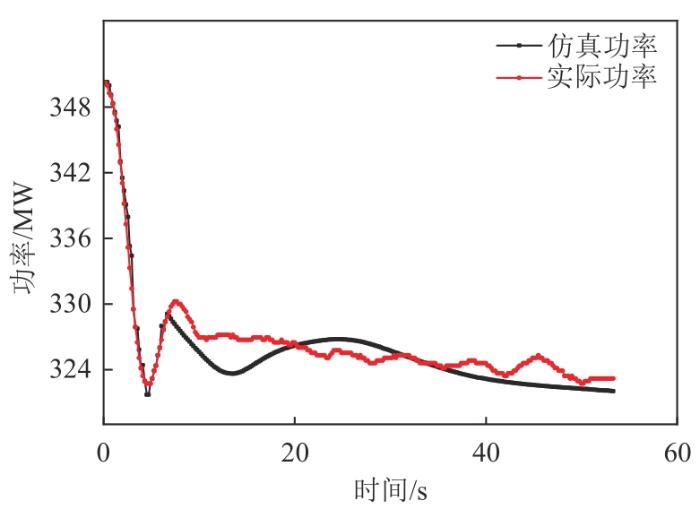
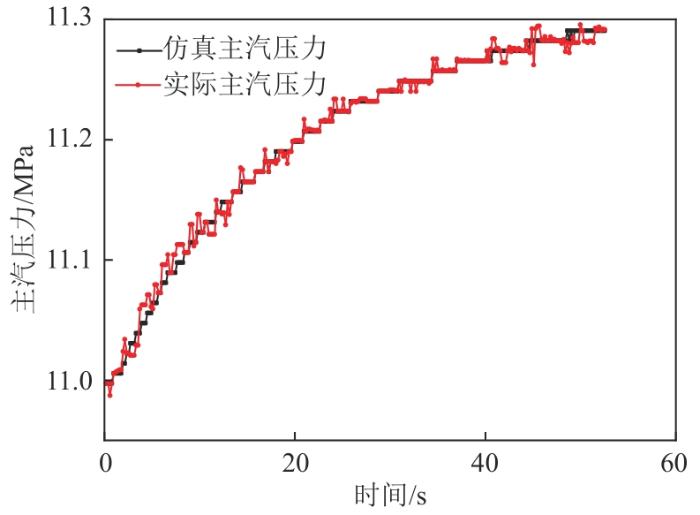
机组在35%
表1
35%
Tab. 1
| 特征参数 | 扰动转差/(r/min) | |
|---|---|---|
机组功率 主汽压力 | 6 | 0.898 |
| 6 | 0.973 |
2 炉侧蓄热系数对一次调频的影响
锅炉蓄热系数可分为蒸发段蓄热系数和过热段蓄热系数2部分,每部分又包含汽水蓄热和金属蓄热。在不同的压力及负荷下,锅炉的蓄热系数变化较大,尤其是在机组低负荷的情况下,锅炉的蓄热系数更加不稳定。随着压力的升高,金属蓄热系数减小,汽水蓄热系数变化较小,总锅炉蓄热系数会减小[16]。
为分析深度调峰工况下蓄热系数(本文所描述的蓄热系数均指总蓄热系数)对机组一次调频能力的影响,选择35%
2.1 蒸发段蓄热系数对一次调频的影响
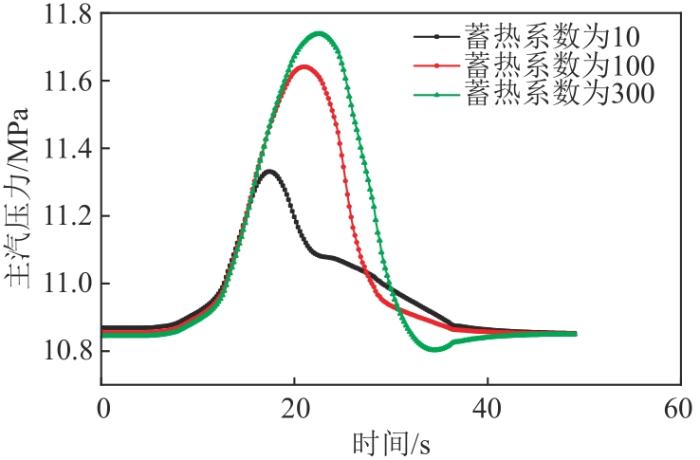
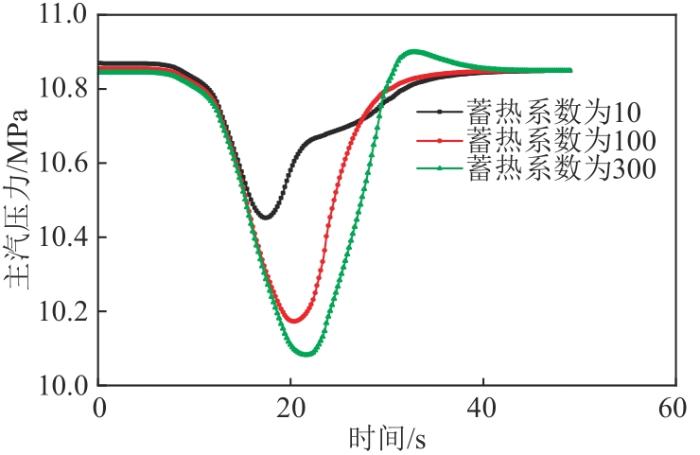
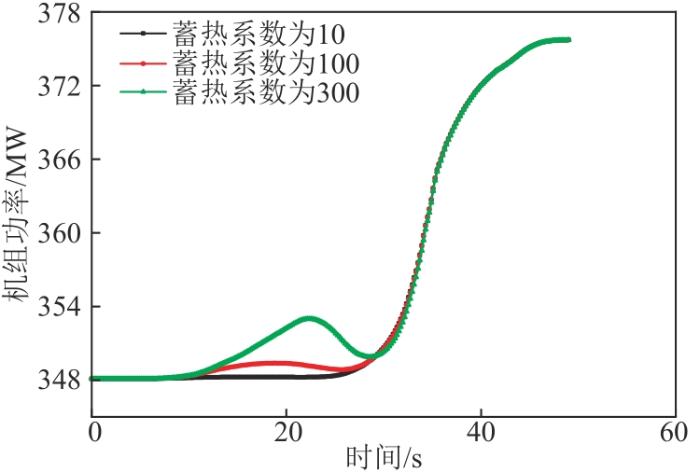
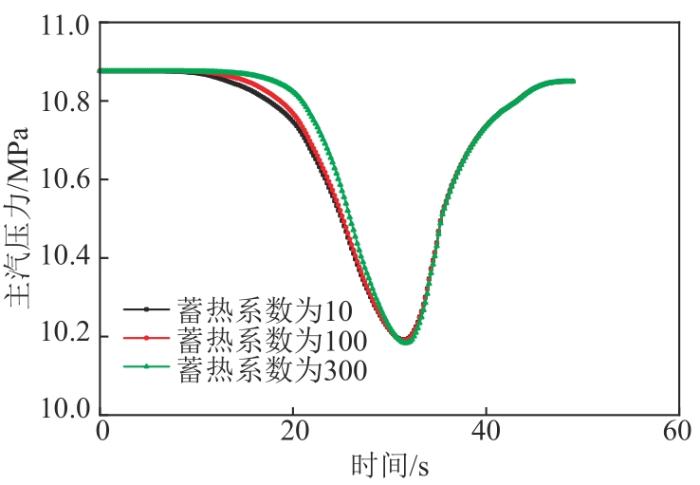
选用文献[13]中的仿真参数作为参考,以蒸发段蓄热系数100为基础,另选择2个对照参数10、300进行仿真实验。在仿真程序加入6 r/min增、减负荷2个方向的扰动,观察机组功率、主汽压力2个特征参数的变化规律。6 r/min减、增负荷2个方向的机组功率变化规律分别如图5、6所示,可以看出,随着蒸发段蓄热系数增加,机组负荷响应时间增长,即蒸发段蓄热系数越大,越不利于机组一次调频。由于汽包炉蒸发段蓄热系数一般比同等容量的直流炉大,进而导致汽包炉的负荷响应比直流炉响应慢。另外,由于一次调频要求机组在短时间内快速动作负荷,同等条件下直流炉在一次调频方面的表现更为出色。图7、8分别为6 r/min增、减负荷扰动下主汽压力变化规律图。可以看出,由于蒸发段蓄热系数不同,在稳定工况且同等数量的燃料及给水情况下,主汽压力会随着蓄热系数的减小而略微升高[17]。但在扰动下,蓄热系数对压力的响应时间基本相同。按常理假设过热蓄热系数相同,蒸发段蓄热系数越大,通过锅炉主控对主汽压力进行调节的惯性延迟时间就会越长,最终会造成机组主汽压力变化幅度增大,与仿真结果相似[18]。
图5
图5
不同蒸发段蓄热系数下6 r/min减负荷方向机组功率变化图
Fig. 5
Power variation diagram of the unit in the direction of 6 r/min load reduction under different evaporation section heat storage coefficient
图6
图6
不同蒸发段蓄热系数下6 r/min增负荷方向机组功率变化图
Fig. 6
Power variation diagram of the unit in the direction of 6 r/min load increase under different evaporation section heat storage coefficient
图7
图7
不同蒸发段蓄热系数下6 r/min减负荷方向主汽压力变化图
Fig. 7
Pressure variation diagram of the unit in the direction of 6 r/min load reduction under different evaporation section heat storage coefficient
图8
图8
不同蒸发段蓄热系数下6 r/min增负荷方向主汽压力变化图
Fig. 8
Pressure variation diagram of the unit in the direction of 6 r/min load increase under different evaporation section heat storage coefficient
2.2 过热段蓄热系数对一次调频的影响
选用文献[13]中的仿真参数作为参考,以过热段蓄热系数10为基础,另选择2个对照参数100、300进行仿真实验。在仿真程序中加入6 r/min增、减负荷2个方向的扰动,以此观察机组的功率、主汽压力2个特征参数的变化规律。
图9
图9
不同过热段蓄热系数下6 r/min减负荷方向机组功率变化图
Fig. 9
Power variation diagram of the unit in the direction of 6 r/min load reduction under different heat storage coefficient of superheat section
图10
图10
不同过热段蓄热系数下6 r/min减负荷方向机组主汽压力变化图
Fig. 10
Pressure variation diagram of the unit in the direction of 6 r/min load reduction under different heat storage coefficient of superheat section
图11
图11
不同过热段蓄热系数下6 r/min增负荷方向机组功率变化图
Fig. 11
Power variation diagram of the unit in the direction of 6 r/min load increase under different heat storage coefficient of superheat section
图12
图12
不同过热段蓄热系数下6 r/min增负荷方向主汽压力变化图
Fig. 12
Pressure variation diagram of the unit in the direction of 6 r/min load increase under different heat storage coefficient of superheat section
3 结论
以暂态稳定程序PSD-BPA中的典型模型为基础,搭建了适用于火电深度调峰工况下的精细化仿真模型,并以此模型为基础,定性研究了蒸发段、过热段蓄热系数对机组一次调频的影响,得出以下结论:
1)通过对某额定功率为1 000 MW的机组在35%
2)随着蒸发段蓄热系数增大,机组负荷响应时间增加,即蒸发段蓄热系数越小,越利于机组一次调频的快速动作。
3)随着过热段蓄热系数增大,机组调频动作时响应时间缩短,即过热段蓄热系数越大,越利于机组一次调频动作。
4)通过减少机组蒸发段受热面积、增大过热段受热面积等改变蓄热系数,可提高火电机组的一次调频能力。
参考文献
电力市场环境下火电机组调频性能提升研究
[J].
Research on frequency modulation performance improvement of thermal power units in the context of power market
[J].
用于电网稳定性计算的再热凝汽式汽轮机数学模型
[J].
A mathematical model of rehear turbine for power grid stability calculation
[J].
超临界机组及其一次调频控制系统的辨识与仿真
[J].
Identification and simulation of a supercritical unit and its primary frequency modulation and control system
[J].
火电机组一次调频功率响应特性精细化建模
[J].
Refined modeling for power response characteristic of thermal power unit under primary frequency control
[J].
基于改进群优化算法的深度调峰机组一次调频建模
[J].
Primary frequency regulation modeling of deep peak regulation unit based on improved group optimization algorithm
[J].
一次调频中的锅炉建模与参数在线确定
[J].
Boiler modeling and online parameters identification for primary frequency regulation
[J].
超超临界百万机组20%负荷深度调峰运行试验研究
[J].
20% load deep peak shaving operation test of ultra-supercritical million units
[J].
新型电力系统下基于深度调峰的火电机组控制技术研究
[J].
Research on control technology of thermal power units based on deep peak regulation in new power systems
[J].
300 MW深度调峰循环流化床机组负荷响应特性研究
[J].
Study on load response characteristics of a 300 MW circulating fluidized bed unit with deep peak regulation
[J].
大规模新能源并网下火电机组深度调峰优化调度
[J].
Optimal scheduling of deep peak regulation for thermal power units in power grid with large-scale new energy
[J].
火电机组一次调频技术研究进展综述
[J].
Review on the research progress of primary frequency modulation technology for thermal power units
[J].
基于最小二乘支持向量机的火电厂烟气含氧量预测模型优化研究
[J].
Study on optimization of prediction model of flue gas oxygen content in thermal power plant based on least squares support vector machine
[J].
考虑主蒸汽压力的燃煤机组调速模型的分析与改进
[J].
Analysis and improvement of speed governor model considering the main steam pressure influences
[J].
飞轮储能辅助燃煤机组调频动态过程仿真研究
[J].
Simulation study on frequency modulation process of coal burning plants with auxiliary of flywheel energy storage
[J].
660 MW超临界火电机组汽轮机及其调速系统精细化模型研究和应用
[J].
Research and application of refined model for 660 MW supercritical thermal power unit steam turbine and its governing system
[J].
超超临界直流锅炉蓄热能力的定量分析
[J].
Quantitative analysis on heat storage capacity of ultra-supercritical once-through boilers
[J].
基于蓄热水箱温度可行域模糊确定的电锅炉优化调度方法
[J].
Optimal scheduling method of electric boiler based on fuzzy determination of temperature feasible region of hot water storage tank
[J].
含储热型热电联产机组的电力系统源荷联合优化调峰方法
[J].
A source-load joint optimization peak regulation method of power system with heat storage combined heat and power units
[J].