0 引言
本文采用有限体积法(finite volume method,FVM)对PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池的器件性能进行模拟,分别对由SiNWs长度造成的表面复合和串联电阻进行研究,得到PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池的性能参数,包括开路电压VOC、短路电流密度JSC、填充因子(fill factor,FF)、转换效率η和电流密度-电压(J-V)曲线。另外,在实验中制备了具有不同长度SiNWs阵列的PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池,以验证模拟结果。
1 光学性能分析
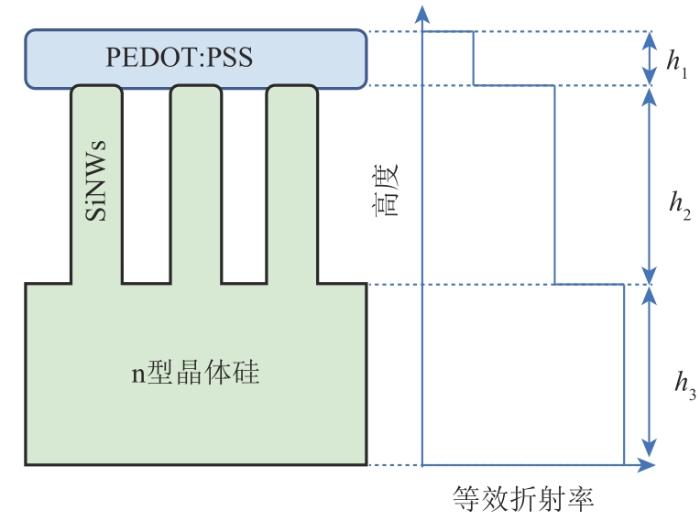
含SiNWs的PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池的结构和等效折射率分布如图1所示,SiNWs的陷光性能可以通过等效介质理论(effective medium approximation,EMA)进行分析,等效介质的计算公式如下:
图1
图1
含SiNWs的PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池的结构和等效折射率分布
Fig. 1
Structure and equivalent refractive index distribution of PEDOT:PSS/Si hybrid solar cell with SiNWs
图2
图2
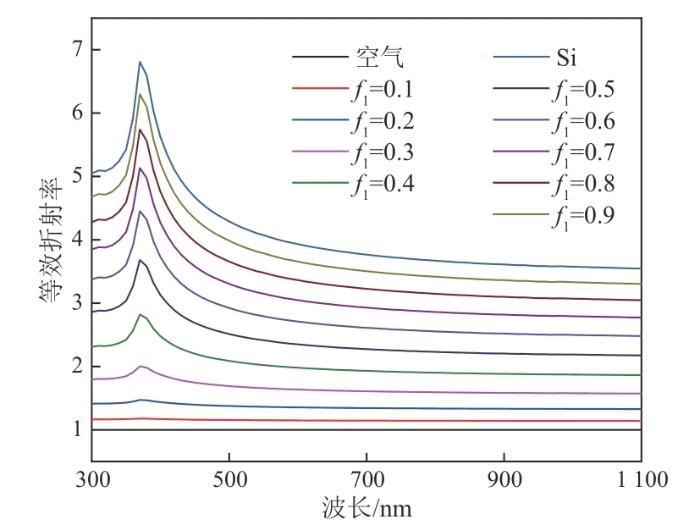
不同f1条件下SiNWs阵列的等效折射率与波长的关系
Fig. 2
Relationship between equivalent refractive index and wavelength of SiNWs array under different f1
因此,可认为SiNWs的光学性能可调性非常大,光学性能优异。对于基于SiNWs的PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池的结构优化,应重点研究SiNWs造成的电学性能损失。在保证光吸收的前提下,通过优化SiNWs来降低电学性能损失,是进一步提升PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池性能的方法。
2 器件性能模拟及结构优化
2.1 器件模拟方法及参数
式中:z是硅表面到内部的深度;λ是波长;α(λ)是光吸收系数,定义为
其中κ(λ)是折射率的虚部;
其中h是普朗克常数,c是光速,F(λ)是AM 1.5G光谱。将表面复合设置在SiNWs、硅表面与空气接触的界面处。
图3
图3
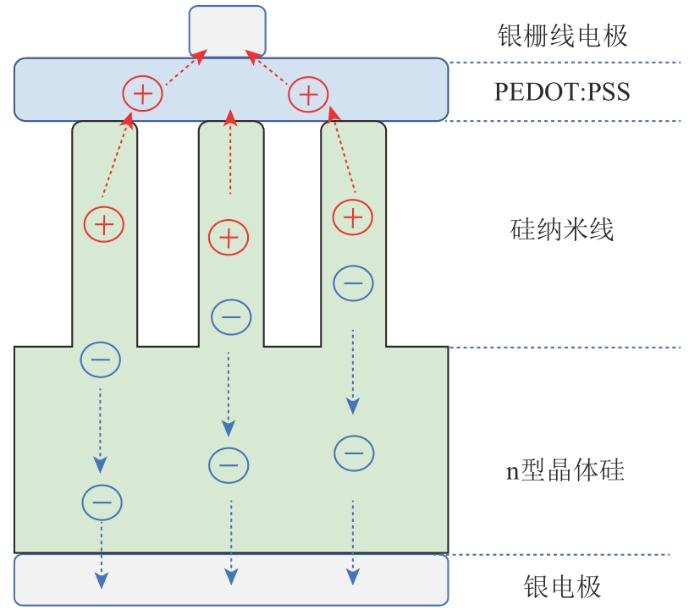
含SiNWs的PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池结构和载流子输运过程示意图
Fig. 3
Schematic diagram of structure and carrier transport process of PEDOT:PSS/Si hybrid solar cell with SiNWs
对载流子输运过程及其对器件性能的影响进行分析,PEDOT:PSS/Si异质接触实现载流子分离,空穴通过漂移运动流向PEDOT:PSS薄膜后被银栅线电极收集,电子通过扩散运动流向硅背表面后被银电极收集。在这个过程中,SiNWs是载流子输运过程中重要的通道。SiNWs的直径从几十纳米到几百纳米不等,载流子在输运过程中很容易被硅表面的陷阱所俘获,产生载流子表面复合。另外,SiNWs在太阳电池中也会产生较大的串联电阻,影响太阳电池的电学性能。表面复合和串联电阻都会随SiNWs长度的增加而增大。
PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池的器件仿真主要围绕Si表面复合速率、SiNWs的表面复合和SiNWs的串联电阻对太阳电池的性能影响展开。SiNWs阵列具有非常好的光吸收性能,研究中将太阳电池的光吸收都设置为1,模拟共分为3组,每组模拟的关键参数如表1所示。
表1 PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池模拟的关键参数
Tab. 1
| 组序号 | SiNWs长度/nm | 表面复合速率/(cm⋅s-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 000 | 0 |
| 1 000 | 200 | |
| 1 000 | 400 | |
| 1 000 | 600 | |
| 1 000 | 800 | |
| 1 000 | 1 000 | |
| 1 000 | 1 200 | |
| 1 000 | 1 400 | |
| 1 000 | 1 600 | |
| 1 000 | 1 800 | |
| 1 000 | 2 000 | |
| 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 200 | 1 000 | |
| 400 | 1 000 | |
| 600 | 1 000 | |
| 800 | 1 000 | |
| 1 000 | 1 000 | |
| 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 200 | 0 | |
| 400 | 0 | |
| 600 | 0 | |
| 800 | 0 | |
| 1 000 | 0 |
2.2 表面复合对太阳电池性能的影响
1)表面复合速率对太阳电池性能的影响
表面载流子复合速率直接影响太阳电池的电流输出,随着表面复合速率的增加,短路电流密度JSC会逐渐降低。从太阳电池内部结构进行分析,表面复合速率会影响中性区域复合相关的暗态饱和电流I01,表面复合速率越大,I01越大。根据太阳电池的等效电路图,可以得到开路电压VOC与I01之间的关系:
式中:k为玻尔兹曼常数;T为温度;q为一个电荷的电量;ISC为短路电流。随着表面复合速率增加,ISC逐渐减小,I01逐渐增大,VOC会逐渐减小。
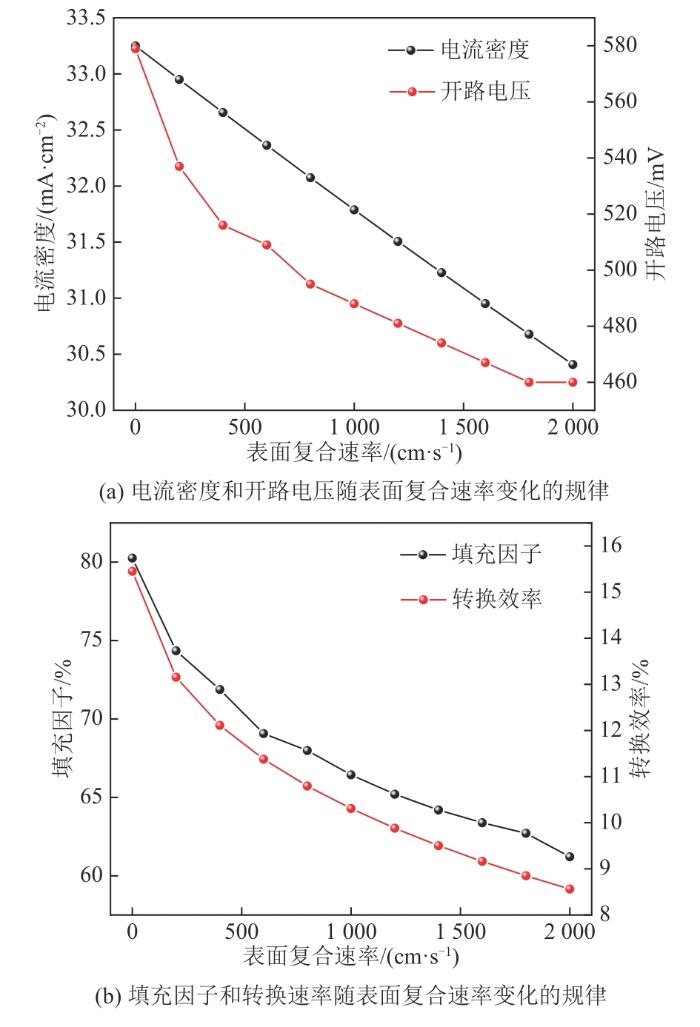
图4
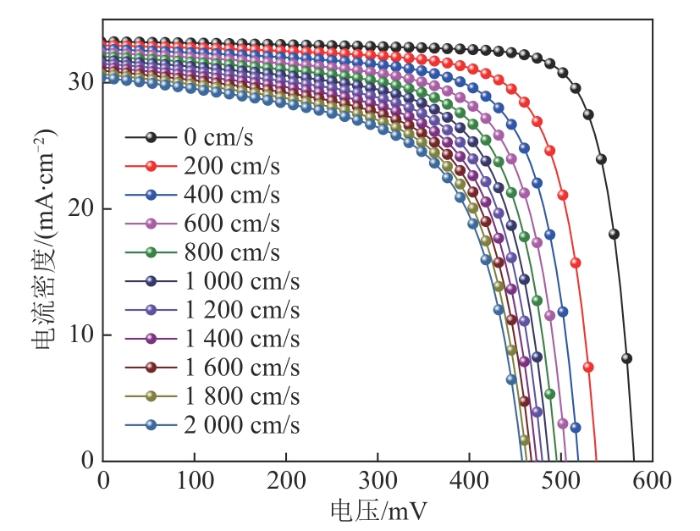
图4
SiNWs长度为1 000 nm的PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池在不同表面复合速率下的J-V曲线
Fig. 4
J-V curves of PEDOT:PSS/Si hybrid solar cell with SiNWs length of 1 000 nm at different surface recombination rates
图5
图5
SiNWs长度为1 000 nm时PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池的性能参数随表面复合速率变化的规律
Fig. 5
Variation of performance parameters of PEDOT:PSS/Si hybrid solar cell with surface recombination rates when SiNWs length is 1 000 nm
表2 PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池在不同表面复合速率下的性能参数
Tab. 2
| 表面复合速率/(cm⋅s-1) | 短路电流密度/(mA⋅cm-2) | 开路电压/mV | 填充因子/ % | 转换效率/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 33.24 | 579 | 80.26 | 15.45 |
| 200 | 32.95 | 537 | 74.34 | 13.15 |
| 400 | 32.65 | 516 | 71.87 | 12.11 |
| 600 | 32.36 | 509 | 69.06 | 11.37 |
| 800 | 32.07 | 495 | 67.98 | 10.79 |
| 1 000 | 31.78 | 488 | 66.43 | 10.30 |
| 1 200 | 31.50 | 481 | 65.19 | 9.88 |
| 1 400 | 31.22 | 474 | 64.19 | 9.50 |
| 1 600 | 30.95 | 467 | 63.38 | 9.16 |
| 1 800 | 30.67 | 460 | 62.70 | 8.84 |
| 2 000 | 30.40 | 460 | 61.20 | 8.56 |
从图5可以看出:JSC随着表面复合速率增大呈现出一种线性变化趋势,从33.24 mA/cm2降低到30.40 mA/cm2,变化相对较小;VOC随着表面复合速率的增大先快速下降后缓慢下降,从579 mV降低到460 mV,降幅较大;FF、η与VOC具有相似的变化规律,随着表面复合速率的增大,FF从80.26%降低到61.20%,η从15.45%降低到8.56%。
综上所述,表面复合速率对PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池的性能影响较大。因此,对SiNWs表面进行钝化、减少表面复合,是提升PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池性能的有效手段。
2)SiNWs长度对太阳电池性能的影响
当硅表面的载流子表面复合速率难以降低到0 cm/s时,应对SiNWs长度进行优化,在保证光吸收的同时实现较低的载流子复合。因此,在表面复合速率一定时,研究SiNWs长度对PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池性能的影响规律具有一定意义。
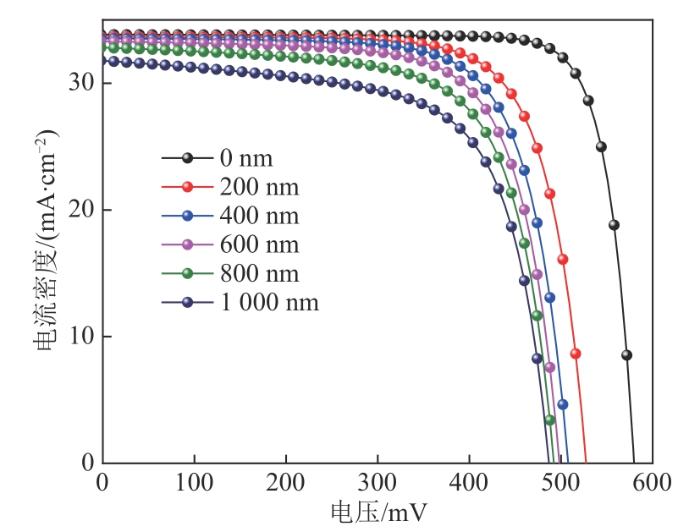
图6
图6
表面复合速率为1 000 cm/s时PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池在不同SiNWs长度下的J-V曲线
Fig. 6
J-V curves of PEDOT:PSS/Si hybrid solar cell with different SiNWs lengths at the surface recombination rate of 1 000 cm/s
图7
图7
表面复合速率为1 000 cm/s时PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池性能参数随SiNWs长度变化的规律
Fig. 7
Variation of performance parameters of PEDOT:PSS/Si hybrid solar cell with SiNWs lengths when the surface recombination rate is 1 000 cm/s
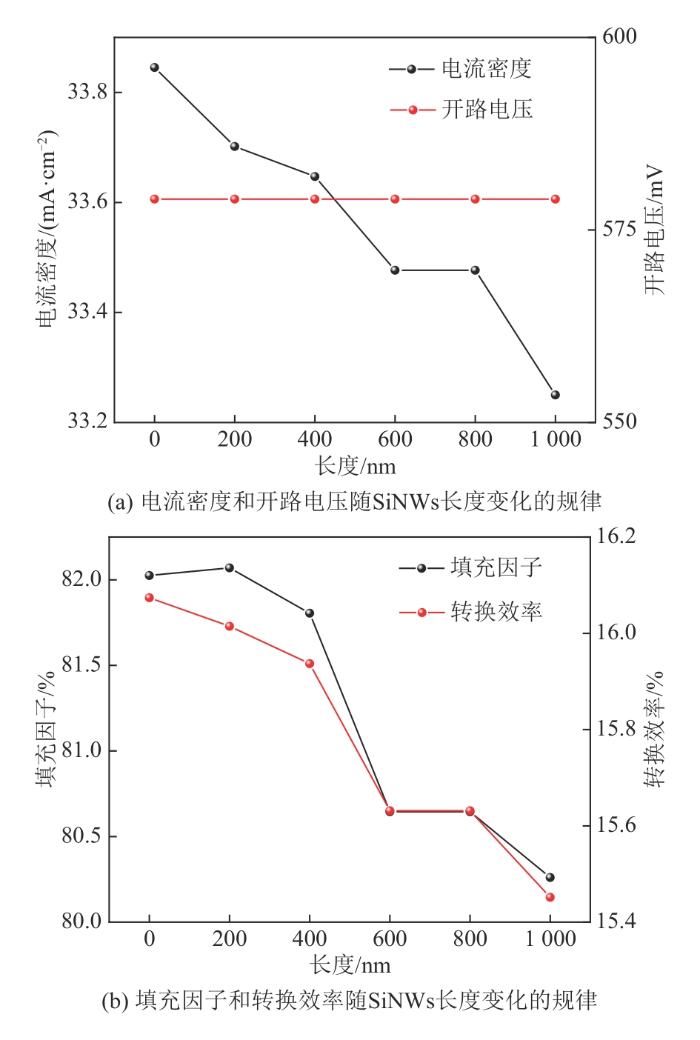
PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池在不同SiNWs长度下的性能参数如表3所示。当光吸收设置为100%,仅从表面复合速率方面分析JSC时,发现有无SiNWs对JSC的影响不大,只有在SiNWs长度从800 nm增至1 000 nm时,JSC才出现较快下降,从32.81 mA/cm2降低到31.78 mA/cm2,降低了1.03 mA/cm2。有无SiNWs对VOC的影响较大,当SiNWs长度从0 nm增至200 nm时,VOC从579 mV降至530 mV,降低了49 mV;随着SiNWs长度继续增加,VOC下降速度逐渐减缓。有无SiNWs对FF的影响也较大,当SiNWs长度从0 nm增加到200 nm时,FF从82.02%降至73.63%,降低了8.39%。当SiNWs长度从0 nm增加到1 000 nm时,η从16.07%降至10.30%,降低了35.90%。
表3 PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池在不同SiNWs长度下的性能参数
Tab. 3
| SiNWs长度/nm | 短路电流密度/ (mA⋅cm-2) | 开路电压/ mV | 填充因子/ % | 转换效率/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 33.84 | 579 | 82.02 | 16.07 |
| 200 | 33.66 | 530 | 73.63 | 13.13 |
| 400 | 33.53 | 509 | 72.52 | 12.38 |
| 600 | 33.30 | 495 | 71.66 | 11.81 |
| 800 | 32.81 | 495 | 68.72 | 11.16 |
| 1 000 | 31.78 | 488 | 66.43 | 10.30 |
这2组实验证明了在光吸收一定时,表面复合速率对PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池性能影响最大的参数是VOC,因此其对太阳电池转换效率的影响很大。由此可知,首先应控制表面复合速率,其次应调控SiNWs长度,控制总的表面复合是提升具有SiNWs的PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池性能的有效手段。
2.3 串联电阻对太阳电池性能的影响
由于SiNWs直径较小,SiNWs长度的增加也会带来串联电阻的增加,因此,第3组模拟实验重点研究SiNWs长度造成的串联电阻对PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池性能的影响。
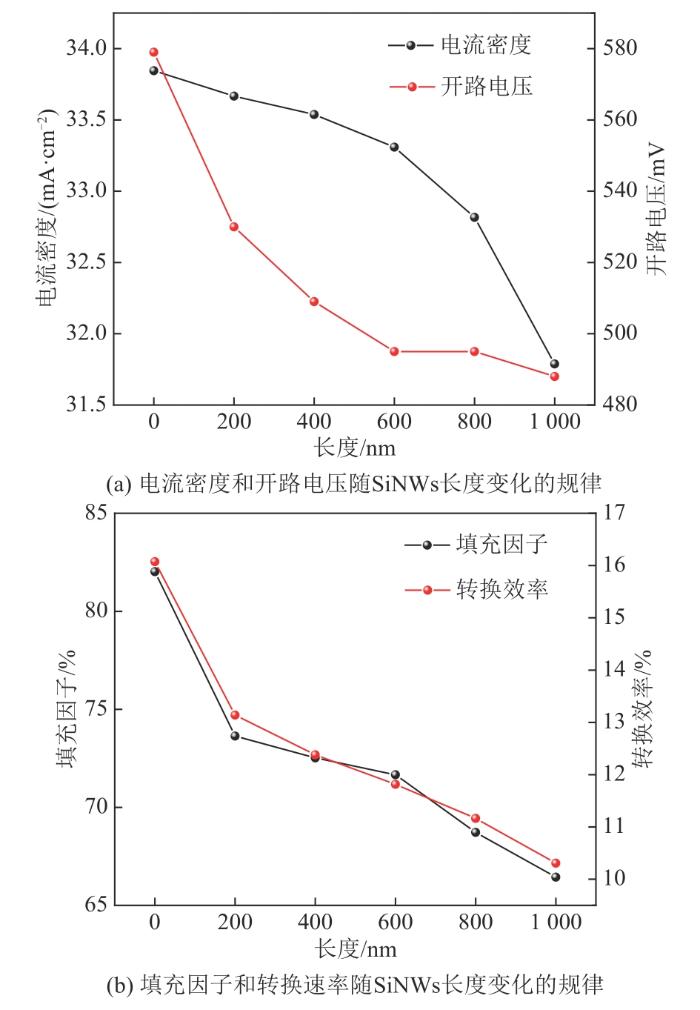
当表面复合速率为0 cm/s时,不同SiNWs长度下PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池的J-V曲线如图8所示。可以发现,SiNWs长度的增加主要影响FF,对J-V曲线整体的影响非常小。
图8
图8
无表面复合条件PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池在不同SiNWs长度下的J-V曲线
Fig. 8
J-V curves of PEDOT:PSS/Si hybrid solar cell without surface recombination under different SiNWs lengths
图9
图9
PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池性能参数随SiNWs长度变化的规律
Fig. 9
Variation of performance parameters of PEDOT:PSS/Si hybrid solar cell with SiNWs lengths
表4 无表面复合条件PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池在SiNWs长度下的性能参数
Tab. 4
| SiNWs长度/nm | 短路电流密度/(mA⋅cm-2) | 开路电压/mV | 填充因子/ % | 转换效率/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 33.84 | 579 | 82.02 | 16.07 |
| 200 | 33.70 | 579 | 82.06 | 16.01 |
| 400 | 33.64 | 579 | 81.80 | 15.93 |
| 600 | 33.47 | 579 | 80.64 | 15.63 |
| 800 | 33.47 | 579 | 80.64 | 15.63 |
| 1 000 | 33.24 | 579 | 80.26 | 15.45 |
综上可知,由SiNWs长度造成的串联电阻对PEDOT:PSS/Si性能的影响较小。因此,在无法降低表面复合速率时,应尽可能地对SiNWs进行优化,在保证光吸收的情况下降低电学损耗,这对于提升基于SiNWs的PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池性能更有效。
3 实验结果与讨论
在前面的模拟实验中,为了探究SiNWs对PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池电学性能的影响,将太阳电池的光吸收设置为100%,实际上光学性能会随着SiNWs长度的变化而变化。因此,需要在实验中考虑光学性能的影响,进一步优化PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池中的SiNWs。
3.1 器件制备及表征
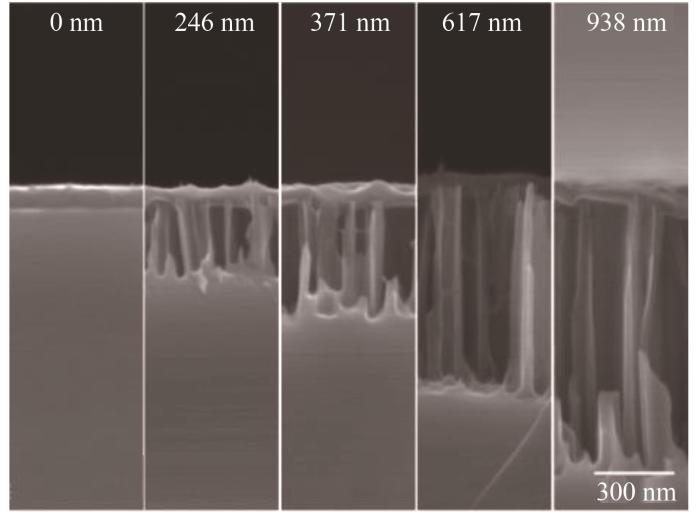
通过SEM对不同反应时间下SiNWs制备的PEDOT:PSS/Si异质结接触界面进行表征,结果如图10所示,上层的薄膜是PEDOT:PSS,下层的薄膜是Si,中间的薄膜是通过金属辅助方法刻蚀的SiNWs,从左到右刻蚀时间依次增加,获得的SiNWs长度分别为0、246、371、617、938 nm。
图10
图10
不同SiNWs长度下PEDOT:PSS/Si异质结接触界面的SEM图像
Fig. 10
SEM images of contact interface of PEDOT:PSS/Si heterojunction with different SiNWs lengths
图11
图11
不同长度下SiNWs阵列的反射光谱
Fig. 11
Reflectance spectra of SiNWs array with different lengths
3.2 器件的光电性能及讨论
图12
图12
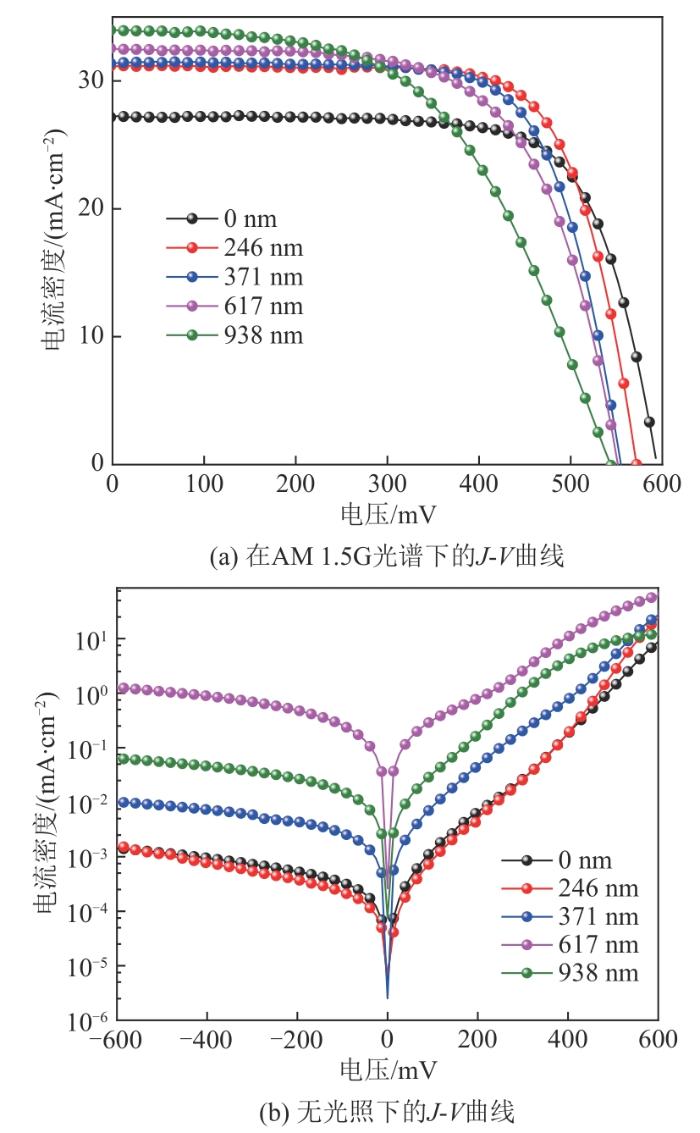
PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池在不同SiNWs长度下的电流电压输出特性
Fig. 12
Current and voltage output characteristics of PEDOT:PSS/Si hybrid solar cell with different SiNWs lengths
表5 PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池在不同SiNWs长度下的性能参数
Tab. 5
| SiNWs长度/nm | 短路电流密度/(mA⋅cm-2) | 开路电压/ mV | 填充因子/ % | 转换效率/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 27.17 | 593 | 72.07 | 11.61 |
| 246 | 31.16 | 572 | 72.27 | 12.88 |
| 371 | 31.38 | 558 | 70.52 | 12.71 |
| 617 | 32.55 | 551 | 64.27 | 11.53 |
| 938 | 33.98 | 544 | 53.22 | 9.83 |
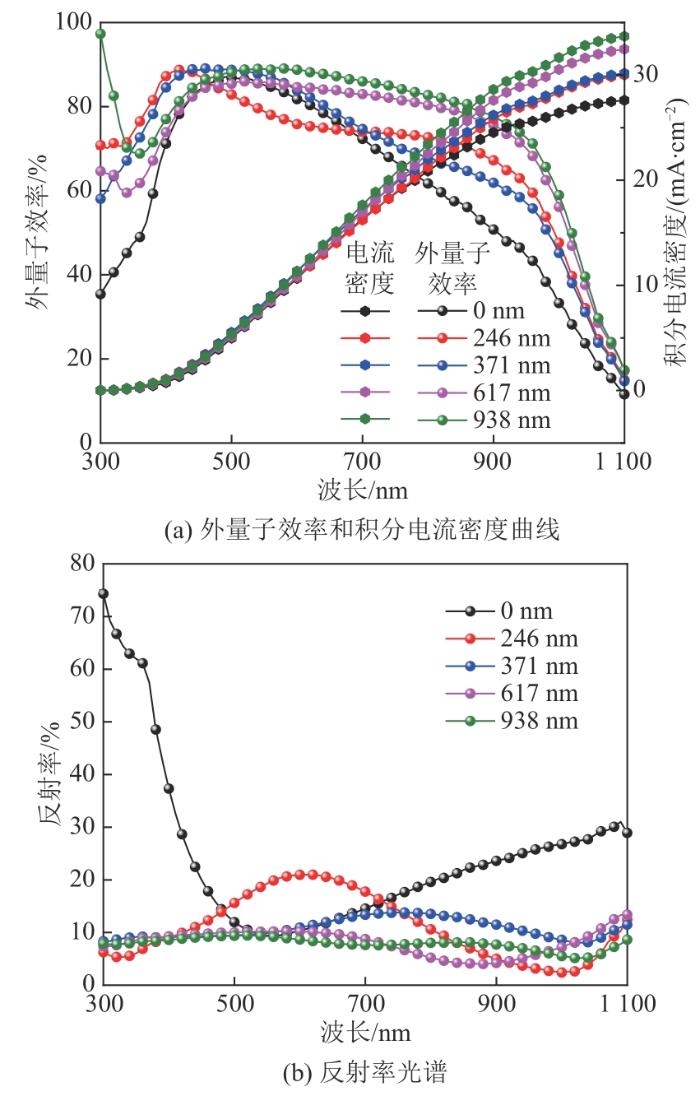
图13是基于SiNWs阵列的PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池在不同SiNWs长度下的光谱特性。不同SiNWs长度对应不同的外量子效率光谱,这是由不同长度的SiNWs阵列产生的光学特性造成的。无SiNWs的外量子效率光谱在波长为500 nm时较高,其他波长对应的外量子效率较低;当有SiNWs时,外量子效率在整个波长范围内都较高。从积分电流密度上可以发现,SiNWs阵列对电流密度有很好的增强作用,但是随着SiNWs的长度的增加,增强作用逐渐减弱。
图13
图13
PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池在不同SiNWs长度下的光谱特性
Fig. 13
Spectral characteristics of PEDOT:PSS/Si hybrid solar cell with different SiNWs lengths
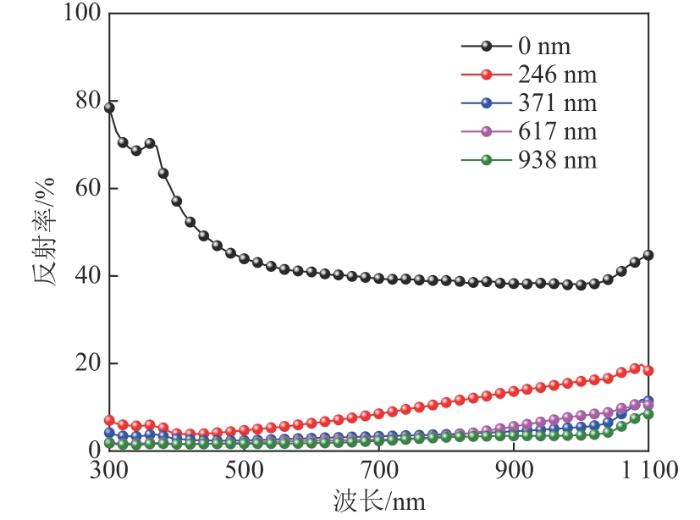
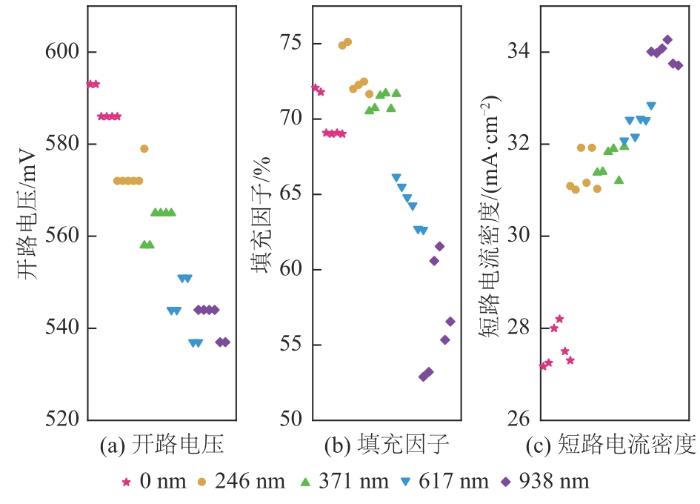
PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池的反射率在无SiNWs、波长为500 nm左右时最低,其他波长对应的反射率较高,这是由于PEDOT:PSS薄膜起到了减少反射的作用。当SiNWs长度为246 nm、波长为600 nm左右时,反射率最高,但是其他波长对应的反射率较低。但是随着SiNWs长度的增加,整个光谱的反射率都在10%左右,对光吸收的影响逐渐减弱。
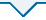
图14
图14
6组PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池在不同SiNWs长度下的电学输出参数分布
Fig. 14
Electrical output parameter distributions of six groups of PEDOT:PSS/Si hybrid solar cells with different SiNWs lengths
4 结论
通过对PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池中SiNWs进行优化,发现:表面复合速率是影响PEDOT:PSS/Si杂化太阳电池性能的重要因素;由SiNWs长度造成的串联电阻对太阳电池性能的影响较小;随着SiNWs长度增加,影响太阳电池性能的主要因素从光学方面转变为电学方面。具体结论如下:
1)表面复合主要影响VOC,当硅表面具有SiNWs时,表面复合速率的增加会使VOC快速下降,进而导致η最多降低了45.59%。
2)SiNWs长度的增加虽然会增加光吸收,但产生的表面复合对太阳电池性能的负面影响更大。当表面复合速率一定时,增加SiNWs长度会使得VOC快速降低,进而导致η最多降低了35.90%。
3)SiNWs长度的增加产生的串联电阻对电池性能的影响较小,主要影响FF。当无表面复合时,SiNWs长度的增加对VOC几乎没有影响,对FF的影响较小,降幅仅为2.14%。
4)实验结果与模拟结果具有一致的规律,获得的最佳SiNWs长度为246 nm左右,随着SiNWs长度的增加,JSC会持续增加,但增幅逐渐减弱,VOC和FF持续降低,η呈现出先增加后减弱的趋势,最高η为12.88%。
参考文献
8% efficiency hybrid Si/organic heterojunction solar cells with MoO3 film as antireflection and inversion induced layer
[J].
Above-11%- efficiency organic-inorganic hybrid solar cells with omnidirectional harvesting characteristics by employing hierarchical photon-trapping structures
[J].
Integrating a silicon solar cell with a triboelectric nanogenerator via a mutual electrode for harvesting energy from sunlight and raindrops
[J].
Self-consistent optical parameters of intrinsic silicon at 300 K including temperature coefficients
[J].
Optical properties of intrinsic silicon at 300 K
[J].
Uncertainty analysis for the coefficient of band-to-band absorption of crystalline silicon
[J].
Hybrid Si microwire and planar solar cells:passivation and characterization
[J].
Realizing high-efficiency omnidirectional n-type Si solar cells via the hierarchical architecture concept with radial junctions
[J].
Hybrid solar cells:enhanced electro-optical properties of nanocone/nanopillar dual-structured arrays for ultrathin silicon/organic hybrid solar cell applications
[J].
Pyramidal texturing of silicon surface via inorganic-organic hybrid alkaline liquor for heterojunction solar cells
[J].
Hybrid silicon honeycomb/organic solar cells with enhanced efficiency using surface etching
[J].
Hybrid silicon nanocone-polymer solar cells
[J].
13.2% efficiency Si nanowire/PEDOT:PSS hybrid solar cell using a transfer-imprinted Au mesh electrode
[J].
太阳能光伏光热高效综合利用技术
[J].
Efficient and comprehensive photovoltaic/photothermal utilization technologies for solar energy
[J].
Electrical characterization of inorganic-organic hybrid photovoltaic devices based on silicon-poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly (styrenesulfonate)
[J].
Simple approach of fabricating high efficiency Si nanowire/conductive polymer hybrid solar cells
[J].
Characteristics of a silicon nanowires/PEDOT:PSS heterojunction and its effect on the solar cell performance
[J].
Effective light absorption using the double-sided pyramid gratings for thin-film silicon solar cell
[J].
Anti-reflecting and photonic nanostructures
[J].
Anti-reflective coatings:a critical,in-depth review
[J].
Effective light absorption and its enhancement factor for silicon nanowire-based solar cell
[J].
Optical properties of organometal halide perovskite thin films and general device structure design rules for perovskite single and tandem solar cells
[J].
Broadband light-concentration with near-surface distribution by silver capped silicon nanowire for high-performance solar cells
[J].
Linear length-dependent light-harvesting ability of silicon nanowire
[J].
Excellent light-capture capability of trilobal SiNW for ultra-high JSC in single-nanowire solar cells
[J].
Silicon nanowire design for ultrahigh extinction by dipole near-field interaction in transparent solar cells
[J].
Helical SiNW design with a dual-peak response for broadband scattering in translucent solar cells
[J].
基于SnO2电子传输层的n-i-p型钙钛矿太阳能电池关键技术研究
[J].
Research of key technologies for n-i-p perovskite solar cells with SnO2 electron transport layer
[J].
14.1% efficiency hybrid planar-Si/organic heterojunction solar cells with SnO2 insertion layer
[J].
Improving junction quality via modifying the Si surface to enhance the performance of PEDOT:PSS/Si hybrid solar cells
[J].
Phase separation to improve the conductivity and work function of the PEDOT:PSS solution for silicon hybrid solar cells
[J].