0 引言
对于燃煤机组,主汽温和再热汽温是评价锅炉运行安全性和经济性的重要指标之一。为了实现火电行业节能减排的目标,燃煤机组逐渐向着高参数、大容量的方向发展,提升主汽温和再热汽温可以有效提高机组的循环效率。然而,随着我国能源结构的转型,新能源的大规模并网使常规燃煤机组需承担越来越多的调峰、调频任务,超温爆管等现象普遍成为制约超(超)临界机组提升变负荷速率的核心瓶颈。
减温水系统通常是针对汽温异常或事故情况设计的,但在机组快速调峰、调频的响应过程中,减温水控制逐渐被迫成为动态过程锅炉壁温和蒸汽温度控制的常用手段。
由于锅炉汽温具有非线性、大惯性和滞后性等特性,使得减温水控制面临巨大挑战,以过热汽温为例,采用常规的串级控制器往往达不到较好的控制效果。目前,国内外学者针对汽温大惯性和大延迟系统控制开展了大量研究,并提出许多先进的控制策略。现代先进控制算法中,模型预测控制(model prediction control,MPC)[1-2]和Smith预估控制[3-4]等常被用于改进汽温控制。模型预测、神经网络等高级算法对模型误差比较敏感,尽管对减温水控制及其目标系统进行建模的研究较多[5-10],但由于实际系统具有较强的非线性、测量不确定性和时变特性,使实际应用过程难以解决模型失配问题。此外,逆神经控制器[7]和回归支持向量机[8]也用于减温水控制的研究,然而这些方法大多用于仿真环境,难以长期保持实际效果,限制了其在实际控制中的应用。本文在前述研究基础上,从喷水减温对象系统工艺特点出发,提出局部Smith预估校正汽温控制策略,规避了算法的模型失配风险同时,有效改善了控制性能。
1 减温水系统非线性特性分析
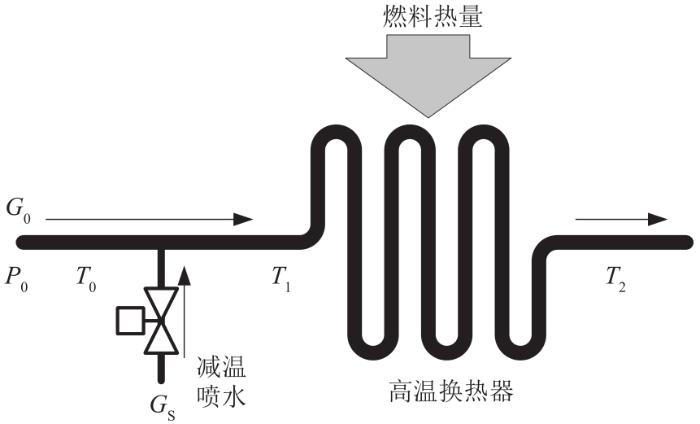
过热汽温一般采用串级控制,再热汽温一般采用单回路控制,均设有减温喷水装置。换热器的减温水结构示意图如图1所示。
图1
换热器出口汽温目标设定值为
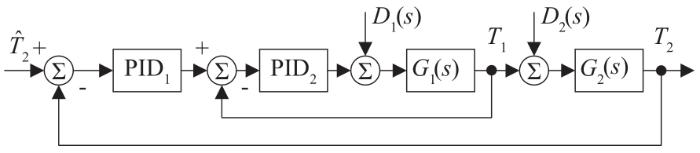
图2
图2
汽温控制系统串级PID控制模型
Fig. 2
Cascade PID control model of steam temperature control system
流动与换热过程使减温喷水控制成为典型的大惯性与大延迟系统,各种先进控制方法被用来尝试代替传统的PID控制。
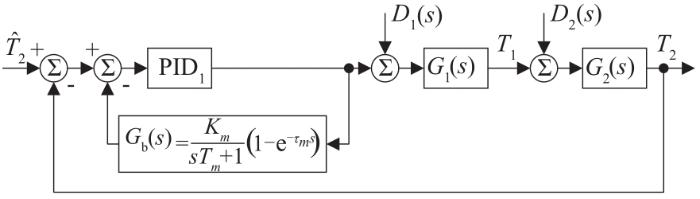
图3
该校正作用的核心在于利用系统近似的响应模型
实践经验表明,减温水阀流量非线性和喷水流量测量不确定性是制约模型预测控制等技术应用的关键问题。一方面,减温水阀的实际运行特性随机组运行工况的变化而变化;另一方面,对于大多数机组,小开度、频繁开关是阀门的常态,这会加速阀门发生气蚀等缺陷,从而改变阀门特性。同时,减温水流量的测量往往偏离孔板流量计的测量线性区域。因此,减温水流量作为一个关键参数,并不能满足精确控制的要求,在建模精确度和模型应用上都存在较大偏差。
综上所述,受减温水阀门的非线性、测量不确定性和时变特性的影响,其流量特性很难建立精确的模型用于模型预测控制方法,这就是Smith预估等依赖模型精度的控制方法和人工神经网络控制难以直接用于减温喷水控制的主要原因之一。
2 基于局部Simith预估的混合控制模型
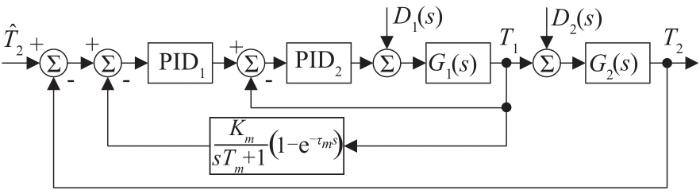
本文提出了一种基于串级和局部Smith预估校正的混合控制模型,如图4所示。为了保证模型预测控制的实际应用、提高模型精度,将减温水与高温蒸气混合过程
图4
在具有可靠性的串级控制的基础上,通过混合后温度
减温水与高温蒸气混合后流经过热器/再热器进行换热,这一换热过程主要由惯性环节和延迟环节组成。忽略锅炉稳态工况下传热能力的变化,混合后蒸汽温度
构建局部Smith预估动态模型为
式中:
此外,局部Smith预估回路可以与串级PID控制器或者一些其他控制器分开使用。
3 参数辨识与模型验证
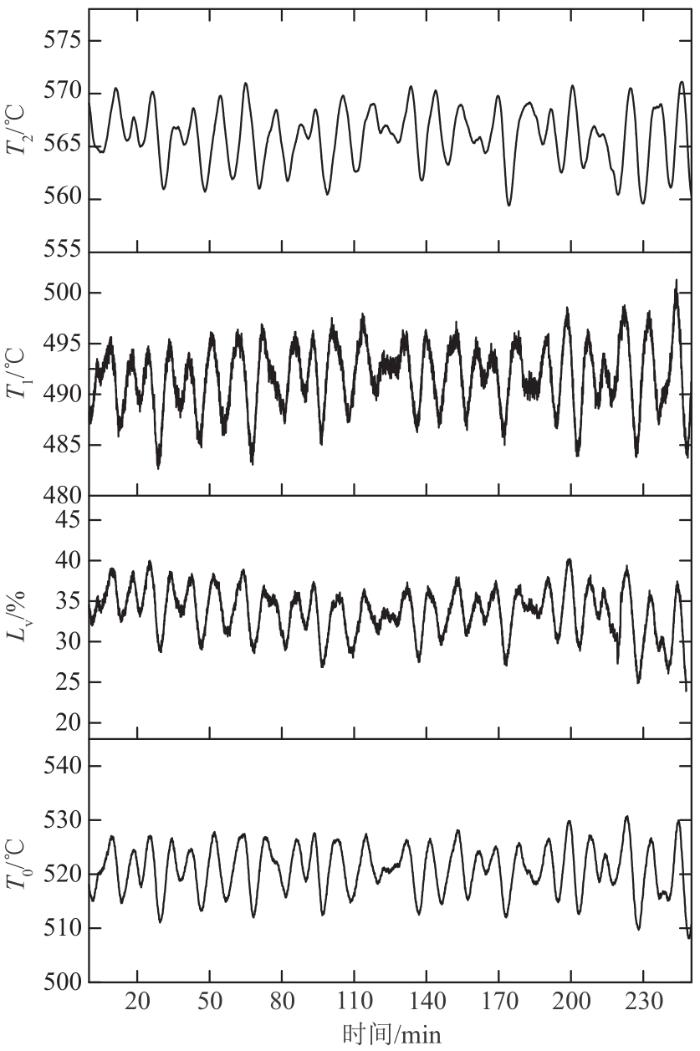
针对某超临界燃煤直流锅炉高温过热器进行了试验研究,在锅炉状态基本稳定情况下,记录4 h左右的数据,如图5所示。
图5
图5
某超临界燃煤直流锅炉过热器的试验数据
Fig. 5
Test data of a superheater in a supercritical coal-fired once-through boiler
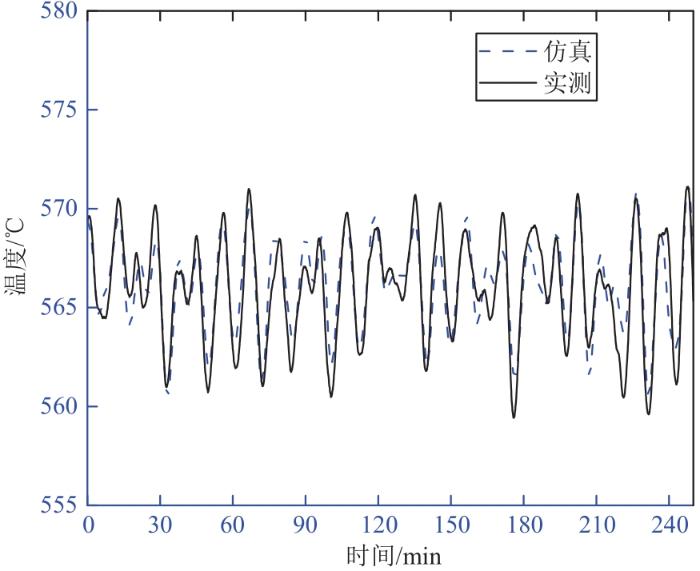
将辨识后的局部Smith预估模型的仿真结果与记录数据进行对比,如图6所示。通过对仿真曲线与4 h左右的实测数据进行比较,可以看出二者达到了良好的一致性,即使在某段时间内存在一定的偏差,曲线的波动趋势仍能与试验数据很好地吻合,有助于控制器准确地预估换热器出口温度。
图6
图6
仿真结果和测量数据的比较
Fig. 6
Comparison of estimated simulation results and test data
4 混合控制模型应用
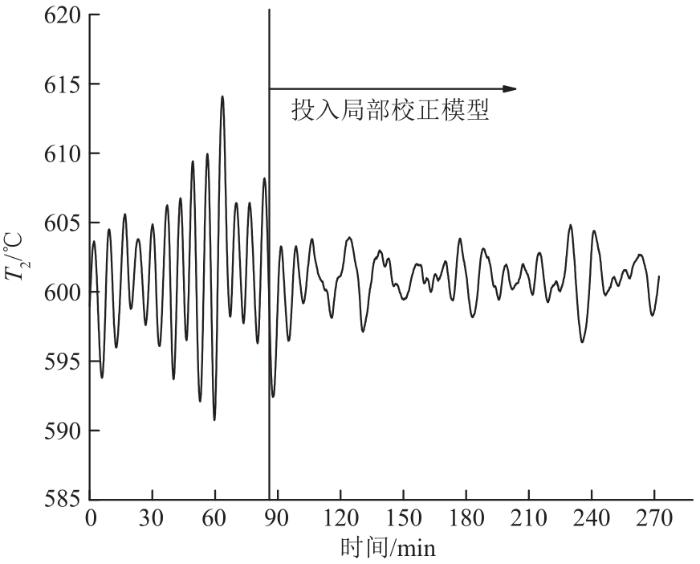
本文设计的混合控制模型在1 000 MW超超临界锅炉减温水控制中进行实际应用,与经典的串级控制相比,结合局部Smith预估校正可以为减温水控制获得更好的效果。图7显示了其在1 000 MW超超临界锅炉上的应用效果,与原串级PID控制相比,本文提出的基于串级与局部Smith预估校正的混合模型控制可以随着机组运行工况的变化有效地改善汽温控制性能,最大控制偏差快速回落至±5 ℃之内。
图7
图7
混合控制模型在1 000 MW直流锅炉中的应用
Fig. 7
Application of the proposed hybrid control model in an ultra-suppercritical 1 000 MW once-through boiler
通过增益因子
5 结论
在普遍提升燃煤机组快速调峰、调频响应灵活性需求的大背景下,将汽温快速地控制在合理的范围区间是关键的核心瓶颈之一。为此,提出了一种基于串级与局部Smith预估的混合控制模型,并于1 000 MW超超临界锅炉减温水系统中进行应用,结果表明:
1)该方法高效、易用、稳定,可有效地改善汽温控制性能,达到良好的控制效果。
2)该模型能有效地解决模型预测控制方法无法应用于实际控制的难题,同时通过局部Smith预估可以获得较为精确的预估模型,从而指导超前减温水的控制,有效地提高经典串级PID的控制效果,获得更好的汽温控制指标。
参考文献
过热汽温多模型预测控制的现场应用
[J].
Field application of multiple model predictive control for superheat temperature in boilers
[J].
Fuzzy model-based smith predictive control and its application in superheated steam temperature control
[C]//
基于Smith预估的模糊/PID串级主汽温控制系统仿真
[J].
Simulation study of fuzzy/PID cascade control system based on smith predictive estimate on main steam temperature
[J].
基于自抗扰Smith预估补偿方法的超临界机组再热汽温控制研究
[J].
Research on reheated steam temperature control of supercritical unit based on active disturbance rejection controller smith predictive compensation method
[J].
一种考虑控制系统耦合关系的汽包锅炉简化模型与分析
[J].
A simplified model for drum boiler considering the coupling relationship of the control systems and its analysis
[J].
采用最优状态估计的主蒸汽温度动态矩阵控制方法
[J].
Dynamic matrix control for main steam temperature control system based on optimal state estimation
[J].
Steam temperature controller with LS-SVR-based predictor and PID gain scheduler in thermal power plant
[J].
Superheater steam temperature control for a 300MW boiler unit with inverse dynamic process models
[EB/OL].(
Neural network based superheater steam temperature control for a large-scale supercritical boiler unit
[C]//
Feedforward DMC-PID cascade strategy for main steam temperature control system in fossil-fired power plant
[C]//
基于改进Smith预估补偿的制冷系统抗干扰控制
[J].
Anti-disturbance control of refrigeration system based on improved Smith predictor compensation
[J].
Smith预估控制器在大延迟系统中的应用
[J].
Application of Smith predictive controller in large delay system
[J].
一类热工不稳定滞后对象的补偿控制方法
[J].
Compensation control method for integrative-plus-dead-time process
[J].
用于SCR喷氨量模型参数辨识的辅助变量递推最小二乘法
[J].
Recursive instrumental variable estimation algorithm for ammonia flow model in SCR denigration reactors
[J].
基于最小二乘法的系统参数辨识
[J].
The system parameter identification based on least squares
[J].